


1. (+-)-isomer Of Carprofen
2. (r)-isomer Of Carprofen
3. (s)-isomer Of Carprofen
4. C 5720
5. Carprofen, (+-)-isomer
6. Carprofen, (r)-isomer
7. Carprofen, (s)-isomer
8. Ro 20-5720
9. Ro 205720
1. 53716-49-7
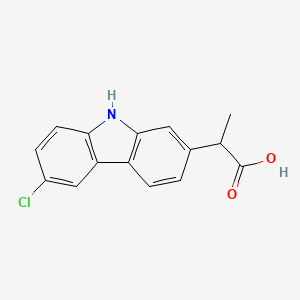
2. 2-(6-chloro-9h-carbazol-2-yl)propanoic Acid
3. Rimadyl
4. Imadyl
5. Ridamyl
6. Carprofeno
7. Carprofene
8. Carprofenum
9. Carprofene [inn-french]
10. Carprofenum [inn-latin]
11. 6-chloro-alpha-methyl-9h-carbazole-2-acetic Acid
12. Carprofeno [inn-spanish]
13. 6-chloro-alpha-methylcarbazole-2-acetic Acid
14. Ro 20-5720/000
15. Mfcd00079028
16. Carprofen-d3
17. (+-)-6-chloro-alpha-methylcarbazole-2-acetic Acid
18. 52263-47-5
19. 2-(6-chloro-9h-carbazol-2-yl)-propionic Acid
20. Nsc-297935
21. Carprofen For Veterinary Use
22. Chembl1316
23. Ffl0d546ho
24. (+/-)-2-(3-chloro-9h-carbazol-7-yl)propanoic Acid
25. Ro-20-5720/000
26. Chebi:364453
27. Nsc297935
28. 9h-carbazole-2-acetic Acid, 6-chloro-.alpha.-methyl-
29. Ncgc00094937-01
30. Carprodyl
31. Carprofeno [spanish]
32. Ro-205720000
33. Dsstox_cid_25871
34. Dsstox_rid_81189
35. Dsstox_gsid_45871
36. (.+-.)-6-chloro-.alpha.-methylcarbazole-2-acetic Acid
37. Carpaquin
38. Norocarp
39. Ro 20-5720
40. Smr000718633
41. Rimadyl (tn)
42. C 5720
43. Cas-53716-49-7
44. Ccris 3507
45. Sr-01000837515
46. Einecs 258-712-4
47. Unii-ffl0d546ho
48. Nsc 297935
49. Brn 0487098
50. Rac Carprofen
51. Carprofen [usan:usp:inn:ban]
52. Ro-20-5720
53. Carprofen (usp/inn)
54. Carprofen [inn]
55. Carprofen [mi]
56. Carprofen [usan]
57. Spectrum2_001236
58. Spectrum3_000939
59. Spectrum4_001038
60. Spectrum5_001802
61. Carprofen [vandf]
62. Carprofen [mart.]
63. C-5720
64. Carprofen [usp-rs]
65. Carprofen [who-dd]
66. Schembl3909
67. (+-)-6-chlor-alpha-methyl-2-carbazolessigsaeure
68. Kbiogr_001595
69. 5-22-03-00391 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
70. Mls001201778
71. Mls001306441
72. Spectrum1502006
73. Spbio_001112
74. Carprofen [green Book]
75. Gtpl7141
76. Carprofen [orange Book]
77. (+/-)-6-chloro-.alpha.-methylcarbazole-2-acetic Acid
78. Carprofen [usp Impurity]
79. Carprofen, >=97% (hplc)
80. Dtxsid1045871
81. Kbio3_001978
82. Carprofen [usp Monograph]
83. Hms1921d04
84. Hms2092b16
85. Hms2234p15
86. Hms3652e20
87. Hms3715f09
88. Hms3748c07
89. Hms3885f07
90. Pharmakon1600-01502006
91. Act03356
92. Hy-b1227
93. Tox21_111363
94. 9h-carbazole-2-acetic Acid, 6-chloro-.alpha.-methyl-, (.+-.)-
95. 9h-carbazole-2-acetic Acid, 6-chloro-alpha-methyl-, (+-)-
96. Bbl009935
97. Bdbm50097346
98. Ccg-39146
99. Nsc758154
100. Stk711093
101. 9h-carbazole-2-acetic Acid, (-)-
102. Akos005530663
103. Tox21_111363_1
104. Ac-1266
105. Cs-4875
106. Db00821
107. Ks-1163
108. Nsc-758154
109. Carprofen 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
110. Ncgc00094937-02
111. Ncgc00094937-04
112. Ncgc00094937-05
113. 9h-carbazole-2-acetic Acid, (.+-.)-
114. Sbi-0052885.p002
115. Ft-0602833
116. Ft-0664393
117. Ft-0664394
118. Ft-0664395
119. S4136
120. Sw199610-3
121. 6-chloro-alpha-methyl-carbazole-2-acetic Acid
122. Carprofen, Vetranal(tm), Analytical Standard
123. C18364
124. D03410
125. D70911
126. 2-(6-chloranyl-9h-carbazol-2-yl)propanoic Acid
127. Ab00876263_06
128. Ab00876263_07
129. 716c497
130. A829748
131. Q905755
132. (+/-)-6-chloro-alpha-methylcarbazole-2-aceticacid
133. Carprofen For Veterinary Use [ep Monograph]
134. Sr-01000837515-2
135. Sr-01000837515-3
136. (+/-)-6-chloro-alpha-methylcarbazole-2-acetic Acid
137. Brd-a17411484-001-05-1
138. Z1814381791
139. 2-(6-chloro-9h-carbazol-2-yl)-propionic Acid(carprofen)
140. Carprofen, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
141. 9h-carbazole-2-acetic Acid, 6-chloro-.alpha.-methyl-, (-)-
142. Carprofen, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
143. 9h-carbazole-2-acetic Acid, 6-chloro-.alpha.-methyl, (+/-)-
144. Carprofen, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
145. Carprofen For System Suitability, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
| Molecular Weight | 273.71 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C15H12ClNO2 |
| XLogP3 | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 273.0556563 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 273.0556563 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 53.1 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 19 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 362 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
For use as a pain reliever in the treatment of joint pain and post-surgical pain.
Carprofen is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) of the propionic acid class that includes ibuprofen, naproxen, and ketoprofen. It is no longer used in the clinical setting, but is approved for use in dogs. Carprofen is non-narcotic and has characteristic analgesic and antipyretic activity approximately equipotent to indomethacin in animal models.
Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal
Anti-inflammatory agents that are non-steroidal in nature. In addition to anti-inflammatory actions, they have analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions. They act by blocking the synthesis of prostaglandins by inhibiting cyclooxygenase, which converts arachidonic acid to cyclic endoperoxides, precursors of prostaglandins. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis accounts for their analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions; other mechanisms may contribute to their anti-inflammatory effects. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal.)
Photosensitizing Agents
Drugs that are pharmacologically inactive but when exposed to ultraviolet radiation or sunlight are converted to their active metabolite to produce a beneficial reaction affecting the diseased tissue. These compounds can be administered topically or systemically and have been used therapeutically to treat psoriasis and various types of neoplasms. (See all compounds classified as Photosensitizing Agents.)
Absorption
Rapidly and nearly completely absorbed (more than 90% bioavailable) when administered orally.
Hepatic.
Approximately 8 hours (range 4.5–9.8 hours) in dogs.
The mechanism of action of carprofen, like that of other NSAIDs, is believed to be associated with the inhibition of cyclooxygenase activity. Two unique cyclooxygenases have been described in mammals. The constitutive cyclooxygenase, COX-1, synthesizes prostaglandins necessary for normal gastrointestinal and renal function. The inducible cyclooxygenase, COX-2, generates prostaglandins involved in inflammation. Inhibition of COX-1 is thought to be associated with gastrointestinal and renal toxicity while inhibition of COX-2 provides anti-inflammatory activity. In an in vitro study using canine cell cultures, carprofen demonstrated selective inhibition of COX-2 versus COX-1.

