

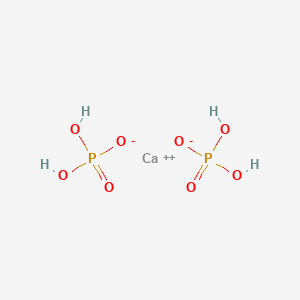

1. Acid Calcium Phosphate
2. Calcium Bisphosphate
3. Calcium Phosphate, Monobasic
4. Calcium Superphosphate
5. Monocalcium Orthophosphate
1. 7758-23-8
2. Monocalcium Phosphate
3. Calcium Dihydrogen Phosphate
4. Calcium Dihydrogen Orthophosphate
5. Monobasic Calcium Phosphate
6. Acid Calcium Phosphate
7. Monocalcium Orthophosphate
8. Calcium Dihydrogenphosphate
9. Primary Calcium Phosphate
10. Monocalcium Phosphate, Monobasic
11. Calcium Monobasic Phosphate
12. Calcium Bis(dihydrogen Phosphate)
13. Calcium Phosphate (1:2)
14. Calcium Phosphate, Monobasic
15. Phosphoric Acid, Calcium Salt (2:1)
16. Calcium;dihydrogen Phosphate
17. 701ekv9rmn
18. Calcium Phosphate Monobasic Anhydrous
19. Calcium Phosphate, Monobasic, Anhydrous
20. C 38 (phosphate)
21. Calcium Diorthophosphate
22. Calcium Tetrahydrogen Phosphate
23. Calcium Bis(dihydrogenphosphate)
24. Hsdb 1441
25. Calcium Tetrahydrogen Orthophosphate
26. Calcium Dihydrogenphoshate
27. Calcium Bis(dihydrogenorthophosphate)
28. Einecs 231-837-1
29. Unii-701ekv9rmn
30. V 90
31. Calcium Hydrogen Phosphate (ca(h2po4)2)
32. Calcium Bisphosphate
33. Calciumphosphatemonobasic&n
34. Dihydromonocalcium Phosphate
35. Ec 231-837-1
36. Ca(h2po4)2
37. Dtxsid2044262
38. Ins No.341(i)
39. Chebi:35433
40. Ins-341(i)
41. Akos015902863
42. Calcium Bis(dihydrogenorthophosphate), With A Fluorine Content Of Less Than 0,005 % By Weight On The Dry Anhydrous Product
43. Calcium Phosphate, Monobasic [mi]
44. E-341(i)
45. Calcium Dihydrogen Phosphate [inci]
46. Calcium Dihydrogen Tetraoxophosphate
47. Calcium Phosphate Monobasic [who-dd]
48. Ft-0623378
49. Monobasic Calcium Phosphate, Anhydrous
50. Calcium Bis(dihydrogen Phosphate) [hsdb]
51. Q414673
| Molecular Weight | 234.05 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | CaH4O8P2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 233.9007319 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 233.9007319 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 161 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 11 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 49.8 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 3 |
/Ortho/ phosphate is absorbed from, and to a limited extent secreted into, the gastrointestinal tract. The transport of phosphate from the lumen of the gut is an active, energy-dependent process, and there are factors that appear to modify the degree of its intestinal absorption. ... Vitamin D stimulates phosphate absorption, and this effect has been reported to precede the action of the vitamin on transport of calcium ion. In general, in adults, about two thirds of the ingested phosphate is absorbed from the bowel, and that which is absorbed from the gut is almost entirely excreted into the urine. In growing children, there is a positive balance of phosphate. Concentrations of phosphate in plasma are higher in children than in adults. This "hyperphosphatemia" decreases the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen and is hypothesized to explain the physiological "anemia" of childhood. /Phosphates/
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 1501
A defect in phosphate metabolism occurs in a variety of diseases. ... Osteoporosis ... Rickets ... Osteomalacia ... Osteitis Fibrosa Cystica ... Secondary Hyperparathyroidism ... Hypoparathyroidism ... . /Phosphates/
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 1503