

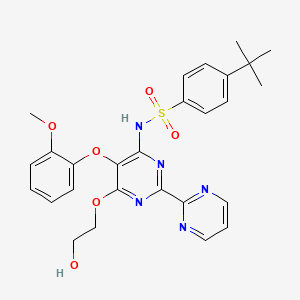

1. 4-t-butyl-n-(6-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-5-(2-methoxyphenoxy)-2,2'-bipyrimidin-4-yl)benzenesulfonamide
2. Bosentan Anhydrous
3. Bosentan Monohydrate
4. Ro 47 0203
5. Ro 47-0203
6. Ro 470203
7. Ro-47-0203
8. Tracleer
1. 147536-97-8
2. Tracleer
3. Actelion
4. Bosentan Anhydrous
5. Ro 47-0203
6. Ro-47-0203
7. Anhydrous Bosentan
8. Bosentan [usan:inn:ban]
9. 4-tert-butyl-n-[6-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-5-(2-methoxyphenoxy)-2-pyrimidin-2-ylpyrimidin-4-yl]benzenesulfonamide
10. P-tert-butyl-n-(6-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-5-(o-methoxyphenoxy)-2-(2-pyrimidinyl)-4-pyrimidinyl)benzenesulfonamide
11. Bosentan (inn)
12. 4-(tert-butyl)-n-(6-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-5-(2-methoxyphenoxy)-[2,2'-bipyrimidin]-4-yl)benzenesulfonamide
13. Chembl957
14. Xul93r30k2
15. N-[6-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-5-(2-methoxyphenoxy)-2-pyrimidin-2-yl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-4-tert-butyl-benzenesulfonamide
16. Chebi:51450
17. 147536-97-8 (free)
18. 174227-18-0
19. Benzenesulfonamide, 4-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-n-(6-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-5-(2-methoxyphenoxy)(2,2'-bipyrimidin)-4-yl)-
20. Ncgc00167440-01
21. Bosentan [inn]
22. Dsstox_cid_26627
23. Dsstox_rid_81776
24. Dsstox_gsid_46627
25. 1174918-31-0
26. 4-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-n-(6-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-5-(2-methoxyphenoxy)-(2,2'-bipyrimidin)-4-yl) Benzenesulfornamide
27. 4-tert-butyl-n-[6-(2-hydroxyethyloxy)-5-(2-methoxyphenoxy)-2-pyrimidin-2-yl-pyrimidin-4-yl]benzenesulfonamide
28. Benzenesulfonamide, 4-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-n-[6-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-5-(2-methoxyphenoxy)[2,2'-bipyrimidin]-4-yl]-
29. Bosentanum
30. Ro-47-0203/029
31. 4-tert-butyl-n-[6-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-5-(2-methoxyphenoxy)-2,2'-bipyrimidin-4-yl]benzenesulfonamide
32. Cas-147536-97-8
33. Ro 47-0203/039
34. Sr-05000001532
35. Ro-470203029
36. Ro-47-0203-029
37. Unii-xul93r30k2
38. 4-tert-butyl-n-(6-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-5-(2-methoxyphenoxy)-2,2'-bipyrimidin-4-yl)benzenesulfonamide
39. 4-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-n-(6-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-5-(2-methoxyphenoxy)-(2,2'-bipyrimidin)-4-yl)benzenesulfornamide
40. Ks-5062
41. Starbld0043886
42. Bosentan [mi]
43. Ro-47-0203/039
44. Bosentan [who-dd]
45. Schembl4218
46. Gtpl3494
47. Dtxsid7046627
48. Hms2090n14
49. Hms3652f15
50. Hms3715n05
51. Hms3750a13
52. Bcp05202
53. Hy-a0013
54. Zinc1538857
55. Tox21_112444
56. Ac-148
57. Bdbm50061101
58. Pdsp1_001731
59. Pdsp2_001714
60. S4220
61. Akos015852063
62. Tox21_112444_1
63. Am84442
64. Bcp9000445
65. Ccg-221182
66. Cs-0381
67. Db00559
68. Sb17356
69. Ncgc00167440-02
70. Bb164259
71. B5118
72. Ft-0658809
73. Sw199648-3
74. D07538
75. W18800
76. Ab01275536-01
77. 212b550
78. A808658
79. L001086
80. Q419769
81. J-008366
82. Sr-05000001532-1
83. Sr-05000001532-2
84. Sr-05000001532-4
85. Z1541632805
86. 4-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-n-(6-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-5-(2-methoxyphenoxy)-(2,2''-bipyrimidin)-4-yl) Benzenesulfornamide
87. 4-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-n-[6-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-5-(2-methoxyphenoxy)[2,2'-bipyrimidin]-4-yl]benzenesulfonamide
88. 4-(tert-butyl)-n-[6-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-5-(2-methoxyphenoxy)[2,2'-bipyrimidin]-4-yl]benzenesulfonamide
89. 4-tert Butyl-n-[4-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-5-(2-methoxyphenoxy)-2-(2-pyrimidinyl)pyrimidin-6-yl]benzenesulphonamide
90. 4-tert-butyl-n-[6-(2-hydroxy-ethoxy)-5-(2-methoxy-phenoxy)-[2,2']bipyrimidinyl-4-yl]-benzenesulfonamide
91. 4-tert-butyl-n-[6-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-5-(2-methoxyphenoxy)-[2,2'-bipyrimidine]-4-yl]benzene-1-sulfonamide
92. 4-tert-butyl-n-[6-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-5-(2-methoxyphenoxy)-2,2''-bipyrimidin-4-yl]benzenesulfonamide
93. 4-tert-butyl-n-[6-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-5-(2-methoxyphenoxy)-2-(2-pyrimidinyl)-4-pyrimidinyl]benzenesulfonamide
94. 4-tert-butyl-n-[6-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-5-(2-methoxyphenoxy)-2-(pyrimidin-2-yl)pyrimidin-4-yl]benzene-1-sulfonamide
95. 4-tert-butyl-n-[6-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-5-(2-methoxyphenoxy)-2-(pyrimidin-2-yl)pyrimidin-4-yl]benzenesulfonamide
96. K86
| Molecular Weight | 551.6 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C27H29N5O6S |
| XLogP3 | 3.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 11 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 11 |
| Exact Mass | 551.18385484 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 551.18385484 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 154 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 39 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 839 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Tracleer |
| PubMed Health | Bosentan (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antihypertensive |
| Drug Label | Tracleer is the proprietary name for bosentan, an endothelin receptor antagonist that belongs to a class of highly substituted pyrimidine derivatives, with no chiral centers. It is designated chemically as 4-tert-butyl-N-[6-(2-hydroxy-ethoxy)-5-(2-me... |
| Active Ingredient | Bosentan |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 125mg; 62.5mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Actelion Pharms |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Tracleer |
| PubMed Health | Bosentan (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antihypertensive |
| Drug Label | Tracleer is the proprietary name for bosentan, an endothelin receptor antagonist that belongs to a class of highly substituted pyrimidine derivatives, with no chiral centers. It is designated chemically as 4-tert-butyl-N-[6-(2-hydroxy-ethoxy)-5-(2-me... |
| Active Ingredient | Bosentan |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 125mg; 62.5mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Actelion Pharms |
Used in the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), to improve exercise ability and to decrease the rate of clinical worsening (in patients with WHO Class III or IV symptoms).
FDA Label
Treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) to improve exercise capacity and symptoms in patients with WHO functional class III. Efficacy has been shown in:
- Primary (idiopathic and familial) PAH;
- PAH secondary to scleroderma without significant interstitial pulmonary disease;
- PAH associated with congenital systemic-to-pulmonary shunts and Eisenmenger's physiology.
Some improvements have also been shown in patients with PAH WHO functional class II.
Tracleer is also indicated to reduce the number of new digital ulcers in patients with systemic sclerosis and ongoing digital ulcer disease.
Bosentan belongs to a class of drugs known as endothelin receptor antagonists (ERAs). Patients with PAH have elevated levels of endothelin, a potent blood vessel constrictor, in their plasma and lung tissue. Bosentan blocks the binding of endothelin to its receptors, thereby negating endothelin's deleterious effects.
Antihypertensive Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of acute or chronic vascular HYPERTENSION regardless of pharmacological mechanism. Among the antihypertensive agents are DIURETICS; (especially DIURETICS, THIAZIDE); ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS; ADRENERGIC ALPHA-ANTAGONISTS; ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS; CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS; GANGLIONIC BLOCKERS; and VASODILATOR AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Antihypertensive Agents.)
Endothelin Receptor Antagonists
Compounds and drugs that bind to and inhibit or block the activation of ENDOTHELIN RECECPTORS. (See all compounds classified as Endothelin Receptor Antagonists.)
C02KX01
C02KX01
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
C - Cardiovascular system
C02 - Antihypertensives
C02K - Other antihypertensives
C02KX - Antihypertensives for pulmonary arterial hypertension
C02KX01 - Bosentan
Absorption
Absolute bioavailability is approximately 50% and food does not affect absorption.
Route of Elimination
Bosentan is eliminated by biliary excretion following metabolism in the liver.
Volume of Distribution
18 L
Clearance
4 L/h [patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension]
Bosentan is metabolized in the liver by the cytochrome P450 enzymes CYP2C9 and CYP3A4 (and possibly CYP2C19), producing three metabolites, one of which, Ro 48-5033, is pharmacologically active and may contribute 10 to 20% to the total activity of the parent compound.
Bosentan has known human metabolites that include 4-tert-butyl-N-[6-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-5-(2-hydroxyphenoxy)-[2,2-]bipyrimidinyl-4-yl]-benzenesulfonamide and Hydroxy Bosentan.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
Terminal elimination half-life is about 5 hours in healthy adult subjects.
Endothelin-1 (ET-1) is a neurohormone, the effects of which are mediated by binding to ETA and ETB receptors in the endothelium and vascular smooth muscle. It displays a slightly higher affinity towards ETA receptors than ETB receptors. ET-1 concentrations are elevated in plasma and lung tissue of patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension, suggesting a pathogenic role for ET-1 in this disease. Bosentan is a specific and competitive antagonist at endothelin receptor types ETA and ETB.
