
1. 14c-labeled Carvedilol
2. Bm 14190
3. Bm-14190
4. Bm14190
5. Carvedilol Hydrochloride
6. Carvedilol, (+)
7. Carvedilol, (+)-isomer
8. Carvedilol, (+-)-isomer
9. Carvedilol, (-)
10. Carvedilol, (-)-isomer
11. Carvedilol, (r)-isomer
12. Carvedilol, (s)-isomer
13. Carvedilol, 14c Labeled
14. Carvedilol, 14c-labeled
15. Coreg
16. Coropres
17. Dilatrend
18. Eucardic
19. Kredex
20. Querto
1. 72956-09-3
2. Coreg
3. Dilatrend
4. Eucardic
5. Kredex
6. Carvedilolum [latin]
7. Carvedilolum
8. Querto
9. Bm 14190
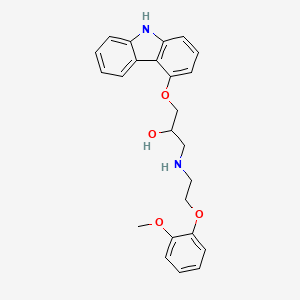
10. 1-(9h-carbazol-4-yloxy)-3-[[2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)ethyl]amino]-2-propanol
11. Bm-14190
12. Dimitone
13. Artist
14. Skf 105517
15. 1-(9h-carbazol-4-yloxy)-3-[2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)ethylamino]propan-2-ol
16. 1-((9h-carbazol-4-yl)oxy)-3-((2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)ethyl)amino)propan-2-ol
17. Coronis
18. Korvasan
19. Talliton
20. Dq 2466
21. Dq-2466
22. C07ag02
23. (+-)-1-(carbazol-4-yloxy)-3-((2-(o-methoxyphenoxy)ethyl)amino)-2-propanol
24. Chembl723
25. Nsc-758694
26. Sk&f-105517
27. Bm 14.190
28. Bm-14-190
29. Bm-14.190
30. Chebi:3441
31. 0k47ul67f2
32. [3-(9h-carbazol-4-yloxy)-2-hydroxypropyl][2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)ethyl]amine
33. 1-(9h-carbazol-4-yloxy)-3-{[2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)ethyl]amino}propan-2-ol
34. Skf-105517
35. (r)-bm 14190
36. (s)-bm 14190
37. Coropress
38. Dibloc
39. R-(+)-carvedilol
40. S-(-)-carvedilol
41. 1-(9h-carbazol-4-yloxy)-3-[(2-{[2-(methyloxy)phenyl]oxy}ethyl)amino]propan-2-ol
42. Smr000449280
43. Artist (tn)
44. Coreg (tn)
45. Hsdb 7044
46. Sr-01000759289
47. Unii-0k47ul67f2
48. Mfcd00869663
49. 1-(9h-carbazol-4-yloxy)-3-(2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)ethylamino)propan-2-ol
50. Carvedilol D5
51. Eg-p042
52. Mfcd00864692
53. Carvedilol - Bio-x
54. Bm14190
55. Carvedilol [usan:usp:inn:ban:jan]
56. Spectrum_001665
57. Carvedilol [mi]
58. Carvedilol [inn]
59. Carvedilol [jan]
60. Spectrum2_001673
61. Spectrum3_001182
62. Spectrum4_000636
63. Spectrum5_001436
64. Carvedilol [hsdb]
65. Carvedilol [usan]
66. Carvedilol [vandf]
67. Carvedilol [mart.]
68. Carvedilol [usp-rs]
69. Carvedilol [who-dd]
70. Schembl22293
71. Gtpl551
72. Kbiogr_001252
73. Kbioss_002145
74. Mls000758299
75. Mls000759508
76. Mls001424092
77. Mls006011886
78. Spbio_001885
79. Carvedilol (jp17/usp/inn)
80. Carvedilol [orange Book]
81. Dtxsid8022747
82. Schembl10082334
83. Schembl13287211
84. Bdbm25759
85. Kbio2_002145
86. Kbio2_004713
87. Kbio2_007281
88. Kbio3_002323
89. Carvedilol [ep Monograph]
90. (r)-1-[(4-carbazolyl)oxy]-3-[[2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)ethyl]amino]-2-propanol
91. Carvedilol [usp Monograph]
92. Hms2051n03
93. Hms2089b09
94. Hms2093e12
95. Hms3261e15
96. Hms3269n11
97. Hms3393n03
98. Hms3413b14
99. Hms3655o14
100. Hms3677b14
101. Hms3715d15
102. Hms3750i15
103. Hms3884e12
104. Pharmakon1600-01504257
105. Carvedilol 1.0 Mg/ml In Methanol
106. ((c)i)-carvedilol-d4(ethyl-d4)
107. Amy40801
108. Bcp23386
109. Ex-a5746
110. Hy-b0006
111. Tox21_500347
112. Bbl029064
113. Mfcd00869664
114. Nsc758694
115. S1831
116. Stk621453
117. Akos005554967
118. Carvedilol, >=98% (hplc), Solid
119. Ac-1641
120. Bcp9000493
121. Ccg-100917
122. Ccg-207952
123. Cs-1194
124. Db01136
125. Ks-1037
126. Lp00347
127. Nc00167
128. Nsc 758694
129. Sb17441
130. Sdccgsbi-0206771.p002
131. 2-propanol, 1-(9h-carbazol-4-yloxy)-3-((2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)ethyl)amino)-, (+-)-
132. Ncgc00167832-01
133. Ncgc00167832-02
134. Ncgc00167832-03
135. Ncgc00167832-04
136. Ncgc00167832-19
137. Ncgc00261032-01
138. Bc164291
139. Sy129821
140. Sy283162
141. Bcp0726000253
142. Sbi-0206771.p001
143. Db-055704
144. Db-057556
145. Db-057557
146. Ft-0603055
147. Ft-0603057
148. Ft-0652640
149. Ft-0664397
150. Sw197547-3
151. C06875
152. D00255
153. F19969
154. Ab00639903-07
155. Ab00639903-09
156. Ab00639903_10
157. Ab00639903_11
158. Ab00639903_12
159. 956c093
160. L001243
161. Q412534
162. Q-200801
163. Sr-01000759289-5
164. Sr-01000759289-6
165. Sr-01000759289-9
166. Brd-a10977446-001-04-8
167. Brd-a10977446-001-05-5
168. Brd-a10977446-045-01-1
169. Z2786051695
170. Carvedilol, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
171. Ethyl 2-(9-(pyridin-4-ylmethyl)-9h-fluoren-9-yl)acetate
172. Carvedilol, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
173. 1-(9h-carbazol-4-yloxy)-3-[2-(2-methoxy-phenoxy)-ethylamino]-propan-2-ol
174. Carvedilol, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
175. (+/-)-1-carbazol-4-yloxy)-3-((2-(o-methoxyphenoxy)ethyl)amino)-2-propanol
176. 1-(carbazol-4-yloxy)-3-((2-(o-methoxy-phenoxy)ethyl)amino)-2-propanol
177. Carvedilol For System Suitability, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
178. 107741-96-8
179. 2-propanol, 1-(9h-carbazol-4-yloxy)-3-((2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)ethyl)amino)-, (+/-)-
| Molecular Weight | 406.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C24H26N2O4 |
| XLogP3 | 4.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 10 |
| Exact Mass | 406.18925731 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 406.18925731 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 75.7 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 30 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 508 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Carvedilol |
| PubMed Health | Carvedilol (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antianginal, Antihypertensive, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | Carvedilol is a nonselective -adrenergic blocking agent with 1-blocking activity. It is ()-1-(Carbazol-4-yloxy)-3-[[2-(o-methoxyphenoxy)ethyl]amino]-2-propanol. Carvedilol is a racemic mixture with the following structure:Carvedilol tablets, US... |
| Active Ingredient | Carvedilol |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 6.25mg; 25mg; 3.125mg; 12.5mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Ranbaxy; Glenmark Generics; Teva; Apotex; Aurobindo Pharma; Sun Pharm Inds; Beximco Usa; Pliva Hrvatska Doo; Taro; Lupin; Zydus Pharms Usa; Dr Reddys Labs; Sandoz; Cipla; Mylan; Hikma |
| 2 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Coreg |
| PubMed Health | Carvedilol (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antianginal, Antihypertensive, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | Carvedilol is a nonselective -adrenergic blocking agent with 1-blocking activity. It is ()-1-(Carbazol-4-yloxy)-3-[[2-(o-methoxyphenoxy)ethyl]amino]-2-propanol. Carvedilol is a racemic mixture with the following structure:COREG is a white, oval... |
| Active Ingredient | Carvedilol |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 6.25mg; 25mg; 3.125mg; 12.5mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Smithkline Beecham |
| 3 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Coreg cr |
| PubMed Health | Carvedilol (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antianginal, Antihypertensive, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Active Ingredient | Carvedilol phosphate |
| Dosage Form | Capsule, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 10mg; 80mg; 40mg; 20mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Sb Pharmco |
| 4 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Carvedilol |
| PubMed Health | Carvedilol (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antianginal, Antihypertensive, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | Carvedilol is a nonselective -adrenergic blocking agent with 1-blocking activity. It is ()-1-(Carbazol-4-yloxy)-3-[[2-(o-methoxyphenoxy)ethyl]amino]-2-propanol. Carvedilol is a racemic mixture with the following structure:Carvedilol tablets, US... |
| Active Ingredient | Carvedilol |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 6.25mg; 25mg; 3.125mg; 12.5mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Ranbaxy; Glenmark Generics; Teva; Apotex; Aurobindo Pharma; Sun Pharm Inds; Beximco Usa; Pliva Hrvatska Doo; Taro; Lupin; Zydus Pharms Usa; Dr Reddys Labs; Sandoz; Cipla; Mylan; Hikma |
| 5 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Coreg |
| PubMed Health | Carvedilol (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antianginal, Antihypertensive, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | Carvedilol is a nonselective -adrenergic blocking agent with 1-blocking activity. It is ()-1-(Carbazol-4-yloxy)-3-[[2-(o-methoxyphenoxy)ethyl]amino]-2-propanol. Carvedilol is a racemic mixture with the following structure:COREG is a white, oval... |
| Active Ingredient | Carvedilol |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 6.25mg; 25mg; 3.125mg; 12.5mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Smithkline Beecham |
| 6 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Coreg cr |
| PubMed Health | Carvedilol (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antianginal, Antihypertensive, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Active Ingredient | Carvedilol phosphate |
| Dosage Form | Capsule, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 10mg; 80mg; 40mg; 20mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Sb Pharmco |
Adrenergic alpha-1 Receptor Antagonists; Adrenergic beta-Antagonists; Antihypertensive Agents; Vasodilator Agents
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 2009)
Carvedilol is indicated for the treatment of mild-to-severe chronic heart failure of ischemic or cardiomyopathic origin, usually in addition to diuretics, ACE inhibitors, and digitalis, to increase survival and, also, to reduce the risk of hospitalization. /Included in US product label/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for CARVEDILOL (carvedilol) tablet (May 2011). Available from, as of September 19, 2011: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=0b802a9c-332f-4ea8-bb34-75c677264654
Carvedilol is indicated to reduce cardiovascular mortality in clinically stable patients who have survived the acute phase of a myocardial infarction and have a left ventricular ejection fraction of greater than 40 percent (with or without symptomatic heart failure). /Included in US product label/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for CARVEDILOL (carvedilol) tablet (May 2011). Available from, as of September 19, 2011: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=0b802a9c-332f-4ea8-bb34-75c677264654
Carvedilol is indicated for the management of essential hypertension. It can be used alone or in combination with other antihypertensive agents, especially thiazide-type diuretics. /Included in US product label/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for CARVEDILOL (carvedilol) tablet (May 2011). Available from, as of September 19, 2011: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=0b802a9c-332f-4ea8-bb34-75c677264654
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for CARVEDILOL (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Carvedilol is contraindicated in the following conditions: Bronchial asthma or related bronchospastic conditions. Deaths from status asthmaticus have been reported following single doses of carvedilol; second- or third-degree AV block; sick sinus syndrome; severe bradycardia (unless a permanent pacemaker is in place); Patients with cardiogenic shock or who have decompensated heart failure requiring the use of intravenous inotropic therapy. Such patients should first be weaned from intravenous therapy before initiating carvedilol; patients with severe hepatic impairment; patients with a history of a serious hypersensitivity reaction (eg, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, anaphylactic reaction, angioedema) to any component of this medication or other medications containing carvedilol.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for CARVEDILOL (carvedilol) tablet (May 2011). Available from, as of September 19, 2011: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=0b802a9c-332f-4ea8-bb34-75c677264654
Patients with coronary artery disease, who are being treated with carvedilol, should be advised against abrupt discontinuation of therapy. Severe exacerbation of angina and the occurrence of myocardial infarction and ventricular arrhythmias have been reported in angina patients following the abrupt discontinuation of therapy with beta-blockers. The last 2 complications may occur with or without preceding exacerbation of the angina pectoris. As with other beta-blockers, when discontinuation of carvedilol is planned, the patients should be carefully observed and advised to limit physical activity to a minimum. Carvedilol should be discontinued over 1 to 2 weeks whenever possible. If the angina worsens or acute coronary insufficiency develops, it is recommended that carvedilol be promptly reinstituted, at least temporarily. Because coronary artery disease is common and may be unrecognized, it may be prudent not to discontinue therapy with carvedilol abruptly even in patients treated only for hypertension or heart failure.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for CARVEDILOL (carvedilol) tablet (May 2011). Available from, as of September 19, 2011: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=0b802a9c-332f-4ea8-bb34-75c677264654
Worsening heart failure or fluid retention may occur during up-titration of carvedilol. If such symptoms occur, diuretics should be increased and the carvedilol dose should not be advanced until clinical stability resumes. Occasionally it is necessary to lower the carvedilol dose or temporarily discontinue it. Such episodes do not preclude subsequent successful titration of, or a favorable response to, carvedilol. In a placebo-controlled trial of patients with severe heart failure, worsening heart failure during the first 3 months was reported to a similar degree with carvedilol and with placebo. When treatment was maintained beyond 3 months, worsening heart failure was reported less frequently in patients treated with carvedilol than with placebo. Worsening heart failure observed during long-term therapy is more likely to be related to the patients' underlying disease than to treatment with carvedilol.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for CARVEDILOL (carvedilol) tablet (May 2011). Available from, as of September 19, 2011: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=0b802a9c-332f-4ea8-bb34-75c677264654
Rarely, use of carvedilol in patients with heart failure has resulted in deterioration of renal function. Patients at risk appear to be those with low blood pressure (systolic blood pressure greater than 100 mm Hg), ischemic heart disease and diffuse vascular disease, and/or underlying renal insufficiency. Renal function has returned to baseline when carvedilol was stopped. In patients with these risk factors it is recommended that renal function be monitored during up-titration of carvedilol and the drug discontinued or dosage reduced if worsening of renal function occurs.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for CARVEDILOL (carvedilol) tablet (May 2011). Available from, as of September 19, 2011: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=0b802a9c-332f-4ea8-bb34-75c677264654
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for CARVEDILOL (24 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Carvedilol is indicated to treat mild to severe heart failure, left ventricular dysfunction after myocardial infarction with ventricular ejection fraction 40%, or hypertension.
FDA Label
Carvedilol reduces tachycardia through beta adrenergic antagonism and lowers blood pressure through alpha-1 adrenergic antagonism. It has a long duration of action as it is generally taken once daily and has a broad therapeutic index as patients generally take 10-80mg daily. Patients taking carvedilol should not abruptly stop taking this medication as this may exacerbate coronary artery disease.
Calcium Channel Blockers
A class of drugs that act by selective inhibition of calcium influx through cellular membranes. (See all compounds classified as Calcium Channel Blockers.)
Antioxidants
Naturally occurring or synthetic substances that inhibit or retard oxidation reactions. They counteract the damaging effects of oxidation in animal tissues. (See all compounds classified as Antioxidants.)
Adrenergic alpha-1 Receptor Antagonists
Drugs that bind to and block the activation of ADRENERGIC ALPHA-1 RECEPTORS. (See all compounds classified as Adrenergic alpha-1 Receptor Antagonists.)
Adrenergic beta-Antagonists
Drugs that bind to but do not activate beta-adrenergic receptors thereby blocking the actions of beta-adrenergic agonists. Adrenergic beta-antagonists are used for treatment of hypertension, cardiac arrhythmias, angina pectoris, glaucoma, migraine headaches, and anxiety. (See all compounds classified as Adrenergic beta-Antagonists.)
Antihypertensive Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of acute or chronic vascular HYPERTENSION regardless of pharmacological mechanism. Among the antihypertensive agents are DIURETICS; (especially DIURETICS, THIAZIDE); ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS; ADRENERGIC ALPHA-ANTAGONISTS; ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS; CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS; GANGLIONIC BLOCKERS; and VASODILATOR AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Antihypertensive Agents.)
Vasodilator Agents
Drugs used to cause dilation of the blood vessels. (See all compounds classified as Vasodilator Agents.)
C07AG02
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
C - Cardiovascular system
C07 - Beta blocking agents
C07A - Beta blocking agents
C07AG - Alpha and beta blocking agents
C07AG02 - Carvedilol
Absorption
Carvedilol has a bioavailability of 25-35%. Carvedilol has a Tmax of 1 to 2 hours. Taking carvedilol with a meal increases Tmax without increasing AUC. Carvedilol doses of 50mg lead to a Cmax of 122-262g/L and an AUC of 717-1600g/L\*h. Carvedilol doses of 25mg lead to a Cmax of 24-151g/L and an AUC of 272-947g/L\*h. Carvedilol doses of 12.5mg lead to a Cmax of 58-69g/L and an AUC of 208-225g/L\*h.
Route of Elimination
16% of carvedilol is excreted in the urine with <2% excreted as unmetabolized drug. Carvedilol is primarily excreted in the bile and feces.
Volume of Distribution
Carvedilol has a volume of distribution of 1.5-2L/kg or 115L.
Clearance
The plasma clearance of carvedilol has been reported as 0.52L/kg or 500-700mL/min.
Carvedilol is rapidly and extensively absorbed following oral administration, with absolute bioavailability of approximately 25 percent to 35 percent due to a significant degree of first-pass metabolism.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for CARVEDILOL (carvedilol) tablet (May 2011). Available from, as of September 19, 2011 https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=0b802a9c-332f-4ea8-bb34-75c677264654
Food decreases the rate of the drug's absorption (ie, increases time to peak plasma concentration), but not the extent (ie, no effect on bioavailability) of absorption. Administration with food may decrease the risk of orthostatic hypotension.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 1888
Following oral administration of radiolabelled carvedilol to healthy volunteers, carvedilol accounted for only about 7 percent of the total radioactivity in plasma as measured by area under the curve (AUC). Less than 2 percent of the dose was excreted unchanged in the urine. ... The metabolites of carvedilol are excreted primarily via the bile into the feces.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for CARVEDILOL (carvedilol) tablet (May 2011). Available from, as of September 19, 2011 https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=0b802a9c-332f-4ea8-bb34-75c677264654
Carvedilol is more than 98 percent bound to plasma proteins, primarily with albumin. The plasma-protein binding is independent of concentration over the therapeutic range.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for CARVEDILOL (carvedilol) tablet (May 2011). Available from, as of September 19, 2011 https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=0b802a9c-332f-4ea8-bb34-75c677264654
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for CARVEDILOL (13 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Carvedilol can be hydroxlated at the 1 position by CYP2D6, CYP1A2, or CYP1A1 to form 1-hydroxypheylcarvedilol; at the 4 position by CYP2D6, CYP2E1, CYP2C9, or CYP3A4 to form 4'-hydroxyphenylcarvedilol; at the 5 position by CYP2D6, CYP2C9, or CYP3A4 to form 5'-hydroxyphenylcarvedilol; and at the 8 position by CYP1A2, CYP3A4, and CYP1A1 to form 8-hydroxycarbazolylcarvedilol. Carvedilol can also be demethylated by CYP2C9, CYP2D6, CYP1A2, or CYP2E1 to form O-desmethylcarvedilol. Carvedilol and its metabolites may undergo further sulfate conjugation or glucuronidation before elimination. Carvedilol can be O-glucuronidated by UGT1A1, UGT2B4, and UGT2B7 to form carvedilol glucuronide.
Carvedilol is metabolized primarily by aromatic ring oxidation and glucuronidation. The oxidative metabolites are further metabolized by conjugation via glucuronidation and sulfation.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for CARVEDILOL (carvedilol) tablet (May 2011). Available from, as of September 19, 2011 https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=0b802a9c-332f-4ea8-bb34-75c677264654
Carvedilol is extensively metabolized; phenol ring demethylation and hydroxylation produce 3 metabolites with beta-adrenergic blocking activity and (weak) vasodilating activity. Plasma concentrations of active metabolites are about 10% those of carvedilol. The 4'-hydroxyphenyl metabolite is 13 times more potent than carvedilol in beta-adrenergic blocking activity.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 1888
Compared to carvedilol, the 3 active metabolites exhibit weak vasodilating activity. Plasma concentrations of the active metabolites are about one-tenth of those observed for carvedilol and have pharmacokinetics similar to the parent.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for CARVEDILOL (carvedilol) tablet (May 2011). Available from, as of September 19, 2011 https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=0b802a9c-332f-4ea8-bb34-75c677264654
Carvedilol undergoes stereoselective first-pass metabolism with plasma levels of R(+)-carvedilol approximately 2 to 3 times higher than S(-)-carvedilol following oral administration in healthy subjects.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for CARVEDILOL (carvedilol) tablet (May 2011). Available from, as of September 19, 2011 https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=0b802a9c-332f-4ea8-bb34-75c677264654
For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for CARVEDILOL (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Carvedilol has known human metabolites that include (2S,3S,4S,5R)-6-[1-(9H-Carbazol-4-yloxy)-3-[2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)ethylamino]propan-2-yl]oxy-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
The half life of carvedilol is between 7-10 hours, though significantly shorter half lives have also been reported.
The half-life of carvedilol is 7-10 hours; 5-9 hours for R(+)-carvedilol, and 7-11 hours for S(-)-carvedilol.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 1888
The pharmacokinetics and absolute bioavailability of carvedilol have been studied in 20 male healthy volunteers in a randomised 4-period, cross-over trial. Carvedilol 12.5 mg was given i.v., 50 mg was administered p.o. as a suspension and 25 and 50 mg were given in a capsule formulation. For the 50 mg capsule Cmax was 66 micrograms.l-1, tmax 1.2 h, t1/2 6.4 h. The t1/2 after i.v. administration was 2.4 h, CL 589 ml/min and VZ 132 l. The absolute bioavailability was 24% (50 mg capsule). The kinetics after the 25 and 50 mg capsules were consistent with dose linearity.
PMID:3428345 von Mollendorff E, et al; Eur J Clin Pharmacol 33(5): 511-513 (1987)
Carvedilol inhibits exercise induce tachycardia through its inhibition of beta adrenoceptors. Carvedilol's action on alpha-1 adrenergic receptors relaxes smooth muscle in vasculature, leading to reduced peripheral vascular resistance and an overall reduction in blood pressure. At higher doses, calcium channel blocking and antioxidant activity can also be seen. The antioxidant activity of carvedilol prevents oxidation of low density lipoprotein and its uptake into coronary circulation.
Carvedilol is a nonselective beta-adrenergic blocking agent with selective alpha1-adrenergic blocking activity. The principal physiologic action of carvedilol is to competitively block adrenergic stimulation of beta-receptors within the myocardium (beta1-receptors) and within bronchial and vascular smooth muscle (beta2-receptors), and to a lesser extent alpha1-receptors within vascular smooth muscle. The beta1-antagonist activity of carvedilol is similar to that of propranolol and greater than that of labetalol, and the duration of carvedilol's effect is longer than those of labetalol and propranolol.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 1888
Studies in animals indicate that the drug may exert an antioxidant effect on the myocardium and an antiproliferative effect on intimal tissue. The commercially available drug is a racemic mixture of the 2 enantiomers, (R)[+] and (S)[-], and both enantiomers have equal alpha1-adrenergic blocking activity; however, only the S(-)-enantiomer of carvedilol has beta-adrenergic blocking activity. Carvedilol does not exhibit intrinsic sympathomimetic (beta1-agonist) activity and possesses only weak membrane-stabilizing (local anesthetic) activity.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 1888
Vasodilation resulting in reduced total peripheral resistance mediated through carvedilol's alpha1-adrenergic blockade and reduced sympathetic tone appear to play a major role in the drug's hypotensive effect. Carvedilol causes reductions in cardiac output, exercise-induced tachycardia, isoproterenol-induced tachycardia, and reflex orthostatic tachycardia. Clinically important beta-adrenergic blocking activity of carvedilol usually is evident within 1 hour of oral administration, and the drug's hypotensive effect is similar to that of metoprolol. Carvedilol's alpha1-adrenergic blocking effects, which contribute to the drug's hypotensive effects, generally are evident within 30 minutes of oral administration and include reductions in phenylephrine-induced pressor effects, vasodilation, and decreased peripheral vascular resistance. The dose-dependent hypotensive effect of carvedilol results in blood pressure (systolic and diastolic) reductions of 5-46% with little, if any, reflex tachycardia. This hypotensive effect occurs approximately 30 minutes after oral administration and has a maximum effect 1.5-7 hours after oral administration.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 1888
The precise mechanism of the beneficial effects of carvedilol in the treatment of congestive heart failure has not been fully elucidated. beta1-Adrenergic blockade and vasodilation generally are associated with reflex tachycardia and peripheral vasoconstriction in therapeutic agents in which one of these pharmacologic effects predominates, but the combined effects of carvedilol appear to attenuate these two major untoward responses by balancing the potential adverse effects associated with adrenergic blockade and vasodilation. The drug's vasodilatory action appears to enable the patient to tolerate the negative inotropic effect of carvedilol during the initiation and titration of therapy in the treatment of compensated heart failure.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 1888
For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for CARVEDILOL (18 total), please visit the HSDB record page.