

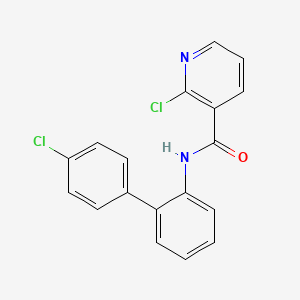

1. 2-chloro-n-(4-chlorobiphenyl-2-yl)nicotinamide
1. 188425-85-6
2. Nicobifen
3. Endura
4. Emerald
5. 2-chloro-n-(4'-chloro-[1,1'-biphenyl]-2-yl)nicotinamide
6. Boscalid [iso]
7. 2-chloro-n-(4'-chlorobiphenyl-2-yl)nicotinamide
8. 2-chloro-n-[2-(4-chlorophenyl)phenyl]pyridine-3-carboxamide
9. 3-pyridinecarboxamide, 2-chloro-n-(4'-chloro[1,1'-biphenyl]-2-yl)-
10. Bas 510
11. Bas-510
12. 32ms8zrd1v
13. Bas 510 F
14. Chebi:81822
15. Ncgc00163735-04
16. Anilide
17. Cantus
18. Bas 510f
19. Unii-32ms8zrd1v
20. 2-chloro-n-(4'-chloro[1,1'-biphenyl]-2-yl)-3-pyridinecarboxamide
21. 2-chloro-n-(4'-chloro(1,1'-biphenyl)-2-yl)-3-pyridinecarboxamide
22. 3-pyridinecarboxamide, 2-chloro-n-(4'-chloro(1,1'-biphenyl)-2-yl)-
23. Hsdb 7499
24. Boscalid [hsdb]
25. Emerald [inci]
26. Boscalid [mi]
27. Dsstox_cid_14392
28. Dsstox_rid_79152
29. Dsstox_gsid_34392
30. Schembl18517
31. Chembl1076544
32. Dtxsid6034392
33. Amy22452
34. Zinc3612929
35. Tox21_400045
36. 2-chloro-n-(4'-chloro[1,1'-biphenyl]-2-yl)pyridine-3-carboxamide
37. Boscalid 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
38. Mfcd06795150
39. Boscalid 10 Microg/ml In Cyclohexane
40. Akos015895938
41. Boscalid 1000 Microg/ml In Methanol
42. Boscalid 10 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
43. Db12792
44. Ds-9792
45. Boscalid 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
46. Ncgc00163735-01
47. Ncgc00163735-02
48. Ncgc00163735-03
49. Ncgc00163735-05
50. B4038
51. Boscalid, Pestanal(r), Analytical Standard
52. Cas-188425-85-6
53. Cs-0078856
54. Ft-0658358
55. C18547
56. 2-chloro-n-(4'-chloro-2-biphenylyl)nicotinamide
57. 425b856
58. A813228
59. Q894358
60. 2-chloro-n-(4'-chlorobiphenyl-2- Yl)-nicotinamide
61. J-012142
62. J-519930
| Molecular Weight | 343.2 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C18H12Cl2N2O |
| XLogP3 | 4.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 342.0326684 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 342.0326684 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 42 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 23 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 399 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Dermal Penetration (rat). Maximum % absorption: 0.01 mg/sq cm = 10.93 (24 hour exposure, 24 hour sacrifice) 0.10 mg/sq cm = 3.76 (24 hour exposure, 24 hour sacrifice) 1.00 mg/sq cm = 1.48 (10 hour exposure, 72 hour sacrifice /From table/
USEPA; Office of Prevention, Pesticides and Toxic Substances; Pesticide Fact Sheet - Boscalid. p.7 (July 2003). Available from, as of June 14, 2016: https://www3.epa.gov/
In the rat, Boscalid was readily absorbed and excreted following single oral 50 mg/kg; at single 500 mg/kg or 15 doses of 500 mg/kg, absorption was saturated. Excretion mainly by feces (80-98%). Biliary excretion 40- 50% of fecal activity at 50 mg/kg, 10% at 500 mg/kg. Urine, about 16% at 50 mg/kg, 3-5% at 500 mg/kg. Absorption about 56% at 50 mg/kg and 13-17% at 500 mg/kg. Excretory patterns similar by gender or radiolabel position. /From table/
USEPA; Office of Prevention, Pesticides and Toxic Substances; Pesticide Fact Sheet - Boscalid. p.7 (July 2003). Available from, as of June 14, 2016: https://www3.epa.gov/
Three ... groups of Wistar rats were treated and sampled ... for qualitative analyses of metabolites. ... Metabolites were separated by HPLC. Primary identification was by mass spectrometry (MS). ... The most important metabolites were hydroxyl or O-glucuronide metabolites on the diphenyl ring (usually para to the amide nitrogen), and S-glucuronide conjugation products displacing the chlorine on the pyridine ring of the parent compound. The sulfur originated from glutathione (GSH) addition to the ring. GSH was often cleaved to cysteine in bile or feces, or further degraded in feces to a thiol, which in turn was sometimes conjugated as a glucuronide). Tissue residues (liver, kidney, and plasma) were scant ... Some parent BAS 510 F was found in kidneys and plasma. Thus BAS 510 F was effectively metabolized and efficiently excreted.
California Environmental Protection Agency/Department of Pesticide Regulation; Summary of Toxicological Data for BAS 510 F, Chemical Code No.5790 p.9 (May 2, 2002, Revised May 20, 2013). Available from, as of June 15, 2016: https://www.cdpr.ca.gov/docs/risk/toxsums/toxsumlist.htm
/In the rat,/ metabolites (hydroxylation and conjugation products) were consistent with Phase I oxidation reactions followed by Phase II conjugation with glucuronic acid or sulfate, or by conjugation of the parent with glutathione with cleavage to sulfate metabolites. /From table/
USEPA; Office of Prevention, Pesticides and Toxic Substances; Pesticide Fact Sheet - Boscalid. p.7 (July 2003). Available from, as of June 14, 2016: https://www3.epa.gov/
In the rat, the predominant route of excretion of BAS 510 F is fecal with urinary excretion being minor. The half-life of BAS 510 F is less than 24 hours.
BASF Submission to EPA; Request for consideration of a tolerances for residues of Boscalid (BAS 510F). EPA-HQ-OPP-2005-0145-004 (EPA Docket) (2005)