

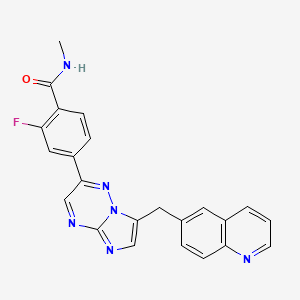

1. 2-fluoro-4-(7-((quinolin-6-yl)methyl)imidazo(1,2-b)(1,2,4)triazin-2-yl)benzoic Acid
2. 2-fluoro-4-(7-((quinolin-6-yl)methyl)imidazo(1,2-b)-(1,2,4)triazin-2-yl)benzamide
3. 2-fluoro-n-methyl-4-(7-((quinolin-6-yl)methyl)imidazo(1,2- B)(1,2,4)triazin-2-yl)benzamide Dihydrochloride Monohydrate
4. 2-fluoro-n-methyl-4-(7-(quinolin-6-yl-methyl)imidazo(1,2-b)(1,2,4)triazin-2-yl)benzamide
5. 2-fluoro-n-methyl-4-(7-(quinolin-6-ylmethyl)imidazo(1,2-b)(1,2,4)triazin-2-yl)benzamide
6. 2-fluoro-n-methyl-4-(7-(quinolin-6-ylmethyl)imidazo(1,2-b)(1,2,4)triazin-2-yl)benzamide Dihydrochloride
7. Capmatinib Dihydrochloride
8. Capmatinib Dihydrochloride Monohydrate
9. Capmatinib Hydrochloride
10. Capmatinib Hydrochloride Anhydrous
11. Capmatinib Metabolite M13
12. Capmatinib Metabolite M18
13. Cmc-583
14. Cmc583
15. Cnj-294
16. Cnj294
17. Inc-280
18. Inc280
19. Incb-28060
20. Incb-28060 Free Base
21. Incb28060
22. Nvp-inc280
23. Nvp-inc280-nx
24. Tabrecta
1. 1029712-80-8
2. Incb28060
3. Inc280
4. Inc-280
5. Nvp-inc280-nx
6. Incb-28060
7. Nvp-inc280
8. 2-fluoro-n-methyl-4-(7-(quinolin-6-ylmethyl)imidazo[1,2-b][1,2,4]triazin-2-yl)benzamide
9. Tabrecta
10. Capmatinib (incb28060)
11. Capmatinib [usan]
12. Incb-28060 Free Base
13. Inc28060
14. 2-fluoro-n-methyl-4-[7-(quinolin-6-ylmethyl)imidazo[1,2-b][1,2,4]triazin-2-yl]benzamide
15. Ty34l4f9oz
16. Incb 28060
17. Benzamide, 2-fluoro-n-methyl-4-[7-(6-quinolinylmethyl)imidazo[1,2-b][1,2,4]triazin-2-yl]-
18. 2-fluoro-n-methyl-4-(7-(quinolin-6-ylmethyl)imidazo(1,2-b)(1,2,4)triazin-2-yl)benzamide
19. Benzamide, 2-fluoro-n-methyl-4-[7-(6-quinolinylmethyl)imidazo[1,2-b][1,2,4]triazin-2-yl]-;benzamide, 2-fluoro-n-methyl-4-[7-(6-quinolinylmethyl)imidazo[1,2-b][1,2,4]triazin-2-yl]-
20. Capmatinib [inn]
21. Unii-ty34l4f9oz
22. Benzamide Hcl
23. Benzamide, 2-fluoro-n-methyl-4-(7-(6-quinolinylmethyl)imidazo(1,2-b)(1,2,4)triazin-2-yl)-
24. Capmatinib [mi]
25. Capmatinib (usan/inn)
26. Capmatinib [usan:inn]
27. Capmatinib(incb28060)
28. Incb28060(capmatinib)
29. Nyp-inc280-nx
30. Capmatinib [who-dd]
31. Mls006010965
32. Gtpl7904
33. Schembl1426819
34. Chembl3188267
35. Dtxsid90145595
36. Ex-a446
37. Amy18553
38. Bcp23444
39. Bdbm50146167
40. Mfcd18633285
41. Nsc777878
42. Nsc800067
43. S2788
44. Zinc43195321
45. Akos025396439
46. Bcp9000785
47. Ccg-268791
48. Cs-1541
49. Db11791
50. Nsc-777878
51. Nsc-800067
52. Sb16608
53. Ncgc00346702-01
54. Ncgc00346702-02
55. Ncgc00346702-05
56. Ac-25890
57. As-74142
58. Da-33530
59. Hy-13404
60. Smr004702769
61. Ft-0746310
62. D10696
63. J-509516
64. Q27075685
65. 2-fluoro-n-methyl-4-(7-(quinolin-6-ylmethyl)imidazo[1,2-b][1,2,4]triazin-2- Yl)benzamide
66. 2-fluoro-n-methyl-4-[7-(6-quinolinylmethyl)imidazo[1,2-b][1,2,4]triazin-2-yl]benzamide
67. 2-fluoro-n-methyl-4-[7-(quinolin-6-ylmethyl)imidazolo[1,2-b][1,2,4]triazin-2-yl]benzamide
68. 2-fluoro-n-methyl-4-{7-[(quinolin-6-yl)methyl]imidazo[1,2-b][1,2,4]triazin-2-yl}benzamide
| Molecular Weight | 412.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C23H17FN6O |
| XLogP3 | 2.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 412.14478735 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 412.14478735 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 85.1 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 31 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 637 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Capmatinib is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose tumors have a mutation that leads to mesenchymal-epithelial transition (MET) exon 14 skipping as detected by an FDA-approved test.
FDA Label
Tabrecta as monotherapy is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with advanced non small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) harbouring alterations leading to mesenchymal epithelial transition factor gene exon 14 (METex14) skipping, who require systemic therapy following prior treatment with immunotherapy and/or platinum based chemotherapy.
Capmatinib inhibits the overactivity of c-Met, a receptor tyrosine kinase encoded by the _MET_ proto-oncogene. Mutations in _MET_ are involved in the proliferation of many cancers, including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Capmatinib may cause photosensitivity reactions in patients following ultraviolet (UV) exposure - patients undergoing therapy with capmatinib should be advised to use sunscreen and protective clothing to limit exposure to UV radiation. Instances of interstitial lung disease/pneumonitis, which can be fatal, occurred in patients being treated with capmatinib. Patients presenting with signs or symptoms of lung disease (e.g. cough, dyspnea, fever) should have capmatinib immediately withheld, and capmatinib should be permanently discontinued if no other feasible causes of the lung-related symptoms are identified.
L01EX17
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01E - Protein kinase inhibitors
L01EX - Other protein kinase inhibitors
L01EX17 - Capmatinib
Absorption
The oral bioavailability of capmatinib is estimated to be >70%. Following oral administration, maximum plasma concentrations are achieved within 1 to 2 hours (Tmax). Co-administration with a high-fat meal increased capmatinib AUC by 46% with no change in Cmax (as compared to fasted conditions), and co-administration with a low-fat meal had no clinically meaningful effects on exposure.
Route of Elimination
Following oral administration of radiolabeled capmatinib, approximately 78% of the radioactivity is recovered in feces, of which ~42% is unchanged parent drug, and 22% is recovered in the urine, of which a negligible amount remains unchanged parent drug.
Volume of Distribution
The apparent volume of distribution at steady-state is 164 L.
Clearance
The mean apparent clearance of capmatinib at steady-state is 24 L/h.
Capmatinib undergoes metabolism primarily via CYP3A4 and aldehyde oxidase. Specific biotransformation pathways and metabolic products have yet to be elucidated.
The elimination half-life is 6.5 hours.
Aberrant activation of c-Met has been documented in many cancers, including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Mutations that result in the skipping of _MET_ exon 14 lead to the formation of a mutant c-Met with a missing regulatory domain - these mutant proteins have a reduced ability to negatively regulate, leading to a pathological increase in their downstream activity. Capmatinib inhibits the phosphorylation of both wild-type and mutant variants of c-Met triggered by the binding of its endogenous ligand, hepatocyte growth factor - in doing so, it prevents c-Met-mediated phosphorylation of downstream signaling proteins, as well as the proliferation and survival of c-Met-dependent tumor cells.
