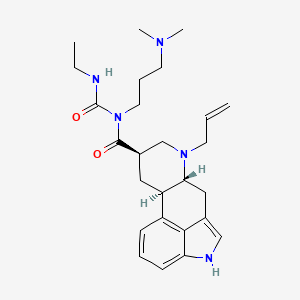

1. 1-((6-allylergolin-8beta-yl)carbonyl)-1-(3-(dimethylamino)propyl)-3-ethylurea
2. 1-ethyl-2-(3'-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-(6'-allylergoline-8'-beta-carbonyl)urea Diphosphate
3. Cabaser
4. Cabaseril
5. Cabergoline Diphosphate
6. Dostinex
7. Fce 21336
8. Fce-21336
9. Galastop
1. 81409-90-7
2. Dostinex
3. Cabaser
4. Cabergolinum [latin]
5. Cabergolina [spanish]
6. Cabergolinum
7. Cabergolina
8. Fce-21336
9. Fce 21336
10. Velactis
11. 1-((6-allylergolin-8beta-yl)carbonyl)-1-(3-(dimethylamino)propyl)-3-ethylurea
12. Cabaseril
13. Chebi:3286
14. Ll60k9j05t
15. Dsstox_cid_2719
16. 1-[(6-allylergoline-8beta-yl)carbonyl]-1-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-3-ethylurea
17. 1-ethyl-3-(3'-dimethylamionpropyl)-2-(6'-allylergoline-8'beta-carbonyl)urea
18. (8r)-6-allyl-n-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-n-(ethylcarbamoyl)ergoline-8-carboxamide
19. Dsstox_rid_76698
20. Dsstox_gsid_22719
21. (6ar,9r,10ar)-7-allyl-n-(3-(dimethylamino)propyl)-n-(ethylcarbamoyl)-4,6,6a,7,8,9,10,10a-octahydroindolo[4,3-fg]quinoline-9-carboxamide
22. (8beta)-n-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-n-[(ethylamino)carbonyl]-6-(2-propenyl)-ergoline-8-carboxamide
23. Sogilen
24. Dostinex (tn)
25. 1-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-3-ethyl-1-{[(2r,4r,7r)-6-(prop-2-en-1-yl)-6,11-diazatetracyclo[7.6.1.0^{2,7}.0^{12,16}]hexadeca-1(16),9,12,14-tetraen-4-yl]carbonyl}urea
26. Cabaser (tn)
27. Cas-81409-90-7
28. Sr-05000001493
29. Brn 6020775
30. Unii-ll60k9j05t
31. Caberlin
32. Ncgc00167821-01
33. Cabergoline [usan:usp:inn:ban]
34. Cg-101
35. Mfcd00867887
36. Cabergoline [mi]
37. Cabergoline [inn]
38. Cabergoline [jan]
39. Cabergoline [usan]
40. Gtpl37
41. Cabergoline [vandf]
42. Cabergoline [mart.]
43. Schembl42292
44. Cabergoline [usp-rs]
45. Cabergoline [who-dd]
46. (8beta)-n-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-n-(ethylcarbamoyl)-6-(prop-2-en-1-yl)ergoline-8-carboxamide
47. Bidd:gt0775
48. Cabergoline (jan/usp/inn)
49. Chembl1201087
50. Dtxsid6022719
51. Cabergoline, >=98% (hplc)
52. Cabergoline [orange Book]
53. Cabergoline [ep Monograph]
54. Hms2090a09
55. Hms3886h05
56. Cabergoline [usp Monograph]
57. Zinc3800008
58. Tox21_112589
59. Bdbm50426497
60. S5842
61. Akos015961587
62. Tox21_112589_1
63. Db00248
64. Fce-21336fce-21336
65. Cabergoline [ema Epar Veterinary]
66. Ncgc00344544-01
67. (8beta)-n-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-n-[(ethylamino)carbonyl]-6-prop-2-en-1-ylergoline-8-carboxamide
68. Ac-26126
69. Ergoline-8-carboxamide, N-(3-(dimethylamino)propyl)-n-((ethylamino)carbonyl)-6-(2-propenyl)-, (8-beta)-
70. Ergoline-8beta-carboxamide, N-(3-(dimethylamino)propyl)-n-((ethylamino)carbonyl)-6-(2-propenyl)-
71. Hy-15296
72. C08187
73. D00987
74. F17353
75. Ab01275484-01
76. 409c907
77. Q423308
78. Sr-05000001493-1
79. Sr-05000001493-2
80. Brd-k86882815-001-01-6
81. Cabergoline, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
82. Cabergoline, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
83. Ethyl4-methyl-2-pyridin-3-yl-1,3-thiazole-5-carboxylate
84. 1-((6-allylergolin-8.beta.-yl)carbonyl)-1-(3-(dimethylamino)propyl)-3-ethylurea
85. 6-allyl-n-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-n-[(ethylamino)carbonyl]-ergoline-8beta-carboxamide
86. N-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-n-(ethylcarbamoyl)-6-allyl-ergoline-8beta-carboxamide
87. (6ar,9r,10ar)-n-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-n-(ethylcarbamoyl)-7-prop-2-enyl-6,6a,8,9,10,10a-hexahydro-4h-indolo[4,3-fg]quinoline-9-carboxamide
88. (9r,10ar)-7-allyl-n-(3-(dimethylamino)propyl)-n-(ethylcarbamoyl)-4,6,6a,7,8,9,10,10a-octahydroindolo[4,3-fg]quinoline-9-carboxamide
89. Ergoline-8.beta.-carboxamide, N-(3-(dimethylamino)propyl)-n-((ethylamino)carbonyl)-6-(2-propenyl)-
| Molecular Weight | 451.6 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C26H37N5O2 |
| XLogP3 | 3.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 8 |
| Exact Mass | 451.29472544 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 451.29472544 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 71.7 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 33 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 713 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 3 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Cabergoline |
| PubMed Health | Cabergoline (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antiparkinsonian, Prolactin Secretion Inhibitor |
| Drug Label | Cabergoline tablets contain cabergoline, a dopamine receptor agonist. The chemical name for cabergoline is 1-[(6-Allylergolin-8-yl)carbonyl]-1-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-3-ethylurea. Its molecular formula is C26H37N5O2, and its molecular weight is 4... |
| Active Ingredient | Cabergoline |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 0.5mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mylan Pharms; Ivax Sub Teva Pharms; Actavis Labs Fl; Apotex; Par Pharm; Impax Labs |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Cabergoline |
| PubMed Health | Cabergoline (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antiparkinsonian, Prolactin Secretion Inhibitor |
| Drug Label | Cabergoline tablets contain cabergoline, a dopamine receptor agonist. The chemical name for cabergoline is 1-[(6-Allylergolin-8-yl)carbonyl]-1-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-3-ethylurea. Its molecular formula is C26H37N5O2, and its molecular weight is 4... |
| Active Ingredient | Cabergoline |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 0.5mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mylan Pharms; Ivax Sub Teva Pharms; Actavis Labs Fl; Apotex; Par Pharm; Impax Labs |
For the treatment of hyperprolactinemic disorders, either idiopathic or due to prolactinoma (prolactin-secreting adenomas). May also be used to manage symptoms of Parkinsonian Syndrome as monotherapy during initial symptomatic management or as an adjunct to levodopa therapy during advanced stages of disease.
For use in the herd management programme of dairy cows as an aid in the abrupt drying-off by reducing milk production to:
- reduce milk leakage at drying off;
- reduce the risk of new intramammary infections during the dry period;
- reduce discomfort.
Cabergoline stimulates centrally-located dopaminergic receptors resulting in a number of pharmacologic effects. Five dopamine receptor types from two dopaminergic subfamilies have been identified. The dopaminergic D1 receptor subfamily consists of D1 and D5 subreceptors, which are associated with dyskinesias. The dopaminergic D2 receptor subfamily consists of D2, D3 and D4 subreceptors, which are associated with improvement of symptoms of movement disorders. Thus, agonist activity specific for D2 subfamily receptors, primarily D2 and D3 receptor subtypes, are the primary targets of dopaminergic antiparkinsonian agents. It is thought that postsynaptic D2 stimulation is primarily responsible for the antiparkinsonian effect of dopamine agonists, while presynaptic D2 stimulation confers neuroprotective effects. This semisynthetic ergot derivative exhibits potent agonist activity on dopamine D2- and D3-receptors. It also exhibits: agonist activity (in order of decreasing binding affinities) on 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT)2B, 5-HT2A, 5-HT1D, dopamine D4, 5-HT1A, dopamine D1, 5-HT1B and 5-HT2C receptors and antagonist activity on α2B, α2A, and α2C receptors. Parkinsonian Syndrome manifests when approximately 80% of dopaminergic activity in the nigrostriatal pathway of the brain is lost. As this striatum is involved in modulating the intensity of coordinated muscle activity (e.g. movement, balance, walking), loss of activity may result in dystonia (acute muscle contraction), Parkinsonism (including symptoms of bradykinesia, tremor, rigidity, and flattened affect), akathesia (inner restlessness), tardive dyskinesia (involuntary muscle movements usually associated with long-term loss of dopaminergic activity), and neuroleptic malignant syndrome, which manifests when complete blockage of nigrostriatal dopamine occurs. High dopaminergic activity in the mesolimbic pathway of the brain causes hallucinations and delusions; these side effects of dopamine agonists are manifestations seen in patients with schizophrenia who have overractivity in this area of the brain. The hallucinogenic side effects of dopamine agonists may also be due to 5-HT2A agonism. The tuberoinfundibular pathway of the brain originates in the hypothalamus and terminates in the pituitary gland. In this pathway, dopamine inhibits lactotrophs in anterior pituitary from secreting prolactin. Increased dopaminergic activity in the tuberoinfundibular pathway inhibits prolactin secretion.
Antiparkinson Agents
Agents used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. The most commonly used drugs act on the dopaminergic system in the striatum and basal ganglia or are centrally acting muscarinic antagonists. (See all compounds classified as Antiparkinson Agents.)
Dopamine Agonists
Drugs that bind to and activate dopamine receptors. (See all compounds classified as Dopamine Agonists.)
QG02CB03
G02CB03
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
G - Genito urinary system and sex hormones
G02 - Other gynecologicals
G02C - Other gynecologicals
G02CB - Prolactine inhibitors
G02CB03 - Cabergoline
N - Nervous system
N04 - Anti-parkinson drugs
N04B - Dopaminergic agents
N04BC - Dopamine agonists
N04BC06 - Cabergoline
Absorption
First-pass effect is seen, however the absolute bioavailability is unknown.
Route of Elimination
After oral dosing of radioactive cabergoline to five healthy volunteers, approximately 22% and 60% of the dose was excreted within 20 days in the urine and feces, respectively. Less than 4% of the dose was excreted unchanged in the urine.
Clearance
renal cl=0,008 L/min
nonrenal cl=3.2 L/min
Hepatic. Cabergoline is extensively metabolized, predominately via hydrolysis of the acylurea bond of the urea moiety. Cytochrome P-450 mediated metabolism appears to be minimal. The main metabolite identified in urine is 6-allyl-8b-carboxy-ergoline (4-6% of dose). Three other metabolites were identified urine (less than 3% of dose).
The elimination half-life is estimated from urinary data of 12 healthy subjects to range between 63 to 69 hours.
The dopamine D2 receptor is a 7-transmembrane G-protein coupled receptor associated with Gi proteins. In lactotrophs, stimulation of dopamine D2 causes inhibition of adenylyl cyclase, which decreases intracellular cAMP concentrations and blocks IP3-dependent release of Ca2+ from intracellular stores. Decreases in intracellular calcium levels may also be brought about via inhibition of calcium influx through voltage-gated calcium channels, rather than via inhibition of adenylyl cyclase. Additionally, receptor activation blocks phosphorylation of p42/p44 MAPK and decreases MAPK/ERK kinase phosphorylation. Inhibition of MAPK appears to be mediated by c-Raf and B-Raf-dependent inhibition of MAPK/ERK kinase. Dopamine-stimulated growth hormone release from the pituitary gland is mediated by a decrease in intracellular calcium influx through voltage-gated calcium channels rather than via adenylyl cyclase inhibition. Stimulation of dopamine D2 receptors in the nigrostriatal pathway leads to improvements in coordinated muscle activity in those with movement disorders. Cabergoline is a long-acting dopamine receptor agonist with a high affinity for D2 receptors. Receptor-binding studies indicate that cabergoline has low affinity for dopamine D1, α1,- and α2- adrenergic, and 5-HT1- and 5-HT2-serotonin receptors.