
1. Carisoma
2. Carisoprodate
3. Isobamate
4. Isomeprobamate
5. Isopropylmeprobamate
6. Mio Relax
7. Soma
8. Somalgit
9. Soprodol
10. Vanadom
1. 78-44-4
2. Isomeprobamate
3. Carisoprodate
4. Soma
5. Carisoprodatum
6. Carisoma
7. Isobamate
8. Isoprotane
9. Isoprothane
10. Sanoma
11. Isopropyl Meprobamate
12. Atonalyt
13. Flexartal
14. Miolisodal
15. Mioratrina
16. Skutamil
17. Somalgit
18. Apesan
19. Arusal
20. Flexal
21. Mioril
22. Nospasm
23. Relasom
24. Somanil
25. Rela
26. Carlsoprol
27. Brianil
28. Calenfa
29. Caprodat
30. Carisol
31. Carlsodol
32. Carlsoma
33. Carsodal
34. Diolene
35. Domarax
36. Isoprotan
37. Izoprotan
38. Mediquil
39. Mioriodol
40. Somadril
41. Stialgin
42. Carisoprodolum
43. Carsodol
44. Carisoprodolum [inn-latin]
45. Tonolyt Isopropyl Meprobamate
46. Nci-c56235
47. Sch 7307
48. Miolisodol
49. Flexartel
50. Cb 8019
51. Carisoprodol Civ
52. 2-methyl-2-propyl-1,3-propanediol Carbamate Isopropylcarbamate
53. [2-(carbamoyloxymethyl)-2-methylpentyl] N-propan-2-ylcarbamate
54. (1-methylethyl)carbamic Acid 2-(((aminocarbonyl)oxy)methyl)-2-methylpentyl Ester
55. Nsc-172124
56. Isopropylcarbamic Acid, Ester With 2-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methylpentyl Carbamate
57. Mls000028401
58. Chebi:3419
59. Artifar
60. Caridolin
61. Chinchen
62. Fibrosona
63. Flexagilt
64. Flexagit
65. Flexidon
66. Listaflex
67. Meprodat
68. Neotica
69. Muslax
70. Scutamil-c
71. Carbamic Acid, Ester With 2-methyl-2-propyl-1,3-propanediol Isopropylcarbamate
72. Carbamic Acid, (1-methylethyl)-, 2-(((aminocarbonyl)oxy)methyl)-2-methylpentyl Ester
73. Carbamic Acid, Isopropyl-, 2-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methylpentyl Ester Carbamate (ester)
74. Ncgc00015278-09
75. Smr000058433
76. 21925k482h
77. (+-)-2-methyl-2-propyl-1,3-propanediol Carbamate Isopropylcarbamate
78. Dsstox_cid_4733
79. Carbamic Acid, (1-methylethyl)-, 2-[[(aminocarbonyl)oxy]methyl]-2-methylpentyl Ester
80. Dsstox_rid_77514
81. Dsstox_gsid_24733
82. Isopropylmeprobamate
83. 2-((carbamoyloxy)methyl)-2-methylpentyl Isopropylcarbamate
84. 2-methyl-2-propyltrimethylene Carbamate Isopropylcarbamate
85. Carisoprodolo [dcit]
86. N-isopropy-2-methyl-2-propyl-1,3-propanediol Dicarbamate
87. Carisoprodolo
88. Prazolamine
89. Carbamic Acid 2-isopropylcarbamoyloxymethyl-2-methyl-pentyl Ester
90. (+/-)-2-methyl-2-propyl-1,3-propanediol Carbamate Isopropylcarbamate
91. Carbamic Acid, Ester With 2-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methylpentylisopropyl Carbamate
92. Ccris 4764
93. Hsdb 3021
94. Sr-01000000076
95. Einecs 201-118-7
96. Nsc 172124
97. Brn 1791537
98. Carisoprodol [usp:inn:ban]
99. 2-{[(aminocarbonyl)oxy]methyl}-2-methylpentyl Isopropylcarbamate
100. Cas-78-44-4
101. Prestwick_50
102. Unii-21925k482h
103. Mfcd00057661
104. Soma (tn)
105. N-isopropyl-2-methyl-2-propyl-1,3-propanediol Dicarbamate
106. Spectrum_000102
107. Opera_id_1100
108. Prestwick0_000423
109. Prestwick1_000423
110. Prestwick2_000423
111. Prestwick3_000423
112. Spectrum2_001153
113. Spectrum3_000328
114. Spectrum4_000265
115. Spectrum5_000661
116. Carisoprodol [mi]
117. Carisoprodol [inn]
118. Carisoprodol [jan]
119. 1,3-propanediol, 2-methyl-2-propyl-, Carbamate Isopropylcarbamate (ester)
120. Carbamic Acid, Ester With 2-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methylpentyl Isopropylcarbamate
121. Carisoprodol [hsdb]
122. Carisoprodol [vandf]
123. Chembl1233
124. Lopac0_000319
125. Schembl33286
126. Bspbio_000406
127. Bspbio_001935
128. Carisoprodol [mart.]
129. Kbiogr_000730
130. Kbioss_000542
131. Mls001148409
132. Mls002454391
133. Carisoprodol [who-dd]
134. Divk1c_000816
135. Spectrum1500162
136. Carisoprodol (jan/usp/inn)
137. Spbio_001105
138. Spbio_002345
139. Bpbio1_000448
140. Gtpl7610
141. Dea No. 8192
142. Dtxsid8024733
143. Hms502i18
144. Kbio1_000816
145. Kbio2_000542
146. Kbio2_003110
147. Kbio2_005678
148. Kbio3_001155
149. Carisoprodol Civ [usp-rs]
150. Ninds_000816
151. Carisoprodol [ep Impurity]
152. Carisoprodol [orange Book]
153. Hms1569e08
154. Hms1920k03
155. Hms2091a06
156. Hms2096e08
157. Hms2234f13
158. Hms3259o15
159. Hms3372h19
160. Hms3713e08
161. Pharmakon1600-01500162
162. Hy-b1380
163. Carisoprodol [usp Monograph]
164. Carisoprodol 1.0 Mg/ml In Methanol
165. Tox21_110122
166. Tox21_200623
167. Ac-212
168. Ccg-40092
169. Nsc172124
170. Nsc756671
171. Akos015842914
172. Tox21_110122_1
173. Wln: Zvo1x3&1&1ovmy1&1
174. Cs-4819
175. Db00395
176. Lp00319
177. Nc00502
178. Nsc-756671
179. Sdccgsbi-0050307.p005
180. Idi1_000816
181. Ncgc00015278-03
182. Ncgc00015278-04
183. Ncgc00015278-05
184. Ncgc00015278-06
185. Ncgc00015278-07
186. Ncgc00015278-08
187. Ncgc00015278-11
188. Ncgc00015278-12
189. Ncgc00015278-14
190. Ncgc00015278-15
191. Ncgc00089734-02
192. Ncgc00089734-03
193. Ncgc00089734-04
194. Ncgc00089734-05
195. Ncgc00089734-06
196. Ncgc00089734-07
197. Ncgc00258177-01
198. Sbi-0050307.p004
199. Soma Compound Component Carisoprodol
200. Carisoprodol 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
201. Ab00051932
202. C3573
203. Eu-0100319
204. Ft-0601536
205. Ft-0656125
206. Carbamic Acid,3-propanediol Isopropylcarbamate
207. Carisoprodol Component Of Soma Compound
208. C 8759
209. D00768
210. N-isopropyl-2-methyl-2-propyl-1, Dicarbamate
211. Ab00051932_15
212. 057c661
213. Carisoprodol Compound Component Carisoprodol
214. Q416905
215. Sr-01000000076-2
216. Sr-01000000076-4
217. Sr-01000000076-6
218. W-104280
219. 1, 2-methyl-2-propyl-, Carbamate Isopropylcarbamate
220. Carisoprodol Component Of Carisoprodol Compound
221. Z1565440360
222. N-isopropyl-2-methyl-2-propyl-1,3-propanediol, Dicarbamate
223. 2-[(carbamoyloxy)methyl]-2-methylpentyl Propan-2-ylcarbamate
224. Carisoprodol, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
225. 1,3-propanediol, 2-methyl-2-propyl-, Carbamate Isopropylcarbamate
226. 2-[(carbamoyloxy)methyl]-2-methylpentyl N-(propan-2-yl)carbamate
227. Carisoprodol, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
228. (rs)-2-{[(aminocarbonyl)oxy]methyl}-2-methylpentyl Isopropylcarbamate
229. Carbamic Acid, Isopropyl-, 2-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methylpentyl Ester Carbamate
230. Carbamic Acid, Isopropyl-, 2-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methylpentyl Ester, Carbamate
231. Carisoprodol Solution, 1.0 Mg/ml In Methanol, Ampule Of 1 Ml, Certified Reference Material
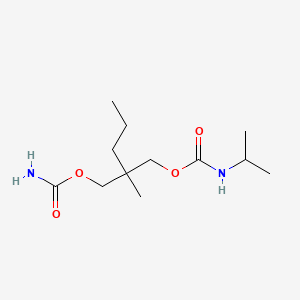
| Molecular Weight | 260.33 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C12H24N2O4 |
| XLogP3 | 1.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 9 |
| Exact Mass | 260.17360725 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 260.17360725 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 90.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 18 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 281 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Carisoprodol |
| PubMed Health | Carisoprodol (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Skeletal Muscle Relaxant, Centrally Acting |
| Drug Label | Carisoprodol tablets USP are available as 350 mg round, white tablets. Carisoprodol is a white, crystalline powder, having a mild, characteristic odor and a bitter taste. It is slightly soluble in water; freely soluble in alcohol, in chloroform, and... |
| Active Ingredient | Carisoprodol |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 350mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Watson Labs; Vintage Pharms; Mutual Pharm; Mirror Pharms; Sciegen Pharms; Aurobindo Pharma; Sun Pharm Inds; Accelrx Labs |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Soma |
| PubMed Health | Carisoprodol (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Skeletal Muscle Relaxant, Centrally Acting |
| Drug Label | SOMA (carisoprodol) Tablets are available as 250 mg and 350 mg round, white tablets. Carisoprodol is a white, crystalline powder, having a mild, characteristic odor and a bitter taste. It is slightly soluble in water; freely soluble in alcohol, in ch... |
| Active Ingredient | Carisoprodol |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 250mg; 350mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Meda Pharms |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Carisoprodol |
| PubMed Health | Carisoprodol (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Skeletal Muscle Relaxant, Centrally Acting |
| Drug Label | Carisoprodol tablets USP are available as 350 mg round, white tablets. Carisoprodol is a white, crystalline powder, having a mild, characteristic odor and a bitter taste. It is slightly soluble in water; freely soluble in alcohol, in chloroform, and... |
| Active Ingredient | Carisoprodol |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 350mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Watson Labs; Vintage Pharms; Mutual Pharm; Mirror Pharms; Sciegen Pharms; Aurobindo Pharma; Sun Pharm Inds; Accelrx Labs |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Soma |
| PubMed Health | Carisoprodol (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Skeletal Muscle Relaxant, Centrally Acting |
| Drug Label | SOMA (carisoprodol) Tablets are available as 250 mg and 350 mg round, white tablets. Carisoprodol is a white, crystalline powder, having a mild, characteristic odor and a bitter taste. It is slightly soluble in water; freely soluble in alcohol, in ch... |
| Active Ingredient | Carisoprodol |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 250mg; 350mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Meda Pharms |
Muscle Relaxants, Central
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
Carisoprodol is used as an adjunct to rest, physical therapy, analgesics, and other measures for the relief of discomfort associated with acute, painful musculoskeletal conditions. /Included in US product label/
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2010. Bethesda, MD. (2010), p. 1391
Occasionally, patients may have allergic or idiosyncratic reactions to carisoprodol. In patients who have not received carisoprodol previously, these reactions are usually evident by the time of the fourth dose of the drug. Idiosyncratic reactions may be characterized by extreme weakness, transient quadriplegia, dizziness, ataxia, temporary loss of vision, diplopia, mydriasis, dysarthria, agitation, euphoria, confusion, and disorientation. These symptoms usually subside within several hours; however, symptomatic and supportive therapy, including hospitalization, may be necessary in some patients. Rash, erythema multiforme, pruritus, urticaria, eosinophilia, and fixed drug eruption have occurred in patients receiving carisoprodol who previously had similar reactions to meprobamate. Severe allergic reactions have been characterized by asthmatic episodes, fever, weakness, dizziness, angioedema, smarting eyes, hypotension, and anaphylactic shock.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2010. Bethesda, MD. (2010), p. 1391
The most frequent adverse effects of carisoprodol are drowsiness and dizziness. Other adverse CNS effects include vertigo, ataxia, tremor, agitation, irritability, headache, depressive reactions, syncope, and insomnia.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2010. Bethesda, MD. (2010), p. 1391
Because carisoprodol is metabolized by the liver and excreted by the kidneys, the drug should be used with caution in patients with impaired hepatic or renal function. Patients should be warned that carisoprodol may impair ability to perform hazardous activities requiring mental alertness or physical coordination such as operating machinery or driving a motor vehicle.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2010. Bethesda, MD. (2010), p. 1391
Adverse GI effects of carisoprodol include nausea, vomiting, hiccups, increased bowel activity, and epigastric distress. Adverse cardiovascular effects include tachycardia, postural hypotension, and facial flushing. Although a causal relationship to carisoprodol has not been established, leukopenia and pancytopenia have occurred rarely in patients receiving carisoprodol along with other drugs.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2010. Bethesda, MD. (2010), p. 1391
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for CARISOPRODOL (13 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Carisoprodol is indicated for the relief of discomfort related to acute, painful musculoskeletal conditions. **Important limitations of use**: Should only be used for acute treatment periods up to two or three weeks Adequate evidence of effectiveness for more prolonged use has not been established Not recommended in pediatric patients less than 16 years of age
FDA Label
Carisoprodol is a centrally acting skeletal muscle relaxant that does not act directly on skeletal muscle but acts directly on the central nervous system (CNS). This drug relieves the painful effects of muscle spasm. A metabolite of carisoprodol, _meprobamate_, possesses both anxiolytic and sedative properties. Clinical studies have shown that this drug causes impairment of psychomotor performance in neuropsychological tests.
Muscle Relaxants, Central
A heterogeneous group of drugs used to produce muscle relaxation, excepting the neuromuscular blocking agents. They have their primary clinical and therapeutic uses in the treatment of muscle spasm and immobility associated with strains, sprains, and injuries of the back and, to a lesser degree, injuries to the neck. They have been used also for the treatment of a variety of clinical conditions that have in common only the presence of skeletal muscle hyperactivity, for example, the muscle spasms that can occur in MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS. (From Smith and Reynard, Textbook of Pharmacology, 1991, p358) (See all compounds classified as Muscle Relaxants, Central.)
M - Musculo-skeletal system
M03 - Muscle relaxants
M03B - Muscle relaxants, centrally acting agents
M03BA - Carbamic acid esters
M03BA02 - Carisoprodol
Absorption
The absolute bioavailability of carisoprodol has not yet been established. The mean time to peak plasma concentrations (Tmax) of this drug was about 1.5-2 hours in clinical studies. Co-administration of a fatty meal with carisoprodol (350 mg tablet) had no impact on carisoprodol pharmacokinetics.
Route of Elimination
Carisoprodol is eliminated by the kidneys as well as other routes. The half-life of meprobamate is approximately 10 hours.
Volume of Distribution
0.93 to 1.3 L/kg, according to 4 different clinical studies.
Clearance
Following an oral dose of carisoprodol, the oral clearance (Cl/F) was 39.52 16.83 L/hour.
Carisoprodol crosses the placenta. The drug distributes into milk in concentrations 2-4 times higher than concurrent maternal plasma concentrations.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2010. Bethesda, MD. (2010), p. 1391
Plasma concentrations of carisoprodol required for sedative, skeletal muscle relaxant, or toxic effects are not known. One manufacturer reports that plasma concentrations of 4-7 ug/mL were attained in 4 hours following oral administration of 350 mg of carisoprodol to healthy adults. Following usual therapeutic dosages, the onset of action is usually within 30 minutes and the duration of action is 4-6 hours.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2010. Bethesda, MD. (2010), p. 1391
The objective of this study was to quantify the excretion of carisoprodol and meprobamate in human milk and estimate the dose received by breast-fed infants. The concentrations of carisoprodol and meprobamate were measured in breast milk on 4 consecutive days at steady-state conditions in one woman using carisoprodol 2100 mg/d. The average milk concentrations were 0.9 microg/mL for carisoprodol and 11.6 ug/mL for meprobamate. Based on the milk concentrations measured, the absolute dose ingested by an exclusively breast-fed infant could be estimated at 1.9 mg/kg per day, and the relative dose would be 4.1% of the weight-adjusted maternal dose. ...
PMID:11360042 Nordeng H et al; Ther Drug Monit 23 (3): 298-300 (2001)
The main pathway of carisoprodol is liver metabolism is by the cytochrome enzyme CYP2C19 to form meprobamate. This enzyme exhibits genetic polymorphism, which may affect the metabolism of this drug.
The major pathway of carisoprodol metabolism is via the liver by cytochrome enzyme CYP2C19 to form meprobamate. This enzyme exhibits genetic polymorphism.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for CARISOPRODOL (carisoprodol ) tablet (May 2010). Available from, as of November 17, 2010: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=19431
Carisoprodol is metabolized in the liver; animal studies indicate the drug may induce liver microsomal enzymes. Animal studies also indicate that the drug is excreted in urine, principally as hydroxycarisoprodol and hydroxymeprobamate, and to a lesser extent as meprobamate; trace amounts of carisoprodol are excreted unchanged in urine. The drug may be removed by hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2010. Bethesda, MD. (2010), p. 1391
Carisoprodol is a muscle relaxant analgesic, which has an active metabolite i.e. meprobamate. We conducted an open three-panel single-dose administration study with 15 healthy volunteers: five poor metabolizers of mephenytoin, five poor metabolizers of debrisoquine and five extensive metabolizers of both substrates. The aim was to investigate if the elimination of carisoprodol and meprobamate is dependent on the two metabolic polymorphisms of mephenytoin and debrisoquine. The subjects were given single oral doses of 700 mg carisoprodol and 400 mg meprobamate on separate occasions. The disposition of carisoprodol was clearly correlated to the mephenytoin hydroxylation phenotype. The mean serum clearance of carisoprodol was four times lower in poor metabolizers of mephenytoin than in extensive metabolizers, which confirms the hypothesis from our previous study that N-dealkylation of carisoprodol cosegregates with the mephenytoin hydroxylation polymorphism. However, mean serum clearance of meprobamate did not differ between the two groups. Also, polymorphic debrisoquine hydroxylation did not influence the elimination of carisoprodol or meprobamate. Poor metabolizers of mephenytoin thus have a lower capacity to metabolize carisoprodol and may therefore have an increased risk of developing concentration dependent side-effects such as drowsiness and hypotension, if treated with ordinary doses of carisoprodol.
PMID:8946470 Dalen P et al; Pharmacogenetics 6 (5): 387-94 (1996)
The terminal half-life is approximately 2 hours.
Carisoprodol is eliminated by both renal and non-renal routes with a terminal elimination half-life of approximately 2 hours. The half-life of meprobamate is approximately 10 hours.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for CARISOPRODOL (carisoprodol ) tablet (May 2010). Available from, as of November 17, 2010: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=19431
The plasma half-life of carisoprodol is approximately 8 hours.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2010. Bethesda, MD. (2010), p. 1391
The mechanism of action of carisoprodol in relieving discomfort associated with acute painful musculoskeletal conditions has not been confirmed. In studies using animal models, the muscle relaxation that is induced by carisoprodol is associated with a change in the interneuronal activity of the spinal cord and of the descending reticular formation, located in the brain. The abuse potential of this drug is attributed to its ability to alter GABAA function. This drug has been shown to modulate a variety of GABAA receptor subunits. GABAA receptor modulation can lead to anxiolysis due to inhibitory effects on neurotransmission.
Carisoprodol is a CNS depressant which has sedative and skeletal muscle relaxant effects. The precise mechanism of action of the drug is not known. The skeletal muscle relaxant effects of orally administered carisoprodol are minimal and are probably related to its sedative effect. The drug does not directly relax skeletal muscle and, unlike neuromuscular blocking agents, does not depress neuronal conduction, neuromuscular transmission, or muscle excitability. In animals, carisoprodol appears to modify central perception of pain without abolishing peripheral pain reflexes and to have slight antipyretic activity, but these effects have not been demonstrated in clinical studies.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2010. Bethesda, MD. (2010), p. 1391
Carisoprodol is an increasingly abused, centrally-acting muscle relaxant. Despite the prevalence of carisoprodol abuse, its mechanism of action remains unclear. Its sedative effects, which contribute to its therapeutic and recreational use, are generally attributed to the actions of its primary metabolite, meprobamate, at GABA(A) receptors (GABA(A)R). Meprobamate is a controlled substance at the federal level; ironically, carisoprodol is not currently classified as such. Using behavioral and molecular pharmacological approaches, we recently demonstrated carisoprodol, itself, is capable of modulating GABA(A)R function in a manner similar to central nervous system depressants. Its functional similarities with this highly addictive class of drugs may contribute to the abuse potential of carisoprodol. The site of action of carisoprodol has not been identified; based on our studies, interaction with benzodiazepine or barbiturate sites is unlikely. ...
PMID:20419052 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2858432 Gonzalez LA et al; Mol Cell Pharmacol 1 (4): 180-186 (2009)