

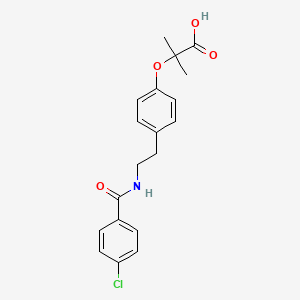

1. Azufibrat
2. Bfizal
3. Befibrat
4. Beza Lande
5. Beza Puren
6. Beza-lande
7. Beza-puren
8. Bezabeta
9. Bezacur
10. Bezafibrat Pb
11. Bezafisal
12. Bezalip
13. Bezamerck
14. Bm 15.075
15. Bm-15.075
16. Bm15.075
17. Cedur
18. Difaterol
19. Durabezur
20. Eulitop
21. Lipox
22. Reducterol
23. Regadrin B
24. Sklerofibrat
25. Solibay
1. 41859-67-0
2. Bezalip
3. Cedur
4. Bezafibrat
5. Difaterol
6. Befizal
7. Azufibrat
8. Sklerofibrat
9. Bezafibrato
10. Bezafibratum
11. Bezatol
12. Bezafibratum [inn-latin]
13. Bezafibrato [inn-spanish]
14. Bezatol Sr
15. Bm-15.075
16. Bezatol Sr (tn)
17. 2-[4-[2-[(4-chlorobenzoyl)amino]ethyl]phenoxy]-2-methylpropanoic Acid
18. Bm 15.075
19. 2-(p-(2-(p-chlorobenzamido)ethyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropionic Acid
20. Bm-15075
21. Nsc-758174
22. 2-[4-[2-(4-chlorobenzamido)ethyl]phenoxy]-2-methylpropanoic Acid
23. Bm15075
24. Propanoic Acid, 2-(4-(2-((4-chlorobenzoyl)amino)ethyl)phenoxy)-2-methyl-
25. Mls000028533
26. Chembl264374
27. Durabezur
28. Reducterol
29. Bezabeta
30. Bezacur
31. Bezamerck
32. Eulitop
33. Solibay
34. Chebi:47612
35. Lipox
36. Bezafibrat Pb
37. Y9449q51xh
38. Beza-lande
39. Beza-puren
40. Regadrin B
41. 2-[4-[2-[(4-chlorobenzoyl)amino]ethyl]phenoxy]-2-methyl-propanoic Acid
42. Propanoic Acid, 2-[4-[2-[(4-chlorobenzoyl)amino]ethyl]phenoxy]-2-methyl-
43. Ncgc00016850-01
44. Smr000058298
45. Bezafibrate 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
46. Bezafibrato [spanish]
47. 2-(4-(2-(4-chlorobenzamido)ethyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic Acid
48. Bezalip Retard
49. Cas-41859-67-0
50. Dsstox_cid_9869
51. Dsstox_rid_78826
52. Dsstox_gsid_29869
53. 2-{4-[2-(4-chlorobenzamido)ethyl]phenoxy}-2-methylpropanoic Acid
54. Lo 44
55. 2-(4-{2-[(4-chlorobenzoyl)amino]ethyl}phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic Acid
56. 2-(4-{2-[(4-chlorophenyl)formamido]ethyl}phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic Acid
57. 2-[p-[2-p-chlorobenzamido)ethyl]phenoxy]-2-methylpropionic Acid
58. Bf-759
59. Ccris 9085
60. Bm 15075
61. Sr-01000000106
62. Einecs 255-567-9
63. Brn 4267656
64. Unii-y9449q51xh
65. Bezalip Sr
66. Bezafibrate,(s)
67. Bezafibrate [usan:inn:ban:jan]
68. Pem
69. Prestwick_724
70. Mfcd00078970
71. Benafibrate
72. Spectrum_001443
73. Opera_id_376
74. Bezafibrate [mi]
75. Prestwick0_000378
76. Prestwick1_000378
77. Prestwick2_000378
78. Prestwick3_000378
79. Spectrum2_000922
80. Spectrum3_001500
81. Spectrum4_000325
82. Spectrum5_001079
83. Spectrum5_001967
84. Bezafibrate [inn]
85. Bezafibrate [jan]
86. Bezafibrate [usan]
87. Bezafibrate [mart.]
88. Schembl16299
89. Bezafibrate [who-dd]
90. Bezafibrate-d6(dimethyl-d6)
91. Bspbio_000535
92. Bspbio_001314
93. Bspbio_003119
94. Kbiogr_000034
95. Kbiogr_000669
96. Kbioss_000034
97. Kbioss_001923
98. Mls001148205
99. Bezafibrate, >=98%, Solid
100. Divk1c_000092
101. Spectrum1502046
102. Spbio_000824
103. Spbio_002456
104. Bpbio1_000589
105. Gtpl2668
106. Dtxsid3029869
107. Bdbm28701
108. Bezafibrate (jp17/usan/inn)
109. Hms500e14
110. Kbio1_000092
111. Kbio2_000034
112. Kbio2_001923
113. Kbio2_002602
114. Kbio2_004491
115. Kbio2_005170
116. Kbio2_007059
117. Kbio3_000067
118. Kbio3_000068
119. Kbio3_002619
120. 2-[4-[2-(4-chlorobenzamido)ethyl]phenoxy]isobutyric Acid
121. Ninds_000092
122. Bezafibrate [ep Monograph]
123. Bio2_000034
124. Bio2_000514
125. Hms1361b16
126. Hms1569k17
127. Hms1791b16
128. Hms1921h16
129. Hms1989b16
130. Hms2089f04
131. Hms2092b12
132. Hms2096k17
133. Hms2233e22
134. Hms3261d21
135. Hms3369b13
136. Hms3402b16
137. Hms3650k22
138. Hms3652m22
139. Hms3713k17
140. Pharmakon1600-01502046
141. Bcp03700
142. Hy-b0637
143. Zinc3956919
144. Tox21_110645
145. Tox21_301845
146. Tox21_500500
147. Ccg-39683
148. Nsc758174
149. S4159
150. Akos005107743
151. Propionic Acid, 2-(4-(2-((4-chlorobenzoyl)amino)ethyl)phenoxy)-2-methyl-
152. Tox21_110645_1
153. Ab03023
154. Ac-6817
155. Bcp9000398
156. Db01393
157. Hs-0040
158. Lp00500
159. Nsc 758174
160. Sb17361
161. Sdccgsbi-0051715.p003
162. Idi1_000092
163. Idi1_033784
164. Ncgc00016850-02
165. Ncgc00016850-03
166. Ncgc00016850-04
167. Ncgc00016850-05
168. Ncgc00016850-06
169. Ncgc00016850-07
170. Ncgc00016850-08
171. Ncgc00016850-09
172. Ncgc00016850-10
173. Ncgc00016850-11
174. Ncgc00016850-12
175. Ncgc00016850-15
176. Ncgc00016850-25
177. Ncgc00023317-03
178. Ncgc00023317-04
179. Ncgc00023317-05
180. Ncgc00023317-06
181. Ncgc00023317-07
182. Ncgc00023317-08
183. Ncgc00255376-01
184. Ncgc00261185-01
185. Bb166159
186. Bezafibrate, Analytical Reference Material
187. Bcp0726000153
188. Sbi-0051715.p002
189. 2-(4-(2-(4-chlorobenzamido)ethyl)phenoxy)
190. Ab00052265
191. B3346
192. Ft-0622617
193. Sw196871-4
194. D01366
195. D70191
196. Ab00052265-15
197. Ab00052265_16
198. Ab00052265_17
199. 859b670
200. Q577387
201. Sr-01000000106-3
202. Sr-01000000106-4
203. Sr-01000000106-5
204. W-106291
205. Brd-k46018455-001-06-0
206. Brd-k46018455-001-17-7
207. Sr-01000000106-10
208. Bezafibrate, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
209. 2-(4-(2-parachlorobenzamidoethyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropionic Acid
210. 2-[4-[2-(4-chlorobezamide)ethyl]phenoxy]-2-methylpropanoic Acid
211. 2-[4-(2-{[(4-chlorophenyl)carbonyl]amino}ethyl)phenoxy]-2-methylpropanoic Acid
212. Bf; 2-[4-[2-[(4-chlorobenzoyl)amino]ethyl]phenoxy]-2-methyl Propanoic Acid
| Molecular Weight | 361.8 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C19H20ClNO4 |
| XLogP3 | 3.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 361.1080858 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 361.1080858 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 75.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 25 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 452 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
For the treatment of primary hyperlipidaemia types IIa, IIb, III, IV and V (Fredrickson classification) corresponding to groups I, II and III of the European Atherosclerosis Society guidelines - when diet alone or improvements in lifestyle such as increased exercise or weight reduction do not lead to an adequate response. Also for the treatment of secondary hyperlipidaemias, e.g. severe hypertriglyceridemias, when sufficient improvement does not occur after correction of the underlying disorder (e.g. diabetes mellitus).
Bezafibrate is an antilipemic agent that lowers cholesterol and triglycerides. It decreases low density lipoproteins and increases high density lipoproteins. Bezafibrate lowers elevated blood lipids (triglycerides and cholesterol). Elevated VLDL and LDL are reduced by treatment with bezafibrate, whilst HDL-levels are increased. The activity of triglyceride lipases (lipoprotein lipase and hepatic lipoproteinlipase) involved in the catabolism of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins is increased by bezafibrate. In the course of the intensified degradation of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins (chylomicrons, VLDL) precursors for the formation of HDL are formed which explains an increase in HDL. Furthermore, cholesterol biosynthesis is reduced by bezafibrate, which is accompanied by a stimulation of the LDL-receptor-mediated lipoprotein catabolism. Elevated fibrinogen appears to be an important risk-factor, alongside the lipids, smoking and hypertension, in the development of atheroma. Fibrinogen plays an important role in viscosity, and therefore blood flow, and also appears to play an important role in thrombus development and lysability. Bezafibrate exerts an effect on thrombogenic factors. A significant decrease in elevated plasma fibrinogen levels can be achieved. This may lead, amongst other things, to a reduction in both blood and plasma viscosity. Inhibition of platelet aggregation has also been observed. A reduction in blood glucose concentration due to an increase in glucose tolerance has been reported in diabetic patients. In the same patients, the concentration of fasting and postprandial free fatty acids was reduced by bezafibrate.
Hypolipidemic Agents
Substances that lower the levels of certain LIPIDS in the BLOOD. They are used to treat HYPERLIPIDEMIAS. (See all compounds classified as Hypolipidemic Agents.)
C10AB02
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
C10AB02
S66 | EAWAGTPS | Parent-Transformation Product Pairs from Eawag | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.3754448
C10AB02
S66 | EAWAGTPS | Parent-Transformation Product Pairs from Eawag | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.3754448
C - Cardiovascular system
C10 - Lipid modifying agents
C10A - Lipid modifying agents, plain
C10AB - Fibrates
C10AB02 - Bezafibrate
Absorption
Bezafibrate is almost completely absorbed after oral administration. The relative bioavailability of bezafibrate retard compared to the standard form is about 70%.
Hepatic.
1-2 hours
It is generally accepted that bezafibrate is likely an agonist of PPAR-alpha. However, certain other investigations have also suggested that the substance might also elicit some effects on PPAR-gamma and PPAR-delta too.