


1. Allergipuran
2. Bufal
3. Bufederm
4. Bufexamac Ratiopharm
5. Bufexamac-ratiopharm
6. Bufexamacratiopharm
7. Droxaryl
8. Duradermal
9. Jomax
10. Malipuran
11. P Butoxyphenylacethydroxamic Acid
12. P-butoxyphenylacethydroxamic Acid
13. Paraderm
14. Parfenac
15. Windol
1. 2438-72-4
2. Bufexamic Acid
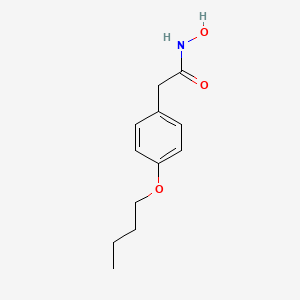
3. 2-(4-butoxyphenyl)-n-hydroxyacetamide
4. Parfenac
5. Feximac
6. Droxaryl
7. Malipuran
8. Mofenar
9. Norfemac
10. Paraderm
11. Parfenal
12. Anderm
13. 4-butoxy-n-hydroxybenzeneacetamide
14. Bufexamaco
15. Bufexamacum
16. Flogicid
17. P-butoxyphenylacetohydroxamic Acid
18. 4-butoxyphenylacetohydroxamic Acid
19. 2-(p-butoxyphenyl)-acetohydroxamic Acid
20. Flogocid N Plastigel
21. Acide P-butoxyphenylacethydroxamique
22. 2-(p-butoxyphenyl)acetohydroxamic Acid
23. Cp 1044 J3
24. Benzeneacetamide, 4-butoxy-n-hydroxy-
25. Cp 1044
26. Chebi:31317
27. Acetohydroxamic Acid, 2-(p-butoxyphenyl)-
28. Cp-1044-j3
29. Nsc-758153
30. Chembl94394
31. Mls000028409
32. 4t3c38j78l
33. J3
34. Ncgc00016611-01
35. Smr000058407
36. Cas-2438-72-4
37. Dsstox_cid_25368
38. Dsstox_rid_80831
39. Dsstox_gsid_45368
40. Bufessamac [dcit]
41. Bufessamac
42. Droxarol
43. Ml392
44. Bufexamacum [inn-latin]
45. Bufexamaco [inn-spanish]
46. Bufexamac [inn:ban:dcf:jan]
47. Sr-01000003067
48. Einecs 219-451-1
49. 2-(4-butoxyphenyl)acetohydroxamic Acid
50. Brn 2646848
51. Unii-4t3c38j78l
52. Acide P-butoxyphenylacethydroxamique [french]
53. Bufexamac,(s)
54. Prestwick_676
55. Anderm (tn)
56. Spectrum_001754
57. Bufexamac (jan/inn)
58. Bufexamac [inn]
59. Bufexamac [jan]
60. Opera_id_1503
61. Prestwick0_000243
62. Prestwick1_000243
63. Prestwick2_000243
64. Prestwick3_000243
65. Spectrum2_001457
66. Spectrum3_000938
67. Spectrum4_001037
68. Spectrum5_001117
69. Bufexamac [mart.]
70. Epitope Id:180855
71. Bufexamac [who-dd]
72. Cid_2466
73. Regid_for_cid_2466
74. Schembl25215
75. Bspbio_000026
76. Kbiogr_001593
77. Kbioss_002234
78. Mls001148632
79. Bufexamac, Analytical Standard
80. Butoxyphenylacethydroxamic Acid
81. Divk1c_000108
82. Spectrum1502003
83. Spbio_001353
84. Spbio_002245
85. Bpbio1_000030
86. Gtpl7498
87. Bufexamac [ep Impurity]
88. Bufexamac [ep Monograph]
89. Dtxsid7045368
90. Benzylchloroacetylcarbamate
91. Hms500f10
92. Kbio1_000108
93. Kbio2_002234
94. Kbio2_004802
95. Kbio2_007370
96. Kbio3_001976
97. Ninds_000108
98. Hms1568b08
99. Hms1921b18
100. Hms2095b08
101. Hms2235i13
102. Hms3371k16
103. Hms3656h16
104. Hms3712b08
105. Hms3885k03
106. Kuc105648n
107. Pharmakon1600-01502003
108. Act07664
109. Caa43872
110. Hy-b0494
111. Zinc3871797
112. Para-butoxyphenylacetohydroxamic Acid
113. Tox21_110522
114. Bdbm50015144
115. Ccg-39191
116. Mfcd00078936
117. Nsc758153
118. S3023
119. Bufexamac 1.0 Mg/ml In Acetonitrile
120. Akos015895401
121. Kuc105648n-02
122. Kuc105648n-03
123. Tox21_110522_1
124. Db13346
125. Ksc-10-210
126. Nsc 758153
127. Idi1_000108
128. Ksc-390-003
129. Ncgc00016611-02
130. Ncgc00016611-03
131. Ncgc00016611-04
132. Ncgc00016611-05
133. Ncgc00016611-06
134. Ncgc00016611-07
135. Ncgc00016611-09
136. Ncgc00016611-10
137. Ncgc00021813-03
138. Ncgc00021813-04
139. 2-(4-butoxy-phenyl)-n-hydroxy-acetamide
140. 2-(4-butoxyphenyl)-n-hydroxyacetamide #
141. Ac-18729
142. As-12207
143. Ksc-285-073-1
144. Sbi-0051694.p002
145. Ab00052252
146. B4179
147. Ft-0603607
148. Sw196831-3
149. C74254
150. D01271
151. Ab00052252_19
152. Ab00052252_20
153. A817259
154. Q412699
155. J-015485
156. Sr-01000003067-3
157. Sr-01000003067-4
158. Brd-k36660044-001-15-0
159. Bufexamac, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
160. A4z
| Molecular Weight | 223.27 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C12H17NO3 |
| XLogP3 | 1.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 223.12084340 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 223.12084340 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 58.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 16 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 200 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Indicated for the treatment of various skin conditions, such as atopic eczema and other inflammatory dermatoses.
Bufexamac is a topically-active anti-inflammatory agent that inhibits the cyclooxygenase enzyme. In cutaneous and deep experimental inflammation, topical administration of bufexamac exerted a dose-related anti-inflammatory effect. In guinea pigs, bufexamax was shown to be more active than topical acetylsalicylic acid 5% or phenylbutazone 5% in delaying the local increase in temperature resulting from UV exposure. Bufexamac is unlikely to have any effect on wound healing.
Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal
Anti-inflammatory agents that are non-steroidal in nature. In addition to anti-inflammatory actions, they have analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions. They act by blocking the synthesis of prostaglandins by inhibiting cyclooxygenase, which converts arachidonic acid to cyclic endoperoxides, precursors of prostaglandins. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis accounts for their analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions; other mechanisms may contribute to their anti-inflammatory effects. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal.)
M - Musculo-skeletal system
M01 - Antiinflammatory and antirheumatic products
M01A - Antiinflammatory and antirheumatic products, non-steroids
M01AB - Acetic acid derivatives and related substances
M01AB17 - Bufexamac
M - Musculo-skeletal system
M02 - Topical products for joint and muscular pain
M02A - Topical products for joint and muscular pain
M02AA - Antiinflammatory preparations, non-steroids for topical use
M02AA09 - Bufexamac
Absorption
Method of application affects the extent of cutaneous absorption. Following rectal administration as suppositories, the systemic absorption was reported to be low.
Route of Elimination
Following topical administration of 5% bufexamac, the recovery in the urine was 3.5% of the applied dose within 144 hours. Studies in healthy volunteers receiving an oral dose of 125 to 500 mg indicate that an average of 80% of the total dose is excreted in the urine within 48 hours.
Volume of Distribution
No data available.
Clearance
No data available.
No data available.
No data available.
The full mechanism of action is unclear. It is proposed that bufexamac acts similarly to other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to inhibit prostaglandin biosynthesis _in vitro_, via inhibiting cyclo-oxygenase (COX) enzymes. Systematically administered bufexamac may accumulate preferentially in the adrenal cortex of rats and may play a role in adrenal stimulation; however its topical anti-inflammatory action is likely to be independent of this effect.
