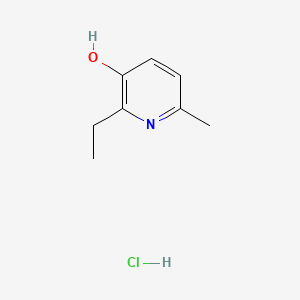

1. 2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-hydroxypyridine
2. 2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-oxypyridine
3. 6-methyl-2-ethyl-3-hydroxypyridine
4. 6-methyl-2-ethyl-3-hydroxypyridine Hydrochloride
5. 6-methyl-2-ethyl-3-hydroxypyridine Monohydrochloride
6. Emoxipin
7. Emoxipine
8. Emoxypin
9. Emoxypine
10. Epigid
11. Hydroxypyridine-6
1. 13258-59-8
2. 2-ethyl-6-methylpyridin-3-ol Hydrochloride
3. Emoxipin Hydrochloride
4. 2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-pyridinol Hydrochloride
5. 2-ethyl-3-hydroxy-6-methylpyridine Hcl
6. 3-pyridinol, 2-ethyl-6-methyl-, Hydrochloride
7. Emoxypine Hydrochloride
8. 2-ethyl-3-hydroxy-6-methylpyridine Hydrochloride
9. Sn1fwz77ae
10. 2-ethyl-6-methylpyridin-3-ol;hydrochloride
11. Hydroxypyridine-6
12. 3-pyridinol, 2-ethyl-6-methyl-, Hydrochloride (1:1)
13. Sd 6 (antioxidant)
14. Op 6 (pharmaceutical)
15. Emoxipin Hcl
16. Mexidol Hydrochloride
17. Unii-sn1fwz77ae
18. Emoxypin Hydrochloride
19. Op-6
20. Schembl1373708
21. Dtxsid80157647
22. Bcp13397
23. Ck1206
24. Mfcd00460776
25. Akos005267199
26. Methylethylpiridinol Hydrochloride
27. Ds-15704
28. 2-ethyl-6-methylpyridin-3-olhydrochloride
29. Db-002447
30. Cs-0061447
31. Ft-0612241
32. 258e598
33. Methylethylpiridinol Hydrochloride [who-dd]
34. Q27289297
35. 3-hydroxy-6-methyl-2-ethylpyridine Hydrochloride
| Molecular Weight | 173.64 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C8H12ClNO |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 173.0607417 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 173.0607417 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 33.1 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 11 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 105 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
Psychotropic Drugs
A loosely defined grouping of drugs that have effects on psychological function. Here the psychotropic agents include the antidepressive agents, hallucinogens, and tranquilizing agents (including the antipsychotics and anti-anxiety agents). (See all compounds classified as Psychotropic Drugs.)
Radiation-Protective Agents
Drugs used to protect against ionizing radiation. They are usually of interest for use in radiation therapy but have been considered for other purposes, e.g. military. (See all compounds classified as Radiation-Protective Agents.)
Mutagens
Chemical agents that increase the rate of genetic mutation by interfering with the function of nucleic acids. A clastogen is a specific mutagen that causes breaks in chromosomes. (See all compounds classified as Mutagens.)
Antioxidants
Naturally occurring or synthetic substances that inhibit or retard oxidation reactions. They counteract the damaging effects of oxidation in animal tissues. (See all compounds classified as Antioxidants.)
Anti-Arrhythmia Agents
Agents used for the treatment or prevention of cardiac arrhythmias. They may affect the polarization-repolarization phase of the action potential, its excitability or refractoriness, or impulse conduction or membrane responsiveness within cardiac fibers. Anti-arrhythmia agents are often classed into four main groups according to their mechanism of action: sodium channel blockade, beta-adrenergic blockade, repolarization prolongation, or calcium channel blockade. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Arrhythmia Agents.)
Platelet Aggregation Inhibitors
Drugs or agents which antagonize or impair any mechanism leading to blood platelet aggregation, whether during the phases of activation and shape change or following the dense-granule release reaction and stimulation of the prostaglandin-thromboxane system. (See all compounds classified as Platelet Aggregation Inhibitors.)
