


1. B 64114
2. B-64114
3. Bumadizone
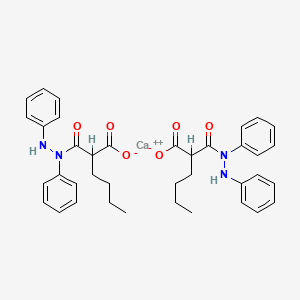
4. Bumadizone Calcium (2:1)
5. Bumadizone Calcium (2:1), Hemihydrate
6. Butylmalonic Acid Mono-(1,2-diphenylhydrazide)
7. Desflam
8. Eumotol
1. Eumotol
2. 34461-73-9
3. 34461-73-9 (calcium)
4. Bumadizone Calcium Anhydrous
5. Butylmalonic Acid Mono(1,2-diphenylhydrazide) Calcium
6. Calcium-n-n-butylmalonic Acid N,n'-diphenylhydrazide
7. 142r7tu2tn
8. Malonic Acid, Butyl-, Mono(1,2-diphenylhydrazide), Calcium Salt (2:1)
9. Bumadizon Calcium
10. Calcium 2-(1,2-diphenylhydrazine-1-carbonyl)hexanoate
11. Calcium Bis(2-butyl-3-(1,2-diphenylhydrazino)-3-oxopropionate)
12. B-64114 Co
13. Einecs 252-048-9
14. Unii-142r7tu2tn
15. Bumadizone Calcium Salt
16. Butyl-malonsaure-mono-(1,2-diphenyl-hydrazid)-calzium [german]
17. Anhydrous Bumadizone Calcium
18. Propanedioic Acid, Butyl-, Mono(1,2-diphenylhydrazide), Calcium Salt (2:1)
19. Butyl-malonsaure-mono-(1,2-diphenyl-hydrazid)-calzium
20. Schembl1648794
21. Chebi:76123
22. Dtxsid30956006
23. Calcium;2-[anilino(phenyl)carbamoyl]hexanoate
24. Q27145769
25. Calcium Bis[2-(1,2-diphenylhydrazinecarbonyl)hexanoate]
26. Calcium Bis{2-[(1,2-diphenylhydrazino)carbonyl]hexanoate}
27. (+/-)-malonic Acid, Butyl-, Mono(1,2-diphenylhydrazide), Calcium Salt (2:1)
28. Propanedioic Acid, 2-butyl-, 1-(1,2-diphenylhydrazide), Calcium Salt (2:1)
| Molecular Weight | 690.8 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C38H42CaN4O6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 14 |
| Exact Mass | 690.2730259 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 690.2730259 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 145 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 49 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 396 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 3 |
Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal
Anti-inflammatory agents that are non-steroidal in nature. In addition to anti-inflammatory actions, they have analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions. They act by blocking the synthesis of prostaglandins by inhibiting cyclooxygenase, which converts arachidonic acid to cyclic endoperoxides, precursors of prostaglandins. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis accounts for their analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions; other mechanisms may contribute to their anti-inflammatory effects. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal.)

LOOKING FOR A SUPPLIER?