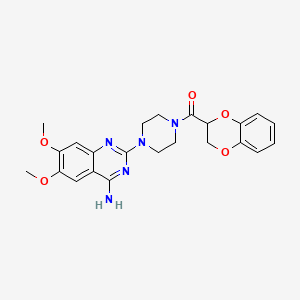

1. 1 (4-amino-6,7-dimethoxy-2-quinazolinyl)-4-((2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-2-yl)carbonyl)piperazine
2. Alfamedin
3. Apo Doxazosin
4. Apo-doxazosin
5. Cardular
6. Cardura
7. Carduran
8. Carduran Neo
9. Ct, Doxazosin Von
10. Diblocin
11. Doxa Puren
12. Doxa-puren
13. Doxacor
14. Doxagamma
15. Doxamax
16. Doxatensa
17. Doxauro
18. Doxazomerck
19. Doxazosin Al
20. Doxazosin Apogepha
21. Doxazosin Azu
22. Doxazosin Beta
23. Doxazosin Findusfit
24. Doxazosin Heumann
25. Doxazosin Klast
26. Doxazosin Mesylate
27. Doxazosin Monohydrochloride
28. Doxazosin Ratiopharm
29. Doxazosin Stada
30. Doxazosin Von Ct
31. Doxazosin Wolff
32. Doxazosin-ratiopharm
33. Doxazosin-wolff
34. Doxazosina Alter
35. Doxazosina Cinfa
36. Doxazosina Combino Pharm
37. Doxazosina Geminis
38. Doxazosina Normon
39. Doxazosina Pharmagenus
40. Doxazosina Ratiopharm
41. Doxazosina Ur
42. Gen Doxazosin
43. Gen-doxazosin
44. Jutalar
45. Mesylate, Doxazosin
46. Monohydrochloride, Doxazosin
47. Mtw Doxazosin
48. Mtw-doxazosin
49. Neo, Carduran
50. Novo Doxazosin
51. Novo-doxazosin
52. Progandol Neo
53. Ratio Doxazosin
54. Ratio-doxazosin
55. Ratiopharm, Doxazosina
56. Uk 33274
57. Uk-33274
58. Uk33274
59. Uriduct
60. Von Ct, Doxazosin
61. Zoxan
1. 74191-85-8
2. Doxazosine
3. Doxazosinum
4. Doxazosina
5. Doxazosin (inn)
6. [4-(4-amino-6,7-dimethoxyquinazolin-2-yl)piperazin-1-yl]-(2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-3-yl)methanone
7. Uk 33274
8. Uk-33274
9. 1-(4-amino-6,7-dimethoxy-2-quinazolinyl)-4-(1,4-benzodioxan-2-ylcarbonyl)piperazin
10. 1-(4-amino-6,7-dimethoxy-2-chinazolinyl)-4-(2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxixin-2-ylcarbonyl)piperazin
11. Chebi:4708
12. (rs)-2-{4-[(2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-2-yl)carbonyl]piperazin-1-yl}-6,7-dimethoxyquinazolin-4-amine
13. Doxazosine [french]
14. C02ca04
15. Nw1291f1w8
16. (4-(4-amino-6,7-dimethoxyquinazolin-2-yl)piperazin-1-yl)(2,3-dihydrobenzo[b][1,4]dioxin-2-yl)methanone
17. Doxazosinum [latin]
18. Doxazosin [inn]
19. Doxazosina [spanish]
20. Doxazosin [inn:ban]
21. Piperazine, 1-(4-amino-6,7-dimethoxy-2-quinazolinyl)-4-((2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-2-yl)carbonyl)-
22. 2-[4-(2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-2-ylcarbonyl)piperazin-1-yl]-6,7-bis(methyloxy)quinazolin-4-amine
23. Methanone, [4-(4-amino-6,7-dimethoxy-2-quinazolinyl)-1-piperazinyl](2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-2-yl)-
24. Cardura Xl (tn)
25. Supress
26. Unii-nw1291f1w8
27. Methanone, (4-(4-amino-6,7-dimethoxy-2-quinazolinyl)-1-piperazinyl)(2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-2-yl)-
28. Piperazine, 1-(4-amino-6,7-dimethoxy-2-quinazolinyl)-4-[(2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-2-yl)carbonyl]-
29. 2-[4-(2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-2-ylcarbonyl)piperazin-1-yl]-6,7-dimethoxyquinazolin-4-amine
30. Cpd000097306
31. Doxazosin [mi]
32. Prestwick0_000858
33. Prestwick1_000858
34. Prestwick2_000858
35. Prestwick3_000858
36. Doxazosin [vandf]
37. Chemdiv2_005017
38. Chembl707
39. Ec 616-059-6
40. Doxazosin [who-dd]
41. (+/-)-doxazosin
42. Lopac0_000474
43. Oprea1_259518
44. Schembl34111
45. Bspbio_000875
46. Doxazosin-d8(piperazine-d8)
47. 2-{4-[(2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-2-yl)carbonyl]piperazin-1-yl}-6,7-dimethoxyquinazolin-4-amine
48. Spbio_002796
49. Bpbio1_000963
50. Gtpl7170
51. Dtxsid7022964
52. Bdbm86731
53. Hms1383e01
54. Hms2090c20
55. Hms3259n21
56. Hms3372l09
57. Hms3886j03
58. Bcp12228
59. Hy-b0098
60. Zca19185
61. (4-benzylmorpholin-2-yl)-aceticacid
62. Nsc768144
63. Nsc768145
64. S5782
65. Akos001681453
66. Akos017343634
67. Ccg-118218
68. Cs-1831
69. Db00590
70. Nc00685
71. Nsc-768144
72. Nsc-768145
73. Sdccgsbi-0050459.p003
74. Idi1_003732
75. Ncgc00018158-02
76. Ncgc00018158-03
77. Ncgc00018158-05
78. Ncgc00018158-06
79. Ncgc00018158-08
80. Ncgc00018158-11
81. Ncgc00018158-20
82. Ncgc00089775-02
83. Ac-11062
84. As-77104
85. Sbi-0050459.p002
86. Cas_74191-85-8
87. Db-055848
88. Uk 33,274
89. Ft-0630831
90. Uk-3327427
91. En300-53055
92. C06970
93. D07874
94. 191d858
95. A838054
96. L000738
97. Q419939
98. Brd-a13188892-066-03-3
99. Brd-a13188892-066-13-2
100. (4-(4-amino-6,7-dimethoxy-2-quinazolinyl)-1-piperazinyl)(2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-2-yl)methanone
101. (4-(4-amino-6,7-dimethoxyquinazolin-2-yl)piperazin-1-yl)(2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-2-yl)methanone
102. [4-(4-amino-6,7-dimethoxy-2-quinazolinyl)-1-piperazinyl]-[(3s)-2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-3-yl]methanone
103. 1-(4-amino-6,7-dimethoxy-2-quinazolinyl)-4-(1,4-benzodioxan-2-ylcarbonyl)piperazine
104. 1-(4-amino-6,7-dimethoxy-2-quinazolinyl)-4-[(2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-2-yl)carbonyl]piperazine
105. 137888-77-8
106. 2-[4-(2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxine-2-carbonyl)piperazin-1-yl]-6,7-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydroquinazolin-4-imine
| Molecular Weight | 451.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C23H25N5O5 |
| XLogP3 | 2.5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 9 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 451.18556891 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 451.18556891 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 112 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 33 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 678 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Cardura |
| PubMed Health | Doxazosin (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antihypertensive, Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy Agent, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | CARDURA (doxazosin mesylate) is a quinazoline compound that is a selective inhibitor of the alpha1 subtype of alpha-adrenergic receptors. The chemical name of doxazosin mesylate is 1-(4-amino-6,7-dimethoxy-2-quinazolinyl)-4-(1,4-benzodioxan-2-ylcar... |
| Active Ingredient | Doxazosin mesylate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | eq 4mg base; eq 2mg base; eq 1mg base; eq 8mg base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pfizer |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Cardura |
| PubMed Health | Doxazosin (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antihypertensive, Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy Agent, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | CARDURA (doxazosin mesylate) is a quinazoline compound that is a selective inhibitor of the alpha1 subtype of alpha-adrenergic receptors. The chemical name of doxazosin mesylate is 1-(4-amino-6,7-dimethoxy-2-quinazolinyl)-4-(1,4-benzodioxan-2-ylcar... |
| Active Ingredient | Doxazosin mesylate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | eq 4mg base; eq 2mg base; eq 1mg base; eq 8mg base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pfizer |
Doxazosin is indicated to treat the symptoms of benign prostatic hypertrophy, which may include urinary frequency, urgency, and nocturia, among other symptoms. In addition, doxazosin is indicated alone or in combination with various antihypertensive agents for the management of hypertension. Off-label uses of doxazosin include the treatment of pediatric hypertension and the treatment of ureteric calculi.
Doxazosin decreases standing and supine blood pressure and relieves the symptoms of benign prostatic hypertrophy through the inhibition of alpha-1 receptors. Doxazosin may cause hypotension due to its pharmacological actions. This frequently occurs in the upright position, leading to a feeling of dizziness or lightheadedness. The first dose of doxazosin may lead to such effects, however, subsequent doses may also cause them. The risk of these effects is particularly high when dose adjustments occur or there are long intervals between doxazosin doses. Treatment should be started with the 1 mg dose of doxazosin, followed by slow titration to the appropriate dose. Patients must be advised of this risk and to avoid situations in which syncope and dizziness could be hazardous following the ingestion of doxazosin. Interestingly doxazosin exerts beneficial effects on plasma lipids. It reduces LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol and triglyceride levels and increases HDL (high-density lipoprotein) cholesterol levels. A note on priapism risk In rare cases, doxazosin and other alpha-1 blockers may cause priapism, a painful occurrence of persistent and unrelievable penile erection that can lead to impotence if medical attention is not sought as soon as possible. Patients must be advised of the priapism risk associated with doxazosin and to seek medical attention immediately if it is suspected.
Antihypertensive Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of acute or chronic vascular HYPERTENSION regardless of pharmacological mechanism. Among the antihypertensive agents are DIURETICS; (especially DIURETICS, THIAZIDE); ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS; ADRENERGIC ALPHA-ANTAGONISTS; ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS; CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS; GANGLIONIC BLOCKERS; and VASODILATOR AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Antihypertensive Agents.)
Adrenergic alpha-1 Receptor Antagonists
Drugs that bind to and block the activation of ADRENERGIC ALPHA-1 RECEPTORS. (See all compounds classified as Adrenergic alpha-1 Receptor Antagonists.)
C - Cardiovascular system
C02 - Antihypertensives
C02C - Antiadrenergic agents, peripherally acting
C02CA - Alpha-adrenoreceptor antagonists
C02CA04 - Doxazosin
Absorption
Doxazosin is rapidly absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract and peak concentrations are achieved within 2-3 hours after administration. The bioavailability is about 60%-70%. The intake of food with doxazosin is not expected to cause clinically significant effects.
Route of Elimination
In a pharmacokinetic study using a 1 mg IV radiolabeled dose and a 2 mg oral dose, 63% of the ingested doxazosin was found to be excreted in the feces and about 9% of the dose was found to be excreted in the urine. Traces of radiolabeled unchanged drug were found in the urine and about 5% of the administered drug was found as unchanged drug excreted in the feces.
Volume of Distribution
The volume of distribution of doxazosin is 1.0-1.9 L/kg. In a study of radiolabeled doxazosin administered to pregnant rats, doxazosin was found to cross the placenta.
Clearance
The clearance of doxazosin is low and ranges from approximately 1-2 ml/min/kg.
Hepatic metabolism of doxazosin produces inactive O-demethylated and C-hydroxylated metabolites. Metabolism occurs via O-demethylation of the quinazoline nucleus of doxazosin or via hydroxylation of its benzodioxan portion. The enzymes involved in the metabolism of doxazosin include CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2C19, and CYP3A4, which is the primary metabolizing enzyme. Doxazosin itself is considered to be mainly responsible for its pharmacological action, however, some active metabolites have been identified whose pharmacokinetics have not been adequately characterized.
The terminal elimination half-life of doxazosin has been estimated at 9-12 hours according to some resources. The FDA label indicates the elimination half-life of doxazosin is 22 hours.
Doxazosin selectively inhibits the postsynaptic alpha-1 receptors on vascular smooth muscle by nonselectively blocking the alpha-1a, alpha-1b, and alpha-1d subtypes. This action on blood vessels decreases systemic peripheral vascular resistance, reducing blood pressure, exerting minimal effects on the heart rate due to its receptor selectivity. Norepinephrine-activated alpha-1 receptors located on the prostate gland and bladder neck normally cause contraction of regional muscular tissue, obstructing urinary flow and contributing to the symptoms of benign prostatic hypertrophy. Alpha-1 antagonism causes smooth muscle relaxation in the prostate and bladder, effectively relieving urinary frequency, urgency, weak urinary stream, and other unpleasant effects of BPH. Recently, doxazosin was found to cause apoptosis of hERG potassium channels in an in vitro setting, possibly contributing to a risk of heart failure with doxazosin use.