
1. Amca
2. Amcha
3. Amchafibrin
4. Anvitoff
5. Cyklokapron
6. Exacyl
7. Kabi 2161
8. Spotof
9. T-amcha
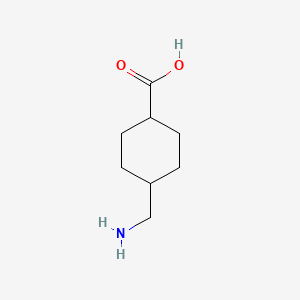
10. Trans-4-(aminomethyl)cyclohexanecarboxylic Acid
11. Transamin
12. Ugurol
1. 1197-18-8
2. Trans-4-(aminomethyl)cyclohexanecarboxylic Acid
3. Cyklokapron
4. 4-(aminomethyl)cyclohexanecarboxylic Acid
5. Trans Amcha
6. Tranexamsaeure
7. Transamin
8. 701-54-2
9. Tranhexamic Acid
10. Cyclocapron
11. Amstat
12. Trans-amcha
13. 1197-17-7
14. Rikavarin
15. Tamcha
16. Amikapron
17. Anvitoff
18. Ugurol
19. Amcha
20. Frenolyse
21. Trasamlon
22. Carxamin
23. Emorhalt
24. Tranexan
25. Mastop
26. Rikavarin-s
27. Amca
28. Cis-4-(aminomethyl)cyclohexanecarboxylic Acid
29. Exacyl
30. Tranexmic Acid
31. Hexapromin
32. Transamlon
33. Hexatron
34. Spiramin
35. Tranex
36. Cis-amcha
37. Cis-tranexamic Acid
38. Trans-4-aminomethylcyclohexane-1-carboxylic Acid
39. 4-(aminomethyl)cyclohexane-1-carboxylic Acid
40. Trans-tranexamic Acid
41. Acidum Tranexamicum
42. Cyclohexanecarboxylic Acid, 4-(aminomethyl)-, Trans-
43. Lysteda
44. Acido Tranexamico
45. Cl 65336
46. Acide Tranexamique
47. Femstrual
48. Bay 3517
49. Cyclo-f
50. Rp 18,429
51. Cyclohexanecarboxylic Acid, 4-(aminomethyl)-
52. 4-(aminomethyl)-cyclohexanecarboxylic Acid
53. Cyclohexanecarboxylic Acid, 4-(aminomethyl)-, Cis-
54. Cyclokapron
55. Espercil
56. Haematrix
57. (1r,4r)-4-(aminomethyl)cyclohexane-1-carboxylic Acid
58. Cis-4-aminomethylcyclohexane-1-carboxylic Acid
59. Trans-p-(aminomethyl)cyclohexanecarboxylic Acid
60. Cl-65336
61. Dv 79
62. Dv79
63. Trans-4-(aminomethyl)-1-cyclohexanecarboxylic Acid
64. Lb1148
65. Mfcd00001466
66. Cis-4-(aminomethyl)cyclohexane-1-carboxylic Acid
67. Nsc-291305
68. Trans-1-(aminomethyl)cyclohexane-4-carboxylic Acid
69. Trans-4-(aminomethyl)cyclohexane-1-carboxylic Acid
70. Tranexamic Acid (transamin)
71. Retavase
72. Chebi:48669
73. 37yd696ii6
74. 6t84r30kc1
75. Nsc291305
76. Trans-4-(aminomethyl)cyclohexanecarboxylic Acid Ester
77. 4-aminomethylcyclohexanecarboxylic Acid
78. Ncgc00016569-01
79. Rp-18429
80. Cas-1197-18-8
81. 4-(aminomethyl)cyclohexanecarboxylic Acid (trans-)
82. Amh
83. Tranexamic Acid Cis-form
84. Acide Tranexamique [inn-french]
85. Acido Tranexamico [inn-spanish]
86. Acidum Tranexamicum [inn-latin]
87. Dv-79
88. Cyklokapron (tn)
89. Rikavarin (tn)
90. Transamin (tn)
91. Haku
92. Sr-05000001794
93. Einecs 214-818-2
94. Trans-1-aminomethylcyclohexane-4-carboxylic Acid
95. Nsc 291305
96. Brn 2207452
97. Tranexamate
98. Tranexamic-acid
99. Unii-37yd696ii6
100. Unii-6t84r30kc1
101. 1ceb
102. Prestwick_476
103. Albb-006013
104. Tranexamic Acid,(s)
105. Spectrum_001391
106. Tranexamic Acid [usan:usp:inn:ban:jan]
107. Prestwick0_000171
108. Prestwick1_000171
109. Prestwick2_000171
110. Prestwick3_000171
111. Spectrum2_000655
112. Spectrum3_001189
113. Spectrum4_000046
114. Spectrum5_001258
115. Chembl877
116. Trans-4-(aminomethyl)cyclohexane-carboxylic Acid
117. Dsstox_cid_25350
118. Dsstox_rid_80817
119. Dsstox_gsid_45350
120. Oprea1_786414
121. Schembl16974
122. Bspbio_000061
123. Bspbio_002837
124. Kbiogr_000511
125. Kbioss_001871
126. Tranexamic Acid [mi]
127. 3-14-00-00868 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
128. Cis-4-(aminomethyl)cyclohexanecarboxylicacid
129. Divk1c_000655
130. Schembl186034
131. Schembl349408
132. Spectrum1502026
133. Tranexamic Acid [inn]
134. Tranexamic Acid [jan]
135. Tranexamic Acid, Cis-
136. Spbio_000689
137. Spbio_001982
138. Tranexamic Acid [inci]
139. Tranexamic Acid [usan]
140. Bpbio1_000069
141. Chembl292500
142. Gtpl6573
143. Schembl6885575
144. Schembl9885628
145. Tranexamic Acid [vandf]
146. Dtxsid3045350
147. Tranexamic Acid [mart.]
148. Chebi:94518
149. Hms502a17
150. Kbio1_000655
151. Kbio2_001871
152. Kbio2_004439
153. Kbio2_007007
154. Kbio3_002337
155. Dtxsid50904827
156. Tranexamic Acid [usp-rs]
157. Tranexamic Acid [who-dd]
158. Wln: L6tj Avq D1z -t
159. Ninds_000655
160. Hms1568d03
161. Hms1921f08
162. Hms2092p03
163. Hms2095d03
164. Hms3712d03
165. Hms3744g07
166. Pharmakon1600-01502026
167. Bcp13133
168. Bcp18146
169. Hy-b0149
170. Tranexamic Acid (jp17/usp/inn)
171. Zinc1542907
172. Tox21_110500
173. Bbl004469
174. Bdbm50428067
175. Ccg-39692
176. Mfcd00064951
177. Mfcd19706018
178. Nsc758176
179. S1875
180. Stk503668
181. Tranexamic Acid [orange Book]
182. Tranexamic Acid(random Configuration)
183. Akos005171632
184. Akos015854573
185. Akos024257901
186. Tranexamic Acid [ep Monograph]
187. Tranexamic Acid [usp Impurity]
188. Tranexamic Acid Cis-form [mi]
189. Zinc100007011
190. Zinc100071256
191. Ab86495
192. Ac-4687
193. Am84352
194. Bs-3867
195. Cs-1965
196. Db00302
197. Nsc-758176
198. Tranexamic Acid [usp Monograph]
199. 4-(aminomethyl)cyclohexanecarboxylicacid
200. 4-aminomethyl-cyclohexanecarboxylic Acid
201. Idi1_000655
202. Ncgc00016569-02
203. Ncgc00016569-03
204. Ncgc00016569-04
205. Ncgc00016569-05
206. Ncgc00016569-06
207. Ncgc00016569-08
208. Ncgc00016569-09
209. Ncgc00094944-01
210. Ncgc00094944-02
211. P-(aminomethyl)cyclohexanecarboxylic Acid
212. As-80121
213. Bp-12345
214. Sy011438
215. Tranexamic Acid Related Compound B
216. Ts-02090
217. Sbi-0051705.p002
218. Trans 4aminomethylcyclohexanecarboxylic Acid
219. Db-074265
220. Tranexamic Acid 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
221. Trans-4-aminomethylcyclohexylcarboxylic Acid
222. Trans-p-aminomethylcyclohexanecarboxylic Acid
223. A0236
224. Ab00052260
225. Bb 0260034
226. Cs-0013687
227. Cs-0055045
228. Ft-0654339
229. Ft-0675360
230. Ft-0700806
231. Trans 4-aminomethylcyclohexanecarboxylic Acid
232. Trans-4-aminomethylcyclohexanecarboxylic Acid
233. En300-91506
234. Trans-4(aminomethyl)cyclohexanecarboxylic Acid
235. Trans-4-(aminomethyl)cyclohexylcarboxylic Acid
236. Trans-4-aminomethyl Cyclohexanecarboxylic Acid
237. Trans-4-aminomethyl-cyclohexanecarboxylic Acid
238. Trans-4-aminomethylcyclohexane Carboxylic Acid
239. D01136
240. P15619
241. P20836
242. T71247
243. Trans-4-aminomethyl Cyclohexane Carboxylic Acid
244. Trans4-aminomethylcyclohexane-1-carboxylic Acid
245. Ab00052260-04
246. Ab00052260_05
247. Ab00052260_06
248. Tranexamic Acid Impurity B [ep Impurity]
249. Trans-4 -(aminomethyl)cyclohexanecarboxylic Acid
250. Trans-4-(aminomethyl)-cyclohexanecarboxylic Acid
251. Trans-4-(aminomethyl)cyclohexane Carboxylic Acid
252. Trans-4-aminomethyl-1-cyclohexanecarboxylic Acid
253. (1r,4r)-4-(aminomethyl)cyclohexanecarboxylic Acid
254. (trans)-4-(aminomethyl)cyclohexanecarboxylic Acid
255. 197t188
256. 4-trans-(aminomethyl)cyclohexanecarboxylic Acid #
257. Q418666
258. Trans-?4-?(aminomethyl)?cyclohexanecarboxylic Acid
259. Trans-4- (aminomethyl) Cyclohexanecarboxylic Acid
260. Trans-4-(aminomethyl)- Cyclohexane Carboxylic Acid
261. Trans-4-(aminomethyl)-cyclohexane Carboxylic Acid
262. Trans-4-aminomethyl-1-cyclohexane Carboxylic Acid
263. 4alpha-aminomethyl-1alpha-cyclohexanecarboxylic Acid
264. Q-201848
265. Sr-05000001794-1
266. Sr-05000001794-2
267. Sr-05000001794-3
268. Tranexamic Acid 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile:water
269. Brd-k15014948-001-01-2
270. Q27256710
271. Trans-4-(aminomethyl)cyclohexanecarboxylic Acid, 97%
272. 4-(aminomethyl)cyclohexanecarboxylic Acid;tranexamic Acid
273. F8886-7867
274. Tranexamic Acid Related Compound B [usp Impurity]
275. Z1741970429
276. Rel-(1r,4r)-4-(aminomethyl)cyclohexane-1-carboxylic Acid
277. Tranexamic Acid, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
278. 4-(aminomethyl)cyclohexanecarboxylic Acid (cis- And Trans- Mixture)
279. Tranexamic Acid, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
280. 4-(aminomethyl)cyclohexanecarboxylic Acid (cis- And Trans- Mixture);
281. Tranexamic Acid, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
| Molecular Weight | 157.21 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C8H15NO2 |
| XLogP3 | -2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 157.110278721 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 157.110278721 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 63.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 11 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 139 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Cyklokapron |
| PubMed Health | Tranexamic Acid |
| Drug Classes | Hemostatic |
| Drug Label | Each mL of the sterile solution for intravenous injection contains 100 mg tranexamic acid and Water for Injection to 1 mL.... |
| Active Ingredient | Tranexamic acid |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 100mg/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pharmacia And Upjohn |
| 2 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Lysteda |
| PubMed Health | Tranexamic Acid |
| Drug Classes | Hemostatic |
| Drug Label | LYSTEDA is an antifibrinolytic drug. The chemical name is trans-4-aminomethyl-cyclohexanecarboxylic acid. The structural formula is:Tranexamic acid is a white crystalline... |
| Active Ingredient | Tranexamic acid |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 650mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Ferring Pharms As |
| 3 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Tranexamic acid |
| PubMed Health | Tranexamic Acid |
| Drug Classes | Hemostatic |
| Drug Label | Tranexamic Acid Tablets is an antifibrinolytic drug. The chemical name is trans-4-aminomethyl-cyclohexanecarboxylic acid. The structural formula is:Tranexamic acid is a white crystalline powder. It is freely soluble in water and in glacial acetic aci... |
| Active Ingredient | Tranexamic acid |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Injectable |
| Route | Injection; Oral |
| Strength | 650mg; 650 mg; 100mg/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Actavis Labs Fl; Apotex; Acic Fine Chems; Emcure Pharms; Fresenius Kabi Usa; Versapharm; Mylan Institutional; X-gen Pharms; Luitpold |
| 4 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Cyklokapron |
| PubMed Health | Tranexamic Acid |
| Drug Classes | Hemostatic |
| Drug Label | Each mL of the sterile solution for intravenous injection contains 100 mg tranexamic acid and Water for Injection to 1 mL.... |
| Active Ingredient | Tranexamic acid |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 100mg/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pharmacia And Upjohn |
| 5 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Lysteda |
| PubMed Health | Tranexamic Acid |
| Drug Classes | Hemostatic |
| Drug Label | LYSTEDA is an antifibrinolytic drug. The chemical name is trans-4-aminomethyl-cyclohexanecarboxylic acid. The structural formula is:Tranexamic acid is a white crystalline... |
| Active Ingredient | Tranexamic acid |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 650mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Ferring Pharms As |
| 6 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Tranexamic acid |
| PubMed Health | Tranexamic Acid |
| Drug Classes | Hemostatic |
| Drug Label | Tranexamic Acid Tablets is an antifibrinolytic drug. The chemical name is trans-4-aminomethyl-cyclohexanecarboxylic acid. The structural formula is:Tranexamic acid is a white crystalline powder. It is freely soluble in water and in glacial acetic aci... |
| Active Ingredient | Tranexamic acid |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Injectable |
| Route | Injection; Oral |
| Strength | 650mg; 650 mg; 100mg/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Actavis Labs Fl; Apotex; Acic Fine Chems; Emcure Pharms; Fresenius Kabi Usa; Versapharm; Mylan Institutional; X-gen Pharms; Luitpold |
Taken orally, tranexamic acid is indicated for the treatment of hereditary angioedema, cyclic heavy menstrual bleeding in premenopausal females, and other instances of significant bleeding in the context of hyperfibrinolysis. Given intravenously, tranexamic acid is indicated for short-term use (2-8 days) in patients with hemophilia to prevent or reduce bleeding following tooth extraction.
Tranexamic acid is an antifibrinolytic that competitively inhibits the activation of plasminogen to plasmin. At much higher concentrations it behaves as a noncompetitive inhibitor of plasmin similar to [aminocaproic acid], a similar antifibrinolytic which is 10-fold less potent. Tranexamic acid binds more strongly than aminocaproic acid to both the strong and weak receptor sites of the plasminogen molecule in a ratio corresponding to the difference in potency between the compounds. In patients with hereditary angioedema, inhibition of the formation and activity of plasmin by tranexamic acid may prevent attacks of angioedema by decreasing plasmin-induced activation of the first complement protein (C1). Off-target antagonism of GABA(A) receptors may be associated with the development of convulsions and hyperexcitability following tranexamic acid administration - the risk appears higher with improper administration or administration during cardiovascular surgery. Consider EEG monitoring of patients with a history of seizure.
Antifibrinolytic Agents
Agents that prevent fibrinolysis or lysis of a blood clot or thrombus. Several endogenous antiplasmins are known. The drugs are used to control massive hemorrhage and in other coagulation disorders. (See all compounds classified as Antifibrinolytic Agents.)
B02AA02
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
B - Blood and blood forming organs
B02 - Antihemorrhagics
B02A - Antifibrinolytics
B02AA - Amino acids
B02AA02 - Tranexamic acid
Absorption
The bioavailability of tranexamic acid after oral administration in humans is approximately 30 to 50% of the ingested dose and is not affected by food intake. The Cmax and Tmax following multiple oral doses (1300 mg three times daily x 5 days) were 16.41 mcg/mL and 2.5 h, respectively.
Route of Elimination
Urinary excretion is the primary means of tranexamic acid elimination, with >95% of an administered dose excreted in the urine as unchanged parent drug. The rate of excretion is dependent on the route of administration - approximately 90% of an intravenously administered dose is excreted within 24 hours whereas only 39% of an orally administered dose is excreted within the same time frame.
Volume of Distribution
The initial volume of distribution of tranexamic acid is 0.18 L/kg and its steady-state volume of distribution is 0.39 L/kg. Tranexamic acid distributes into cerebrospinal fluid and the aqueous humor of the eye at concentrations approximately 1/10th of typical plasma concentrations. Tranexamic acid is also able to cross the placenta, found in cord blood at concentrations equivalent to maternal plasma concentrations.
Clearance
The plasma clearance of tranexamic acid is 110-116 mL/min.
Tranexamic acid metabolism is poorly characterized but does not appear to be a significant means of drug elimination. According to prescribing information, approximately 1% and 0.5% of an orally administered dose are excreted as a dicarboxylic acid and acetylated metabolite, respectively.
Following intravenous administration, the apparent elimination half-life is approximately 2 hours and the mean terminal half-life is approximately 11 hours.
Tranexamic acid competitively and reversibly inhibits the activation of plasminogen via binding at several distinct sites, including four or five low-affinity sites and one high-affinity site, the latter of which is involved in its binding to fibrin. The binding of plasminogen to fibrin induces fibrinolysis - by occupying the necessary binding sites tranexamic acid prevents this dissolution of fibrin, thereby stabilizing the clot and preventing hemorrhage.