
1. Anxut
2. Apo Buspirone
3. Apo-buspirone
4. Bespar
5. Busp
6. Buspar
7. Buspirone Hydrochloride
8. Gen Buspirone
9. Gen-buspirone
10. Hydrochloride, Buspirone
11. Lin Buspirone
12. Lin-buspirone
13. Mj 9022 1
14. Mj-9022-1
15. Mj90221
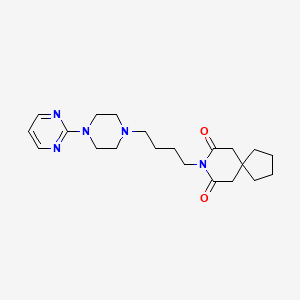
16. N-(4-(4-(2-pyrimidinyl)-1-piperazinyl)butyl)-1-cyclopentanediacetamide
17. Neurosine
18. Novo Buspirone
19. Novo-buspirone
20. Nu Buspirone
21. Nu-buspirone
22. Pms Buspirone
23. Pms-buspirone
24. Ratio Buspirone
25. Ratio-buspirone
1. 36505-84-7
2. Buspirona
3. Buspironum
4. Buspironum [inn-latin]
5. Buspirona [inn-spanish]
6. Gen-buspirone
7. Buspin
8. Buspirone Free Base
9. 8-(4-(4-(pyrimidin-2-yl)piperazin-1-yl)butyl)-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane-7,9-dione
10. 8-[4-(4-pyrimidin-2-ylpiperazin-1-yl)butyl]-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane-7,9-dione
11. 8-(4-(4-(2-pyrimidinyl)-1-piperizinyl)butyl)-8-azaspiro(4,5)decane-7,9-dione
12. Buspirone (inn)
13. Chembl49
14. Ansial
15. Tk65wks8hl
16. 8-azaspiro[4.5]decane-7,9-dione, 8-[4-[4-(2-pyrimidinyl)-1-piperazinyl]butyl]-
17. Chebi:3223
18. Bci-024
19. 8-{4-[4-(pyrimidin-2-yl)piperazin-1-yl]butyl}-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane-7,9-dione
20. 8-[4-(4-pyrimidin-2-yl-piperazin-1-yl)-butyl]-8-aza-spiro[4.5]decane-7,9-dione
21. 8-azaspiro(4.5)decane-7,9-dione, 8-(4-(4-(2-pyrimidinyl)-1-piperazinyl)butyl)-
22. Ncgc00015162-04
23. Buspirone [inn]
24. Dsstox_cid_2707
25. Buspirone [inn:ban]
26. 8-azaspiro(4,5)decane-7,9-dione, 8-(4-(4-(2-pyrimidinyl)piperizinyl)butyl)-
27. Dsstox_rid_76696
28. Dsstox_gsid_22707
29. 116753-41-4
30. Buspirone-mdts
31. 8-[4-[4-(2-pyrimidinyl)-1-piperazinyl]butyl]-8-azaspiro[4,5]decane-7,9-dione
32. 8-[4-[4-(2-pyrimidinyl)-1-piperazinyl]butyl]-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane-7,9-dione
33. 8-{4-[4-(2-pyrimidinyl)-1-piperazinyl]butyl}-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane-7,9-dione
34. 8-azaspiro[4.5]decane-7,9-dione,8-[4-[4-(2-pyrimidinyl)-1-piperazinyl]butyl]-
35. Cas-36505-84-7
36. Gen-buspirone (tn)
37. Einecs 253-072-2
38. Unii-tk65wks8hl
39. Brn 0964904
40. Spectrum_001756
41. Tocris-0962
42. Buspirone [mi]
43. Prestwick0_000369
44. Prestwick1_000369
45. Prestwick2_000369
46. Prestwick3_000369
47. Buspirone [vandf]
48. Lopac-b-7148
49. Biomol-nt_000108
50. Gtpl36
51. Buspirone [who-dd]
52. Buspironehydrochloride
53. Lopac0_000223
54. Schembl16398
55. Bspbio_000497
56. Kbioss_002236
57. Bidd:gt0519
58. Divk1c_000921
59. Spbio_002418
60. Bpbio1_000547
61. Bpbio1_001403
62. Dtxsid2022707
63. Kbio1_000921
64. Kbio2_002236
65. Kbio2_004804
66. Kbio2_007372
67. Ninds_000921
68. Hms2090k19
69. Zinc1530571
70. Tox21_110092
71. Tox21_302371
72. Bdbm50001859
73. Stk086268
74. Akos002313325
75. Tox21_110092_1
76. Ccg-204318
77. Db00490
78. Sdccgsbi-0050211.p004
79. 8-[4-[4-(pyrimidine-2-yl)-piperazine-1-yl]-butyl]-8-aza-spiro[4.5]decane-7,9-dione
80. Idi1_000921
81. Mrf-0000691
82. Buspirone 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
83. Ncgc00015162-01
84. Ncgc00015162-02
85. Ncgc00015162-03
86. Ncgc00015162-05
87. Ncgc00015162-06
88. Ncgc00015162-07
89. Ncgc00015162-08
90. Ncgc00015162-10
91. Ncgc00015162-11
92. Ncgc00015162-22
93. Ncgc00016820-01
94. Ncgc00024905-01
95. Ncgc00024905-02
96. Ncgc00024905-03
97. Ncgc00255227-01
98. Buspirone 1000 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
99. Sbi-0050211.p003
100. Cas-33386-08-2
101. Ab00053432
102. Ft-0621488
103. C06861
104. D07593
105. Ab00053432-12
106. Ab00053432_13
107. 505b847
108. A924049
109. L001110
110. Q412194
111. W-106606
112. Brd-k93461745-001-01-5
113. Brd-k93461745-003-03-7
114. Brd-k93461745-003-14-4
115. 8-(4-[4-(2-pyrimidinyl)-1-piperazinyl]butyl)-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane-7,9-dione #
116. 8-[4-(4-pyrimidin-2-ylpiperazin-1-yl)butyl]-8-azaspiro[4,5]decane-7,9-dione
117. 8-[4-[4-(2-pyrimidinyl)-1-piperazinyl]-butyl]-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane-7,9-dione
118. 8-[4-[4-(pyrimidine-2yl)-piperazine-1-yl]-butyl]-8-aza-spiro[4.5]decane-7.9-dione
119. (buspirone) 8-[4-(4-pyrimidin-2-yl-piperazin-1-yl)-butyl]-8-aza-spiro[4.5]decane-7,9-dione
120. 8-[4-(4-pyrimidin-2-yl-piperazin-1-yl)-butyl]-8-aza-spiro[4.5]decane-7,9-dione : (hydrochloride)
121. 8-[4-(4-pyrimidin-2-yl-piperazin-1-yl)-butyl]-8-aza-spiro[4.5]decane-7,9-dione; Hydrochloride(buspirone)
| Molecular Weight | 385.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C21H31N5O2 |
| XLogP3 | 2.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 385.24777525 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 385.24777525 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 69.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 28 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 529 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Indicated for the management of anxiety disorders or the short-term relief of the symptoms of anxiety.
The clinical effect of buspirone in alleviating the symptoms of generalized anxiety disorders typically takes 2 to 4 weeks to achieve. The delayed onset of action of buspirone suggests that the therapeutic effectiveness in generalized anxiety may involved more than its molecular mechanism of action at the 5-HT1A receptors, or buspirone may induce adaptations of 5-HT1A receptors. Buspirone was not shown to alter the psychomotor or cognitive function in healthy volunteers, and the risk of developing sedation is relatively low compared to other anxiolytics, such as benzodiazepines. Unlike benzodiazepines and barbiturates used in anxiety disorders, buspirone is not associated with a risk for developing physical dependence or withdrawal, or any significant interaction with central nervous system depressants such as ethanol. This is due to the lack of effects on GABA receptors. Buspirone also does not exhibit any anticonvulsant or muscle-relaxing properties, but may interfere with arousal reactions due to its inhibitory action on the aactivity of noradrenergic locus coerulus neurons. Despite its clinical effectiveness in generalized anxiety, buspirone demonstrated limited clinical effectiveness on panic disorders, severe anxiety, phobias, and obsessive compulsive disorders. The clinical effectiveness of the long-term use of buspirone, for more than 3 to 4 weeks, has not demonstrated in controlled trials but there were no observable significant adverse events in patients receiving buspirone for a year in a study of long-term use.
Anti-Anxiety Agents
Agents that alleviate ANXIETY, tension, and ANXIETY DISORDERS, promote sedation, and have a calming effect without affecting clarity of consciousness or neurologic conditions. ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS are commonly used in the symptomatic treatment of anxiety but are not included here. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Anxiety Agents.)
Serotonin Receptor Agonists
Endogenous compounds and drugs that bind to and activate SEROTONIN RECEPTORS. Many serotonin receptor agonists are used as ANTIDEPRESSANTS; ANXIOLYTICS; and in the treatment of MIGRAINE DISORDERS. (See all compounds classified as Serotonin Receptor Agonists.)
N - Nervous system
N05 - Psycholeptics
N05B - Anxiolytics
N05BE - Azaspirodecanedione derivatives
N05BE01 - Buspirone
Absorption
Buspirone is rapidly absorbed following oral administration. Bioavailability is low and variable (approximately 5%) due to extensive first pass metabolism. While absorption of buspirone is decreased with concomitant food intake, the first-pass metabolism of the drug is also decreased, resulting in an increased bioavailability as well as increased Cmax and AUC. Following oral administration of single oral doses of 20 mg, the Cmax ranged from 1 to 6 ng/mL and the Tmax ranged from 40 to 90 minutes.
Route of Elimination
A single-dose pharmacokinetic studies using 14C-labeled buspirone demonstrated that about 29-63% of the dose administered was excreted in the urine within 24 hours, primarily in the form of metabolites. About 18% to 38% of the dose was eliminated via fecal excretion.
Volume of Distribution
In a pharmacokinetic study assessing buspirone over the dose range of 10 to 40 mg, the volume of distribution was 5.3 L/kg.
Clearance
In a pharmacokinetic study assessing buspirone over the dose range of 10 to 40 mg, the systemic clearance was 1.7 L/h/kg.
Buspirone is extensively metabolized upon administration, where it primarily undergoes hepatic oxidation mediated by the CYP3A4 enzyme. Hydroxylated derivatives are produced, including a pharmacologically active metabolite 1-pyrimidinylpiperazine (1-PP). In animal studies, 1-PP possessed about one quarter of the pharmacological activity of buspirone.
In a single-dose pharmacokinetic study of 14C-labeled buspirone, the average elimination half-life of unchanged buspirone following administration of single doses ranging from 10 to 40 mg was about 2 to 3 hours.
The therapeutic action of buspirone in generalized anxiety disorders is thought to be mainly derived from its interaction with two major 5-HT1A receptor subtypes that are involved in the brain's anxiety and fear circuitry to enhance the serotonergic activity in these brain areas. Buspirone acts as a full agonist at presynaptic 5-HT1A receptors, or 5-HT1A autoreceptors, expressed at dorsal raphe while acting as a partial agonist at the postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptors expressed on hippocampus and cortex. 5-HT1A receptors function as inhibitory autoreceptors by being expressed on the soma or dendrites of serotonergic neurons or mediate postsynaptic actions of 5-HT by being highly expressed on the corticolimbic circuits. They are inhibitory G-protein coupled receptors that couple to Gi/Go proteins. When activated, presynaptic 5-HT1A autoreceptors causes neuron hyperpolarization and reduces the firing rate of the serotonergic neuron, thereby decreasing extracellular 5-HT levels in the neuron's projection areas. Activated postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptors promote hyperpolarization to released 5-HT on pyramidal neurons. The anxiolytic action of buspirone is mainly thought to arise from the interaction at presynaptic 5-HT1A autoreceptors. Acting as a potent agonist in these receptors, buspirone initially causes activation of these autoreceptors and inhibition of 5-HT release. It is proposed that buspirone induces desensitization of somatodendritic autoreceptors over time, which may explain the delayed onset of action of the drug. Desensitization of the autoreceptors ultimately results in heightened excitation of serotonergic neurons and enhanced 5-HT release. Buspirone also displays a weak affinity for serotonin 5HT2 receptors and acts as a weak antagonist on dopamine D2 autoreceptors, although there is not much evidence that the action at these receptors contribute to the anxiolytic effect of buspirone. It acts as an antagonist at presynaptic dopamine D3 and D4 receptors and may bind to alpha-1 adrenergic receptors as a partial agonist.