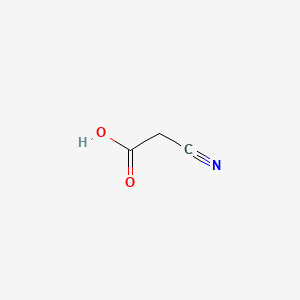

1. Cyanoacetic Acid, Copper (+2) Salt
1. 372-09-8
2. 2-cyanoacetic Acid
3. Acetic Acid, Cyano-
4. Malonic Mononitrile
5. Acide Cyanacetique
6. Cyanessigsaeure
7. Cyanoaceticacid
8. Monocyanoacetic Acid
9. Malonic Acid Mononitrile
10. Usaf Kf-17
11. Cyanoethanoic Acid
12. Kyselina Kyanoctova
13. Acetic Acid, 2-cyano-
14. Nsc 5571
15. Mfcd00002677
16. Qzt550h2y9
17. Dtxsid0027149
18. Chebi:51889
19. Nsc-5571
20. Dtxcid707149
21. Cyanessigsaeure [german]
22. Acide Cyanacetique [french]
23. Kyselina Kyanoctova [czech]
24. Cas-372-09-8
25. Hsdb 272
26. Einecs 206-743-9
27. Brn 0506325
28. Unii-qzt550h2y9
29. Cyanacetic Acid
30. Ai3-15026
31. Cyano Acetic Acid
32. Cyano-acetic Acid
33. Alphacyanoacetic Acid
34. 2-cyano-acetic Acid
35. Alpha Cyanoacetic Acid
36. Alpha-cyanoacetic Acid
37. Ncch2cooh
38. Cyanoacetic Acid, 99%
39. Wln: Qv1cn
40. Ec 206-743-9
41. Cyanoacetic Acid, >=99%
42. 4-02-00-01888 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
43. Cyanoacetic Acid [mi]
44. Cyanoacetic Acid [hsdb]
45. Chembl3185860
46. Nsc5571
47. Str00053
48. Tox21_201645
49. Tox21_303155
50. Akos000119706
51. Ncgc00249091-01
52. Ncgc00257182-01
53. Ncgc00259194-01
54. Ft-0624125
55. Ns00004053
56. En300-19926
57. P20002
58. J-200091
59. Q1146963
60. F2191-0053
61. Z104476112
62. Inchi=1/c3h3no2/c4-2-1-3(5)6/h1h2,(h,5,6
| Molecular Weight | 85.06 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C3H3NO2 |
| XLogP3 | -0.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 61.1 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 6 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 98.6 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
200 to 300 milligrams for an adult human (cyanide salts). (T86)
... In vivo and in vitro metabolism of 3-dimethylaminopropionitrile (DMAPN) and its urotoxic effect on male Sprague-Dawley rats /were investigated/. Rats were given 175, 350, or 525 mg/kg DMAPN or DMAPN metabolites orally for 5 days, and urinary metabolites and volumes were measured. By day 5, 44% of the DMAPN dose was excreted unchanged. Beta-aminopropionitrile and cyanoacetic acid were the major urinary metabolites, as identified by gas chromatography. /It was/ concluded that DMAPN is metabolized via a cytochrome P450 mixed-function oxidase system and the urotoxic effects of DMAPN may be related to its metabolism.
Bingham, E.; Cohrssen, B.; Powell, C.H.; Patty's Toxicology Volumes 1-9 5th ed. John Wiley & Sons. New York, N.Y. (2001)., p. 4:1423
... Cyanoacetic acid has been studied with reference to its possible role in the production of the symptoms of lathyrism by 3-aminopropionitrile. Injection of 14C-labeled 3-aminopropionitrile in rats showed that 25-30% could be recovered as cyanoacetic acid ... /However/ cyanoacetic acid is not responsible for the skeletal deformities, and such produced by feeding 3-aminopropionitrile.
Bingham, E.; Cohrssen, B.; Powell, C.H.; Patty's Toxicology Volumes 1-9 5th ed. John Wiley & Sons. New York, N.Y. (2001)., p. 4:1431
Organic nitriles are converted into cyanide ions through the action of cytochrome P450 enzymes in the liver. Cyanide is rapidly absorbed and distributed throughout the body. Cyanide is mainly metabolized into thiocyanate by either rhodanese or 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfur transferase. Cyanide metabolites are excreted in the urine. (L96)