
1. Bufalin, (3alpha,5beta)-isomer
1. 465-21-4
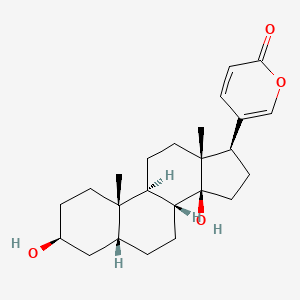
2. 3-beta,14-dihydroxy-5-beta-bufa-20,22-dienolide
3. 3,14-dihydroxy-bufa-20,22-dienolide
4. U549s98qlw
5. 5-((3s,5r,8r,9s,10s,13r,14s,17r)-3,14-dihydroxy-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-1h-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl)-2h-pyran-2-one
6. Chebi:517248
7. 3beta,14beta-dihydroxy-5beta-bufa-20,22-dienolide
8. 5-[(3s,5r,8r,9s,10s,13r,14s,17r)-3,14-dihydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,15,16,17-tetradecahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]pyran-2-one
9. Unii-u549s98qlw
10. Nsc-89595
11. Ch'an Su
12. Buf
13. Nsc 89595
14. Brn 5141601
15. Bufalin [mi]
16. (3beta,5beta)-3,14-dihydroxybufa-20,22-dienolide
17. Bufalin [who-dd]
18. Schembl165666
19. Bufa-20,22-dienolide, 3,14-dihydroxy-, (3.beta.,5.beta.)-
20. Chembl399680
21. Bufa-20,22-dienolide, 3,14-dihydroxy-, (3b,5b)-
22. Dtxsid90873563
23. Amy40632
24. Bufalin: Bufa-20,22-dienolide, 3,14-dihydroxy-, (3b,5b)-,
25. Hy-n0877
26. Zinc4215121
27. Hsci1_000110
28. Lmst01130001
29. Mfcd30207876
30. S7821
31. Akos015965454
32. Cs-3694
33. Smp2_000290
34. Ac-20197
35. Ac-34068
36. Bs-17080
37. C16922
38. 5beta-bufa-20,22-dienolide, 3beta,14-dihydroxy-
39. Brd-k63606607-001-01-8
40. Brd-k63606607-001-02-6
41. Q18379323
42. 5-beta-bufa-20,22-dienolide, 3-beta,14-dihydroxy-
43. Bufa-20,22-dienolide, 3,14-dihydroxy-, (3beta,5beta)-
44. Bufa-20,22-dienolide, 3,14-dihydroxy-, (3-beta,5-beta)-
45. (3beta,5beta,10alpha,17alpha)-3,14-dihydroxybufa-20,22-dienolide
| Molecular Weight | 386.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C24H34O4 |
| XLogP3 | 3.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 386.24570956 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 386.24570956 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 66.8 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 28 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 741 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 8 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Antineoplastic Agents
Substances that inhibit or prevent the proliferation of NEOPLASMS. (See all compounds classified as Antineoplastic Agents.)
Cardiotonic Agents
Agents that have a strengthening effect on the heart or that can increase cardiac output. They may be CARDIAC GLYCOSIDES; SYMPATHOMIMETICS; or other drugs. They are used after MYOCARDIAL INFARCT; CARDIAC SURGICAL PROCEDURES; in SHOCK; or in congestive heart failure (HEART FAILURE). (See all compounds classified as Cardiotonic Agents.)
Enzyme Inhibitors
Compounds or agents that combine with an enzyme in such a manner as to prevent the normal substrate-enzyme combination and the catalytic reaction. (See all compounds classified as Enzyme Inhibitors.)