


1. Ananase
2. Bromelain
3. Bromelain Pos
4. Bromelain-pos
5. Bromelainpos
6. Bromelains
7. Bromelin
8. Bromelins
9. Dayto Anase
10. Debrase
11. Dontisanin
12. Extranase
13. Mucozym
14. Proteozym
15. Traumanase
1. Muxf
2. M0xf(3)
3. Bromelain, Technical Grade
4. Chebi:53469
5. 9001-00-7
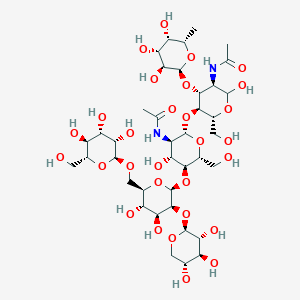
6. Fuc-alpha-(1->3)-[man-alpha-(1->6)-[xyl-beta-(1->2)]-man-beta-(1->4)-glcnac-beta-(1->4)]-glcnac
7. Alpha-l-fuc-(1->3)-[alpha-d-man-(1->6)-[beta-d-xyl-(1->2)]-beta-d-man-(1->4)-beta-d-glcnac-(1->4)]-d-glcnac
8. Alpha-l-fucopyranosyl-(1->3)-[alpha-d-mannopyranosyl-(1->6)-[beta-d-xylopyranosyl-(1->2)]-beta-d-mannopyranosyl-(1->4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-d-glucopyranosyl-(1->4)]-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-d-glucopyranose
9. Alpha-l-fucosyl-(1->3)-[alpha-d-mannosyl-(1->6)-[beta-d-xylosyl-(1->2)]-beta-d-mannosyl-(1->4)-n-acetyl-beta-d-glucosaminyl-(1->4)]-n-acetyl-d-glucosamine
10. Alpha-l-fucp-(1->3)-[alpha-d-manp-(1->6)-[beta-d-xylp-(1->2)]-beta-d-manp-(1->4)-beta-d-glcpnac-(1->4)]-d-glcpnac
11. Bromelaine
12. Epitope Id:115005
13. Q27124066
14. N_full_22100100000000_gs_1023_c1
15. Man(a1-6)[xyl(b1-2)]man(b1-4)glcnac(b1-4)[fuc(a1-3)]glcnac
16. Wurcs=2.0/6,6,5/[a2122h-1x_1-5_2*ncc/3=o][a1221m-1a_1-5][a2122h-1b_1-5_2*ncc/3=o][a1122h-1b_1-5][a212h-1b_1-5][a1122h-1a_1-5]/1-2-3-4-5-6/a3-b1_a4-c1_c4-d1_d2-e1_d6-f1
| Molecular Weight | 1026.9 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C39H66N2O29 |
| XLogP3 | -11.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 18 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 29 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 16 |
| Exact Mass | 1026.37512407 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 1026.37512407 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 483 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 70 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 1680 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 28 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Bromelain has /shown/ some success as a substitute for trypsin and pepsin in cases of pancreatic insufficiency and post-pancreatectomy.
Medical Economics Co; Physicians Desk Reference for Nutritional Supplements 1st ed p.72 (2001)
Acute postoperative and post-traumatic conditions of swelling, especially of the nasal and paranasal sinuses.
Blumenthal M, ed; The Complete German Commission E Monographs: Therapeutic Guide to Herbal Medicines p.94 (1998)
In an open case observation study involving patients with blunt injuries to the musculoskeletal system, the efficacy and tolerability of high-dose Bromelain POS, a plant-derived enzyme preparation, were investigated. The investigating physician was an orthopedic surgeon who, in addition to the usual therapeutic measures, treated 59 of his patients with the bromelaine preparation. The duration of the application was determined by the nature and severity of the lesion, and varied between one and three weeks. The test criteria were swelling, pain at rest and during movement, and tenderness. These parameters were evaluated on the day of the injury and on five subsequent dates. Treatment with bromelaine resulted in a clear reduction in all four parameters tested. Both swelling and the symptoms of pain had improved appreciably at all evaluation time points as compared with baseline. The tolerability of the preparation was very good, and patient compliance was correspondingly high.
PMID:7672747 Masson M; Fortschr Med 113 (19): 303-6 (1995)
Gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea and vomiting, diarrhea and cramping have been reported. There are occasional reports of metrorrhagia and menorrhagia.
Medical Economics Co; Physicians Desk Reference for Nutritional Supplements 1st ed p.72 (2001)
As with papain and other proteases, bromelain may cause contact allergenic reactions in certain individuals.
Leung, A.Y., Foster, S. Encyclopedia of Common Natural Ingredients Used in Food, Drugs, and Cosmetics. New York, NY. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1996., p. 101
Bromelain supplements should be avoided by pregnant women and nursing mothers.
Medical Economics Co; Physicians Desk Reference for Nutritional Supplements 1st ed p.70 (2001)
In one double-blind study of 73 patients with acute thrombophlebitis, bromelain, used with analgesics, reduced pain, edema, redness, tenderness, elevated skin temperature and disability.
Medical Economics Co; Physicians Desk Reference for Nutritional Supplements 1st ed p.72 (2001)
Those on anticoagulants or antithrombotic agents should exercise caution in the use of bromelain. Bromelain may have blood thinning activity in some.
Medical Economics Co; Physicians Desk Reference for Nutritional Supplements 1st ed p.70 (2001)
Evidence that bromelains (I) is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract of rats after oral administration is demonstrated in a bioavailability study in which 125I is given by oral route to rats and blood levels sampled at various times thereafter. A maximum level of 270 ng/ml I was found at one hr after administration.
PMID:3207859 White RR et al; Biopharm Drug Dispos 9 (Jul-Aug): 397-403 (1988)
Bromelain, a standardized complex of proteases from the pineapple plant, is absorbed unchanged from the intestine of animals at a rate of 40% ... .
PMID:2203073 Lotz-Winter H; Planta Med 56 (3): 249-53 (1990)
It has been postulated that a minor enzymatic component present in bromelain is responsible for the release of a kinin, which stimulates the production of prostaglandin E1-like compounds; These PGE1-like compounds are then responsible for the physiological activities of bromelain.
Leung, A.Y., Foster, S. Encyclopedia of Common Natural Ingredients Used in Food, Drugs, and Cosmetics. New York, NY. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1996., p. 101
Bromelain's digestant activity is based on its ability to hydrolyze proteins to oligopeptides and amino acids. Bromelain's proteolytic enzymes are cysteine proteases. Cysteine proteases cleave peptide bonds by nucleophilic attack via active-site cysteine residues.
Medical Economics Co; Physicians Desk Reference for Nutritional Supplements 1st ed p.71 (2001)
The mechanism of the putative anti-inflammatory activity ... may be accounted for, in part, by activation of plasmin production from plasminogen and reduction of kinin via inhibition of the conversion of kininogen to kinin. Other possibilities, may include proteolytic degradation of circulating immune complexes and inhibition of signaling by extracellular regulated kinase (ERK-2) and p21 ras.
Medical Economics Co; Physicians Desk Reference for Nutritional Supplements 1st ed p.71 (2001)
Bromelain has been shown to increase CD2-mediated T cell activation, to enhance antigen-independent binding to monocytes and to increase interferon (IFN)-gamma-dependant, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, Interleukin (IL)-1 beta, and interleukin (IL)-6 production in peripheral blood monocytes. These effects are thought to be due to bromelains proteolytic activity at cell surfaces, whereby it either removes surface molecules or reveals ones that already exist on cell membranes, thereby altering receptor-ligand interactions.
Medical Economics Co; Physicians Desk Reference for Nutritional Supplements 1st ed p.71 (2001)
For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for BROMELAINS (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.