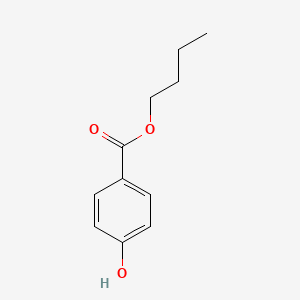

1. Butyl-p-hydroxybenzoate
1. Butyl 4-hydroxybenzoate
2. 94-26-8
3. Butyl Paraben
4. Butyl P-hydroxybenzoate
5. Butyl Parahydroxybenzoate
6. Nipabutyl
7. Butoben
8. Butyl Chemosept
9. Butyl Parasept
10. Tegosept B
11. Butyl Tegosept
12. Butyl Butex
13. Tegosept Butyl
14. Aseptoform Butyl
15. Preserval B
16. Solbrol B
17. N-butyl P-hydroxybenzoate
18. Butyl-parasept
19. Benzoic Acid, 4-hydroxy-, Butyl Ester
20. 4-(butoxycarbonyl)phenol
21. N-butyl 4-hydroxybenzoate
22. N-butyl Parahydroxybenzoate
23. N-butyl Hydroxybenzoate
24. Butyl P-hydroxy Benzoate
25. Fema No. 2203
26. N-butyl-p-hydroxybenzoate
27. 4-hydroxybenzoic Acid Butyl Ester
28. Benzoic Acid, P-hydroxy-, Butyl Ester
29. N-butyl-paraben
30. P-hydroxybenzoic Acid Butyl Ester
31. Lexgard B
32. N-butyl-4-hydroxybenzoate
33. Nsc 8475
34. P-hydroxybenzoic Acid N-butyl Ester
35. Butylparaben (nf)
36. Butylparaben (tn)
37. Butylparaben [nf]
38. Spf
39. P-hydroxybenzoic Acid, Butyl Ester
40. 4-hydroxybenzoic Acid, Butyl Ester
41. P-hydroxybenzoic Butyl Ester
42. 3qpi1u3fv8
43. Butyl Parahydroxybenzoate (tn)
44. Chebi:88542
45. 4-hydroxybenzoic Acid-n-butyl Ester
46. Nsc-13164
47. Cas-94-26-8
48. Ncgc00016354-03
49. Dsstox_cid_209
50. Dsstox_rid_75434
51. Dsstox_gsid_20209
52. Butylparaben [usan]
53. Butyl-p-hydroxybenzoate
54. Caswell No. 130a
55. Fema Number 2203
56. N-butyl Paraben
57. 4-hydroxybenzoic Acid-n-butyl Ester 1000 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
58. Butyl Par Asept
59. Smr000462402
60. Ccris 2462
61. Hsdb 286
62. P-hydroxy Butyl Benzoate
63. Sr-01000389296
64. Einecs 202-318-7
65. Unii-3qpi1u3fv8
66. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 061205
67. Brn 1103741
68. Butyl-paraben
69. Ai3-02930
70. 27k
71. Mfcd00016478
72. Butyl Paraben-[d9]
73. 4mg9
74. Prestwick0_000894
75. Prestwick1_000894
76. Prestwick2_000894
77. Prestwick3_000894
78. Butylparaben [ii]
79. Butylparaben [mi]
80. Wln: Qr Dvo4
81. Butylparaben [hsdb]
82. Butylparaben [inci]
83. Cid_7184
84. Schembl3647
85. Butylparaben [vandf]
86. Bspbio_000708
87. Butyl //p//-hydroxybenzoate
88. Mls000575004
89. Mls002154054
90. Mls002303045
91. Bidd:er0231
92. Butylparaben [usp-rs]
93. Spbio_002917
94. Bpbio1_000780
95. Chembl459008
96. F0266-0124
97. N-butyl-p-hydroxybenzoate,(s)
98. Dtxsid3020209
99. Bdbm23448
100. Fema 2203
101. Nsc8475
102. Butyl Parahydroxybenzoate (jp15)
103. Butyl Parahydroxybenzoate (jp17)
104. Butyl 4-hydroxybenzoate, >=99%
105. Butyl Para Hydroxy Benzoate
106. Hms1570d10
107. Hms2094a21
108. Hms2097d10
109. Hms2220g15
110. Hms3327p04
111. Hms3714d10
112. Pharmakon1600-01505995
113. Hy-b1431
114. Nsc-8475
115. Zinc1586769
116. Tox21_110393
117. Tox21_201785
118. Tox21_300332
119. Nsc759303
120. P-hydroxybenzoic Acid, N-butyl Ester
121. S4584
122. Butyl Hydroxybenzoate [mart.]
123. Akos000121421
124. Butyl Hydroxybenzoate [who-dd]
125. Tox21_110393_1
126. Butyl Parahydroxybenzoate [jan]
127. Ccg-213596
128. Cs-4783
129. Db14084
130. Nsc-759303
131. Butyl P-hydroxy Benzoate [fhfi]
132. Butyl 4-?hydroxybenzoate(butyl Paraben)
133. Butyl 4-hydroxybenzoate (butyl Paraben)
134. Ncgc00016354-01
135. Ncgc00016354-02
136. Ncgc00016354-04
137. Ncgc00016354-05
138. Ncgc00016354-06
139. Ncgc00016354-07
140. Ncgc00016354-11
141. Ncgc00091142-01
142. Ncgc00091142-02
143. Ncgc00254294-01
144. Ncgc00259334-01
145. Ac-34535
146. As-14309
147. Sbi-0206946.p001
148. Butyl 4-hydroxybenzoate, >=99.0% (gc)
149. Ds-010619
150. Ab00513951
151. B3771
152. Ft-0623315
153. H0210
154. A16382
155. Butyl Parahydroxybenzoate [ep Impurity]
156. Butyl Parahydroxybenzoate [ep Monograph]
157. D01420
158. Ab00513951_09
159. A844895
160. Q3302873
161. Sr-01000389296-1
162. Sr-01000389296-3
163. W-100204
164. Brd-k08287586-001-03-6
165. Brd-k08287586-001-08-5
166. Butyl 4-hydroxybenzoate, Saj First Grade, >=99.0%
167. Propyl Hydroxybenzoate Impurity D [ep Impurity]
168. Z291799028
169. Methyl Parahydroxybenzoate Impurity D [ep Impurity]
170. 4-hydroxybenzoic Acid-n-butyl Ester 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
171. 4-hydroxybenzoic Acid-n-butyl Ester 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
172. 4-hydroxybenzoic Acid-n-butyl Ester 1000 Microg/ml In Methanol
| Molecular Weight | 194.23 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C11H14O3 |
| XLogP3 | 3.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 194.094294304 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 194.094294304 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 46.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 14 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 171 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
It is used as a pharyngeal antiseptic in combination with other parabens.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 1090
By the oral route, parabens are rapidly absorbed, metabolized, and excreted. The metabolic reactions and conversions in mammals vary with the chain length of the ester, the animal species, route of administration, and quantity tested. The metabolism of parabens in humans appears to be most closely related to that of dogs. The rate of metabolite excretion appears to decrease with increasing molecular weight of the ester. /4-Hydroxybenzoates (Parabens)/
Bingham, E.; Cohrssen, B.; Powell, C.H.; Patty's Toxicology Volumes 1-9 5th ed. John Wiley & Sons. New York, N.Y. (2001)., p. v6 639
After butylparaben is intravenously infused into the dog, nonhydrolyzed butylparaben is found in brain, spleen, and pancreas. In liver, kidney, and muscle, it is immediately hydrolyzed to p-hydroxybenzoic acid. Six hours after oral administration of 1.0 g/kg to dogs, the peak plasma concentration of free and total butyl paraben (15 and 141 ug/cu cm) is reached. After 48 hr, butylparaben is eliminated.
Bingham, E.; Cohrssen, B.; Powell, C.H.; Patty's Toxicology Volumes 1-9 5th ed. John Wiley & Sons. New York, N.Y. (2001)., p. v6 672
Skin penetration of methyl, ethyl, propyl and butyl parabens through excised guinea pig dorsal skin was examined, and effects of the penetration enhancers, l-menthol plus ethanol itself and N-dodecyl-2-pyrrolidone, were observed. Permeability of coefficients of the parabens correlated with n-octanol/water partition coefficients. Addition of 1% l-menthol in 15% ethanol about sixteen times increased the permeability coefficient of methyl paraben, whereas this enhancer decreased that of butyl paraben to about one fifth of the control value. A similar, though weaker, tendency was observed for the effects of 15% ethanol itself. 0.025% suspension of N-dodecyl-2-pyrrolidone increased the permeability coefficient of methyl paraben about seven times, whereas it did not change that of butylparaben significantly. Therefore, dependency of the permeability coefficients of the parabens on n-octanol/water partition coefficients almost disappeared in the presence of this compound. A spin label study with stratum corneum lipid liposomes revealed that increase of fluidity of the lipid bilayer by these penetration enhancers corresponded with their enhancement effects on skin penetration of methyl paraben. Perturbation of stratum corneum lipid lamella thus seems to be related with their enhancement of the absorption of hydrophilic paraben.
PMID:9301035 Kitagawa S et al; Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 45 (8): 13454-7 (1997)
Intravenous (IV) injections at 50 mg/kg methylparaben, ethylparaben, propylparaben, or butylparaben were administered to groups of three or more fasted dogs. Similarly, these compounds were administered orally at a dose of 1.0 g/kg. Blood and urine were analyzed at predetermined intervals. Immediately following IV injection, very little ester remained in the blood. Metabolites were detectable in the blood up to 6 hr postinjection and 24 hr postingestion. Recovery of all esters but butylparaben ranged from 58 to 94% of the administered dose. Absorption was essentially complete. Recovery of butylparaben after oral administration was 40% and 48 after IV administration. The authors considered this finding a result of less effective hydrolysis of butylparaben. Dogs given 50 mg/kg were then killed and the distribution of esters and metabolites to organs was determined. Pure ester was recovered only in the brain, spleen, and pancreas. High concentrations of metabolites were detected in the liver and kidneys. With in vitro assays, it was found that esterases in the liver and kidneys of the dog were extremely efficient in hydrolyzing parabens --- complete hydrolysis after 3 minutes for all parabens except butylparaben, which took 30 to 60 minutes. No accumulation of parabens was observed in the tissues of dogs given orally 1 g/kg/day methylparaben or propylparaben for 1 year. The rate of urinary excretion of esters and metabolites in these dogs increased to such an extent that after 24 hr, 96 % of the dose was excreted in the urine. This is contrasted with dogs given a single dose of paraben in which the 96 % excretion level was not attained until 48 hr. When 10 % methylparaben or propylparaben in hydrophilic ointment was applied to the skin of a white rabbit for 48 h, esters and metabolites were not detected in the kidneys.
Cosmetic Ingredient Review; Final Amended Report on the Safety Assessment of Methylparaben, Ethylparaben, Propylparaben, Isopropylparaben, Butylparaben, Isobutylparaben, and Benzylparaben as used in Cosmetic Products p 26. Int J Toxicol 27 Suppl 4: 1-82 (2008). Available from, as of November 21, 2016: https://online.personalcarecouncil.org/ctfa-static/online/lists/cir-pdfs/PR427.pdf
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for BUTYLPARABEN (9 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
In mice, rats, rabbits, or dogs, butyl paraben is excreted in the urine as unchanged benzoate, p-hydroxybenzoic acid, p-hydroxyhippuric acid (p-hydroxybenzoylglycine), ester glucuronides, ether glucuronides, or ether sulfates.
Bingham, E.; Cohrssen, B.; Powell, C.H.; Patty's Toxicology Volumes 1-9 5th ed. John Wiley & Sons. New York, N.Y. (2001)., p. v6 672
By the oral route, parabens are rapidly absorbed, metabolized, and excreted. The metabolic reactions and conversions in mammals vary with the chain length of the ester, the animal species, route of administration, and quantity tested. The metabolism of parabens in humans appears to be most closely related to that of dogs. The rate of metabolite excretion appears to decrease with increasing molecular weight of the ester. /4-Hydroxybenzoates (Parabens)/
Bingham, E.; Cohrssen, B.; Powell, C.H.; Patty's Toxicology Volumes 1-9 5th ed. John Wiley & Sons. New York, N.Y. (2001)., p. v6 639
The penetration and metabolism of butylparaben using viable, full-thickness human skin /is described/. ... A total of 21% of the radiolabel penetrated to the receptor fluid after 24 hr. ... the principle metabolite, hydroxybenzoic acid, was detected in the receptor fluid, with barely detectable levels of butylparaben and no ethylparaben, in this study of full-thickness skin. ... This work was repeated to again examine the penetration and metabolism of butylparaben (0.4%) in an oil/water emulsion applied to the same full thickness viable human skin ... A finite dose (10 L/cm ) of the 2 emulsion was applied to the skin surface and remained in contact over a 24 hr period without occlusion. (14)C-butylparaben (labeled in the carbon ring) was measured in the receptor fluid. A mean value of 14.9% (+ or - 3.73%) of the radioactive label penetrated the full thickness human skin after 24 hr. The principle metabolite, hydroxybenzoic acid, was found in the receptor fluid (mean of 15.2% + or - 5.23%) of all 10 replications (skin donated from two individuals), but barely detectable levels of the parent butylparaben (mean of 0.225% 0.063%) were found only in 5 of 10 replications. The authors interpreted these results to confirm the near complete first-pass metabolism of butylparaben to p-hydroxybenzoic acid in human skin.
Cosmetic Ingredient Review; Final Amended Report on the Safety Assessment of Methylparaben, Ethylparaben, Propylparaben, Isopropylparaben, Butylparaben, Isobutylparaben, and Benzylparaben as used in Cosmetic Products p 29. Int J Toxicol 27 Suppl 4: 1-82 (2008). Available from, as of November 21, 2016: https://online.personalcarecouncil.org/ctfa-static/online/lists/cir-pdfs/PR427.pdf
... A study /was conducted/ of the in vitro dermal penetration and metabolism of methylparaben and butylparaben in rat and human skin. For each paraben, an oil in water emulsion with both radiolabeled ( C in the carbon 14 ring) and non-radiolabeled paraben was prepared to a target concentration (0.8% for methylparaben and 0.4% for butylparaben). Skin samples (10 replicates for rat skin and 13 replicates for human skin) were mounted in flow-through diffusion cells. Test emulsions were applied evenly at 10 L/cm , one time, with no occlusion. Samples of the receptor 2 fluid from a single skin were pooled, along with reference standards, were mixed with acetonitrile, filtered, and analyzed for methylparaben, butylparaben, and hydroxybenzoic acid using liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectroscopy. ... For Butylparaben, 52.3% was metabolized to hydroxybenzoic acid, with only 5.5% as unmetabolized butylparaben. Metabolism was different in human skin ... For butylparaben, 32.8% appeared as hydroxybenzoic acid and 49.7% as unmetabolized butylparaben.
Cosmetic Ingredient Review; Final Amended Report on the Safety Assessment of Methylparaben, Ethylparaben, Propylparaben, Isopropylparaben, Butylparaben, Isobutylparaben, and Benzylparaben as used in Cosmetic Products p 28. Int J Toxicol 27 Suppl 4: 1-82 (2008). Available from, as of November 21, 2016: https://online.personalcarecouncil.org/ctfa-static/online/lists/cir-pdfs/PR427.pdf
For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for BUTYLPARABEN (9 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Butyl-4-hydroxybenzoate has known human metabolites that include (2S,3S,4S,5R)-6-(4-butoxycarbonylphenoxy)-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
BPB was rapidly cleared in hepatocytes from rat (t(1/2) = 3-4 min) and human (t(1/2) = 20-30 min).
PMID:22830980 Mathews JM et al; Xenobiotica 43 (2): 169-81 (2013)