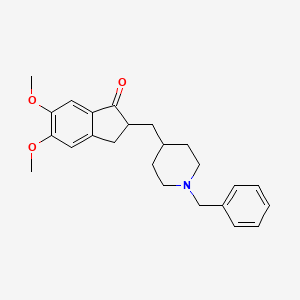

1. 1-benzyl-4-((5,6-dimethoxy-1-indanon)-2-yl)methylpiperidine Hydrochloride
2. Aricept
3. Donepezil Hydrochloride
4. Donepezilium Oxalate Trihydrate
5. E 2020
6. E-2020
7. E2020
8. Eranz
1. 120014-06-4
2. Aricept
3. 2-((1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl)methyl)-5,6-dimethoxy-2,3-dihydro-1h-inden-1-one
4. Donepezilo
5. Donaz
6. 2-[(1-benzyl-4-piperidyl)methyl]-5,6-dimethoxy-2,3-dihydroinden-1-one
7. 2-[(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl)methyl]-5,6-dimethoxy-2,3-dihydro-1h-inden-1-one
8. Hsdb 7743
9. 142057-79-2
10. Chembl502
11. (s)-e2020 (free Base)
12. Chebi:53289
13. 8ssc91326p
14. Donepezil (inn)
15. 2-[(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl)methyl]-5,6-dimethoxy-2,3-dihydroinden-1-one
16. Donepezil [inn]
17. D-797
18. 1h-inden-1-one, 2,3-dihydro-5,6-dimethoxy-2-((1-(phenylmethyl)-4-piperidinyl)methyl)-
19. 142057-80-5
20. Donepezil [inn:ban]
21. (rs)-2-[(1-benzyl-4-piperidyl)methyl]-5,6-dimethoxyindan-1-one
22. 1h-inden-1-one, 2,3-dihydro-5,6-dimethoxy-2-[[1-(phenylmethyl)-4-piperidinyl]methyl]-
23. 2,3-dihydro-5,6-dimethoxy-2-[[1-(phenylmethyl)-4-piperidinyl]methyl]-1h-inden-1-one
24. Nsc 737535
25. Nsc 758882
26. Ncgc00167537-01
27. Donepezilum
28. Domepezil
29. Unii-8ssc91326p
30. 2-((1-benzyl-4-piperidyl)methyl)-5,6-dimethoxy-2,3-dihydroinden-1-one
31. 2,3-dihydro-5,6-dimethoxy-2-((1-(phenylmethyl)-4-piperidinyl)methyl)-1h-inden-1-one
32. Donaz (tn)
33. Spectrum_001664
34. Donepezil [jan]
35. Donepezil [mi]
36. Donepezil [hsdb]
37. Spectrum5_001662
38. Donepezil [vandf]
39. Donepezil [who-dd]
40. Schembl2149
41. Oprea1_188452
42. Kbioss_002144
43. Bdbm8960
44. Gtpl6599
45. Schembl8265876
46. Dtxsid8048317
47. Kbio2_002144
48. Kbio2_004712
49. Kbio2_007280
50. Amy8939
51. Chebi:145499
52. Bcpp000253
53. Hms3886m11
54. Bcp07590
55. Mfcd00912833
56. S5073
57. Stk003905
58. Akos000277311
59. Akos016842349
60. Ac-6969
61. Bcp9000622
62. Ccg-268401
63. Db00843
64. Mrf-0000323
65. D797
66. Hy-14566
67. Sbi-0206789.p001
68. Ft-0601545
69. D07869
70. Ab00640013-07
71. Ab00640013-08
72. Ab00640013_09
73. Ab00640013_10
74. 014d064
75. Q415081
76. Q-100098
77. Brd-a49160188-003-04-4
78. Z1741977105
79. 2-[(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl)methyl]-5,6-dimethoxyindan-1-one
80. (+/-)-2-((1-benzyl-4-piperidyl)methyl)-5,6-dimethoxy-1-indanone
81. (+/-)-2-[(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl)methyl]-5,6-dimethoxy-indan-1-one
82. 2-[(1-benzyl-4-piperidyl)methyl]- 5,6-dimethoxy-2,3-dihydroinden-1-one
83. 2,3-dihydro-5,6-dimethoxy-2 [[1-(phenyl Methyl)-4-piperidinyl]methyl]-1h-inden-1-one
84. 2,3-dihydro-5,6-dimethoxy-2[[1-(phenyl Methyl)-4-piperidinyl]methyl]-1h-inden-1-one
85. 5,6-dimethoxy-2-[[1-(phenylmethyl)piperidin-4-yl]methyl]-2,3-dihydroinden-1-one
86. 5,6-dimethoxy-2-((1-(phenylmethyl)-4-piperidinyl)methyl)-2,3-dihydro-1h-inden-1-one
| Molecular Weight | 379.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C24H29NO3 |
| XLogP3 | 4.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 379.21474379 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 379.21474379 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 38.8 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 28 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 510 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | ARICEPT ODT |
| Active Ingredient | DONEPEZIL HYDROCHLORIDE |
| Company | EISAI INC (Application Number: N021720) |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | ARICEPT |
| Active Ingredient | DONEPEZIL HYDROCHLORIDE |
| Company | EISAI INC (Application Number: N020690); EISAI INC (Application Number: N022568. Patent: 8481565) |
Cholinesterase Inhibitors; Nootropic Agents
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 2009)
Donepezil hydrochloride tablets are indicated for the treatment of dementia of the Alzheimer's type. Efficacy has been demonstrated in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer's Disease. /Included in US product label/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Donepezil Hydrochloride (donepezil hydrochloride) tablets, film coated (May 2008). Available from, as of June 29, 2009: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=7596
/EXPTL Ther:/ ... Officially approved for mild-to-moderate and severe /Alzheimer's Disease/ (AD), donepezil has also been shown to be effective in early-stage AD, vascular dementia, Parkinson's disease dementia/Lewy body disease and cognitive symptoms associated with multiple sclerosis. In addition, one study suggested that donepezil may delay the onset of AD in subjects with mild cognitive impairment, a prodrome to AD.
PMID:17472546 Seltzer B; Expert Opin Pharmacother 8 (7): 1011-23 (2007).
Donepezil hydrochloride tablets are contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to donepezil hydrochloride or to piperidine derivatives.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Donepezil Hydrochloride (donepezil hydrochloride) tablets, film coated (May 2008). Available from, as of June 29, 2009: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=7596
Because of their pharmacological action, cholinesterase inhibitors may have vagotonic effects on the sinoatrial and atrioventricular nodes. This effect may manifest as bradycardia or heart block in patients both with and without known underlying cardiac conduction abnormalities. Syncopal episodes have been reported in association with the use of donepezil hydrochloride. Syncopal episodes have been reported in association with the use of donepezil hydrochloride.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Donepezil Hydrochloride (donepezil hydrochloride) tablets, film coated (May 2008). Available from, as of June 29, 2009: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=7596
Through their primary action, cholinesterase inhibitors may be expected to increase gastric acid secretion due to increased cholinergic activity. Therefore, patients should be monitored closely for symptoms of active or occult gastrointestinal bleeding, especially those at increased risk for developing ulcers, eg, those with a history of ulcer disease or those receiving concurrent non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS).
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Donepezil Hydrochloride (donepezil hydrochloride) tablets, film coated (May 2008). Available from, as of June 29, 2009: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=7596
Donepezil hydrochloride, as a predictable consequence of its pharmacological properties, has been shown to produce diarrhea, nausea and vomiting. These effects, when they occur, appear more frequently with the 10 mg/day dose than with the 5 mg/day dose. In most cases, these effects have been mild and transient, sometimes lasting one to three weeks, and have resolved during continued use of donepezil hydrochloride.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Donepezil Hydrochloride (donepezil hydrochloride) tablets, film coated (May 2008). Available from, as of June 29, 2009: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=7596
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Donepezil (12 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Donepezil is indicated for the management of mild to moderate Alzheimers Disease at doses of 5 mg or 10 mg. It is also indicated for the management of moderate to severe Alzheimers Disease in a higher dose of 10 mg or 23 mg administered once daily. Off-label uses include the management of vascular dementia, Parkinson's Disease-associated dementia, and Lewy body dementia, among others. When combined with memantine, the extended-release form of donepezil is indicated to treat the symptoms of moderate to severe dementia.
By inhibiting the acetylcholinesterase enzyme, donepezil improves the cognitive and behavioral signs and symptoms of Alzheimer's Disease, which may include apathy, aggression, confusion, and psychosis.
Cholinesterase Inhibitors
Drugs that inhibit cholinesterases. The neurotransmitter ACETYLCHOLINE is rapidly hydrolyzed, and thereby inactivated, by cholinesterases. When cholinesterases are inhibited, the action of endogenously released acetylcholine at cholinergic synapses is potentiated. Cholinesterase inhibitors are widely used clinically for their potentiation of cholinergic inputs to the gastrointestinal tract and urinary bladder, the eye, and skeletal muscles; they are also used for their effects on the heart and the central nervous system. (See all compounds classified as Cholinesterase Inhibitors.)
Nootropic Agents
Drugs used to specifically facilitate learning or memory, particularly to prevent the cognitive deficits associated with dementias. These drugs act by a variety of mechanisms. (See all compounds classified as Nootropic Agents.)
N06DA02
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
N - Nervous system
N06 - Psychoanaleptics
N06D - Anti-dementia drugs
N06DA - Anticholinesterases
N06DA02 - Donepezil
Absorption
Donepezil is slowly absorbed via the gastrointestinal tract after oral administration. Tmax is 3 to 4 hours with a bioavailability of 100% and steady-state concentrations are attained within 15 to 21 days of administration. The Tmax in one pharmacokinetic study determined a Tmax of 4.1 1.5 hours. The Cmax of 5 mg donepezil tablets is estimated to be 8.34 ng/mL, according to the Canadian monograph. The AUC of 5 mg donepezil tablets has been determined to be 221.90-225.36 ng.hr/mL.
Route of Elimination
In a study of radiolabeled administration donepezil in healthy adults, 57% of measured radioactivity was identified in the urine, and 5% was identified in the feces.
Volume of Distribution
The volume of distribution of donepezil is 11.8 1.7 L/kg for a 5-mg dose and 11.6 1.91 L/kg for a 10-mg dose. It is largely distributed in the extravascular compartments. Donepezil crosses the blood-brain barrier and cerebrospinal fluid concentrations at the above doses have been measured at 15.7%. The volume of distribution at steady-state according to the FDA label for donepezil ranges from 12 - 16 L/kg.
Clearance
According to the FDA label, the average apparent plasma clearance of this drug is 0.13 0.19 L/hr/kg. A 5 mg dose of donepezil in healthy patients was shown to have a plasma clearance of 0.1100.02 L/h/kg. In 10 patients diagnosed with alcoholic cirrhosis, showed a mean decrease in clearance by 20% when compared to the clearance in 10 healthy subjects. In 4 patients with severe renal impairment compared to 4 healthy subjects, no significant change in clearance was noted.
Donepezil is well absorbed with a relative oral bioavailability of 100% and reaches peak plasma concentrations in 3 to 4 hours. Pharmacokinetics are linear over a dose range of 1 to 10 mg given once daily. Neither food nor time of administration (morning vs. evening dose) influences the rate or extent of absorption of donepezil hydrochloride tablets.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Donepezil Hydrochloride (donepezil hydrochloride) tablets, film coated (May 2008). Available from, as of June 29, 2009: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=7596
... The mean apparent plasma clearance (Cl/F) is 0.13 L/hr/kg. Following multiple dose administration, donepezil accumulates in plasma by 4 to 7 fold and steady state is reached within 15 days. The steady state volume of distribution is 12 L/kg.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Donepezil Hydrochloride (donepezil hydrochloride) tablets, film coated (May 2008). Available from, as of June 29, 2009: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=7596
In a study of 10 patients with stable alcoholic cirrhosis, the clearance of donepezil hydrochloride was decreased by 20% relative to 10 healthy age and sex matched subjects.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Donepezil Hydrochloride (donepezil hydrochloride) tablets, film coated (May 2008). Available from, as of June 29, 2009: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=7596
In a study of 11 patients with moderate to severe renal impairment (ClCr < 18 mL/min/1.73 sq m) the clearance of donepezil hydrochloride did not differ from 11 age and sex matched healthy subjects.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Donepezil Hydrochloride (donepezil hydrochloride) tablets, film coated (May 2008). Available from, as of June 29, 2009: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=7596
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Donepezil (12 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Donepezil is metabolized by first pass metabolism in the liver, primarily by CYP3A4, in addition to CYP2D6. After this, O-dealkylation, hydroxylation, N-oxidation, hydrolysis, and O-glucuronidation occur, producing various metabolites with similar half-lives to the unchanged parent drug. A study of the pharmacokinetics of radiolabeled donepezil demonstrated that about 53% of plasma radioactivity appeared as donepezil in the unchanged form, and 11% was identified as the metabolite 6-O-desmethyl donepezil, which exerts similar potency inhibition of the acetylcholinesterase enzyme. This drug is heavily metabolized to four primary metabolites, two of which are considered pharmacologically active, as well as to multiple inactive and unidentified metabolites.
Donepezil is both excreted in the urine intact and extensively metabolized to four major metabolites, two of which are known to be active, and a number of minor metabolites, not all of which have been identified. Donepezil is metabolized by CYP 450 isoenzymes 2D6 and 3A4 and undergoes glucuronidation. Following administration of 14C-labeled donepezil, plasma radioactivity, expressed as a percent of the administered dose, was present primarily as intact donepezil (53%) and as 6-O-desmethyl donepezil (11%), which has been reported to inhibit AChE to the same extent as donepezil in vitro and was found in plasma at concentrations equal to about 20% of donepezil.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Donepezil Hydrochloride (donepezil hydrochloride) tablets, film coated (May 2008). Available from, as of June 29, 2009: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=7596
The aim of this study was to investigate the metabolism and elimination of donepezil HCl in humans, following the administration of a single 5 mg (liquid) oral dose containing a mixture of unlabelled and 14C-labelled donepezil. ... Unchanged donepezil accounted for the largest component of the recovered dose in each matrix. Three metabolic pathways were identified: (i) O-dealkylation and hydroxylation to metabolites M1 and M2, with subsequent glucuronidation to metabolites M11 and M12; (ii) hydrolysis to metabolite M4; and (iii) N-oxidation to metabolite M6. In plasma, the parent compound accounted for about 25% of the dose recovered during each sampling period, as well as of the cumulative dose recovered. The recovered residue showed higher levels of the hydroxylated metabolites M1 and M2 than of their glucuronide conjugates M11 and M12, respectively. In urine, the parent compound accounted for 17%, on average, of the dose recovered from each pooled sample, as well as of the total recovered dose. The major metabolite was the hydrolysis product M4, followed by the glucuronidated conjugates M11 and M12. In feces, the parent compound also predominated, although it accounted for only 1%, of the recovered dose. A large percentage of the radioactivity in feces consisted of unidentified very polar metabolites, which were retained at the TLC origin. Of the extracted metabolites, the hydroxylation products M1 and M2 were the most abundant, followed by the hydrolysis product M4 and the N-oxidation product M6. Donepezil is hepatically metabolized and the predominant route for the elimination of both parent drug and its metabolites is renal, as 79% of the recovered dose was found in the urine with the remaining 21% found in the feces. Moreover, the parent compound, donepezil, is the predominant elimination product in urine. The major metabolites of donepezil include M1 and M2 (via O-dealkylation and hydroxylation), M11 and M12 (via glucuronidation of M1 and M2, respectively), M4 (via hydrolysis) and M6 (via N-oxidation).
PMID:9839761 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1873810 Tiseo PJ et al; Br J Clin Pharmacol 46 (Suppl 1): 19-24 (1998).
Donepezil has known human metabolites that include 5,6-dimethoxy-2-(piperidin-4-ylmethyl)-2,3-dihydroinden-1-one, 5-O-Desmethyl Donepezil, and 6-O-Desmethyl Donepezil.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
The average elimination half-life of donepezil is about 70 hours according to the results of various studies and the FDA label for donepezil.. One pharmacokinetic study determined the average terminal half-life to be 81.522.0 h
The elimination half life of donepezil is about 70 hours.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Donepezil Hydrochloride (donepezil hydrochloride) tablets, film coated (May 2008). Available from, as of June 29, 2009: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=7596
A 79-year-old woman with Alzheimer's disease was admitted due to acute cholinergic symptoms induced by overdose (45 mg) of donepezil (DPZ) ... The plasma concentration of DPZ was 54.6 ng/mL on admission and gradually decreased to the normal limits in about 90 hr. The calculative half-life of DPZ was about 55 hr ...
PMID:14658400 Yano H et al; Rinsho Shinkeigaku 43 (8): 482-6 (2003).
The commonly accepted cholinergic hypothesis proposes that a portion of the cognitive and behavioral decline associated with Alzheimer's are the result of decreased cholinergic transmission in the central nervous system. Donepezil selectively and reversibly inhibits the acetylcholinesterase enzyme, which normally breaks down acetylcholine. The main pharmacological actions of this drug are believed to occur as the result of this enzyme inhibition, enhancing cholinergic transmission, which relieves the symptoms of Alzheimer's dementia. In addition to the above, other mechanisms of action of donepezil are possible, including the opposition of glutamate-induced excitatory transmission via downregulation of NMDA receptors and the regulation of amyloid proteins, which have demonstrated significant effects on the disease process of Alzheimer's. Other possible targets for donepezil may also include the inhibition various inflammatory signaling pathways, exerting neuroprotective effects.
Donepezil hydrochloride, a piperidine derivative, is a centrally active, reversible inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase. The drug is structurally unrelated to other anticholinesterase agents (eg, tacrine, physostigmine).
American Society of Health System Pharmacists. AHFS Drug Information 2008. Bethesda, Maryland 2008, p. 1293
The precise mechanism(s) of action of donepezil in patients with dementia of the Alzheimer's type (Alzheimer's disease) has not been fully elucidated. The drug is an anticholinesterase agent that binds reversibly with and inactivates cholinesterases (eg, acetylcholinesterase), thus inhibiting hydrolysis of acetylcholine. As a result, the concentration of acetylcholine increases at cholinergic synapses. In vitro data and data in animals indicate that the anticholinesterase activity of donepezil is relatively specific for acetylcholinesterase in the brain compared with butyrylcholinesterase inhibition in peripheral tissues.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists. AHFS Drug Information 2008. Bethesda, Maryland 2008, p. 1293
A deficiency of acetylcholine caused by selective loss of cholinergic neurons in the cerebral cortex, nucleus basalis, and hippocampus is recognized as one of the early pathophysiologic features of Alzheimer's disease associated with memory loss and cognitive deficits. Because the resultant cortical deficiency of this neurotransmitter is believed to account for some of the clinical manifestations of mild to moderate dementia, enhancement of cholinergic function with an anticholinesterase agent, such as tacrine or donepezil, is one of the pharmacologic approaches to treatment. Because widespread degeneration of multiple central neuronal systems eventually occurs in patients with Alzheimer's disease, potentially beneficial effects of anticholinesterase agents theoretically would diminish as the disease process advances and fewer cholinergic neurons remain functioning.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists. AHFS Drug Information 2008. Bethesda, Maryland 2008, p. 1293
Current theories on the pathogenesis of the cognitive signs and symptoms of Alzheimer's Disease attribute some of them to a deficiency of cholinergic neurotransmission. Donepezil hydrochloride is postulated to exert its therapeutic effect by enhancing cholinergic function. This is accomplished by increasing the concentration of acetylcholine through reversible inhibition of its hydrolysis by acetylcholinesterase. There is no evidence that donepezil alters the course of the underlying dementing process.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Donepezil Hydrochloride (donepezil hydrochloride) tablets, film coated (May 2008). Available from, as of June 29, 2009: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=7596
For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for Donepezil (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.