


1. Acetate, Buserelin
2. Bigonist
3. Buserelin Acetate
4. Hoe 766
5. Hoe-766
6. Hoe766
7. Profact
8. Receptal
9. Suprecur
10. Suprefact
11. Tiloryth
1. 57982-77-1
2. Pxw8u3yxdv
3. Ici 123215
4. Hoe 766
5. Etilamide
6. (des-gly10,d-ser(tbu)6,pro-nhet9)-lhrh
7. Buserelin (inn)
8. Buserelin [inn]
9. 68630-75-1
10. Buserelina
11. Busereline
12. Buserelinum
13. Luteinizing Hormone-releasing Factor (pig), 6-(o-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-d-serine)-9-(n-ethyl-l-prolinamide)-10-deglycinamide-
14. Buserelin [inn:ban]
15. Unii-pxw8u3yxdv
16. Busereline [inn-french]
17. Buserelinum [inn-latin]
18. Buserelina [inn-spanish]
19. Metrelef
20. Ccris 2657
21. Hoe 766a
22. Tiloryth (tn)
23. Einecs 261-061-9
24. D-ser-(tbu)(sup 6)-lhrh-ethylamide
25. Buserelin [mi]
26. (d-ser(tbu)(sup 6)-ea(sup 10))-lhrh
27. Buserelin [mart.]
28. Buserelin [who-dd]
29. Schembl13354
30. S 746766
31. Gtpl3860
32. Buserelin [ep Monograph]
33. Buserelin For Nmr Identification
34. Chembl2110824
35. D-ser(tbu(sup 6))-lh-rh-(1-9)-nonapeptide Ethylamide
36. Schembl19409318
37. Schembl19459955
38. Buserelin For Peak Identification
39. Chebi:135907
40. Dtxsid301024155
41. (d-ser(bu(sup T)(sup 6)))-lh-rh(1-9)nonapeptide-ethylamide
42. (d-ser(tbu)(sup 6)-ea(sup 10))-luteinizing Hormone-releasing Hormone
43. Akos015994645
44. Akos030213242
45. Luteinizing Hormone-releasing Hormone, (d-ser(tbu)(sup 6)-ea(sup 10))-
46. Hs-2005
47. Ncgc00181295-01
48. D07259
49. 982b771
50. A831694
51. Q414745
52. W-105422
53. (2s)-n-[(2s)-1-[[(2s)-1-[[(2s)-1-[[(2s)-1-[[(2r)-1-[[(2s)-1-[[(2s)-5-(diaminomethylideneamino)-1-[(2s)-2-(ethylcarbamoyl)-1-pyrrolidinyl]-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-4-methyl-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-3-[(2-methylpropan-2-yl)oxy]-1-oxopropan-2-yl]amino]-3-(4-hy
54. (2s)-n-[(2s)-1-[[(2s)-1-[[(2s)-1-[[(2s)-1-[[(2r)-1-[[(2s)-1-[[(2s)-5-[bis(azanyl)methylideneamino]-1-[(2s)-2-(ethylcarbamoyl)pyrrolidin-1-yl]-1-oxidanylidene-pentan-2-yl]amino]-4-methyl-1-oxidanylidene-pentan-2-yl]amino]-3-[(2-methylpropan-2-yl)oxy]-1-oxi
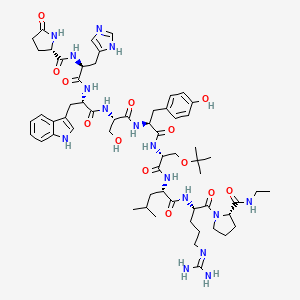
55. 5-oxo-l-prolyl-l-histidyl-l-tryptophyl-l-seryl-l-tyrosyl-o-tert-butyl-d-seryl-l-leucyl-l-arginyl-n-ethyl-l-prolinamide
56. Luteinizing Hormone-releasing Hormone (pig), 6-(o-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-d-serine)-9-(n-ethyl-l-prolinamide)-10-deglycinamide-
| Molecular Weight | 1239.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C60H86N16O13 |
| XLogP3 | -0.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 15 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 15 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 33 |
| Exact Mass | 1238.65602686 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 1238.65602686 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 441 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 89 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 2450 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 9 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Buserelin may be used in the treatment of hormone-responsive cancers such as prostate cancer or breast cancer, estrogen-dependent conditions (such as endometriosis or uterine fibroids), and in assisted reproduction.
The substitution of glycine in position 6 by D-serine, and that of glycinamide in position 10 by ethylamide, leads to a nonapeptide with a greatly enhanced LHRH effect. The effects of buserelin on FSH and LH release are 20 to 170 times greater than those of LHRH. Buserelin also has a longer duration of action than natural LHRH. Investigations in healthy adult males and females have demonstrated that the increase in plasma LH and FSH levels persist for at least 7 hours and that a return to basal values requires about 24 hours. Clinical inhibition of gonadotropin release, and subsequent reduction of serum testosterone or estradiol to castration level, was found when large pharmacologic doses (50-500 mcg SC/day or 300-1200 mcg IN/day) were administered for periods greater than 1 to 3 months. Chronic administration of such doses of buserelin results in sustained inhibition of gonadotropin production, suppression of ovarian and testicular steroidogenesis and, ultimately, reduced circulating levels of gonadotropin and gonadal steroids. These effects form the basis for buserelin use in patients with hormone-dependent metastatic carcinoma of the prostate gland as well as in patients with endometriosis.
Fertility Agents, Female
Compounds which increase the capacity to conceive in females. (See all compounds classified as Fertility Agents, Female.)
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L02 - Endocrine therapy
L02A - Hormones and related agents
L02AE - Gonadotropin releasing hormone analogues
L02AE01 - Buserelin
Absorption
Buserelin is water soluble and readily absorbed after subcutaneous injection (70% bioavailable). However, bioavailability after oral absorption. When administered correctly via the nasal route, it may be absorbed in the nasal mucosa to achieve sufficient plasma levels.
Route of Elimination
Buserelin and its inactive metabolites are excreted via the renal and biliary routes. In man it is excreted in urine at 50% in its intact form.
Volume of Distribution
Buserelin circulates in serum predominantly in intact active form. Preferred accumulation is preferentially in the liver and kidneys as well as in the anterior pituitary lobe, the biological target organ.
It is metabolized and subsequently inactivated by peptidase (pyroglutamyl peptidase and chymotrypsin-like endopeptidase) in the liver and kidneys as well as in the gastrointestinal tract. In the pituitary gland, it is inactivated by membrane-located enzymes.
The elimination half-life is approximately 50 to 80 minutes following intravenous administration, 80 minutes after subcutaneous administration and approximately 1 to 2 hours after intranasal administration.
Buserelin stimulates the pituitary gland's gonadotrophin-releasing hormone receptor (GnRHR). Buserelin desensitizes the GnRH receptor, reducing the amount of gonadotropin. In males, this results in a reduction in the synthesis and release of testosterone. In females, estrogen secretion is inhibited. While initially, there is a rise in FSH and LH levels, chronic administration of Buserelin results in a sustained suppression of these hormones.