

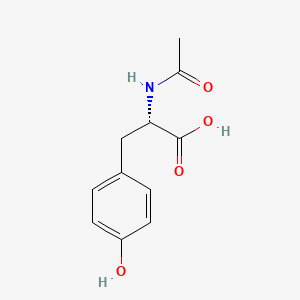

1. Acetyl-l-tyrosine
2. N-acetyltyrosine
3. N-acetyltyrosine, (d)-isomer
4. N-acetyltyrosine, (dl)-isomer
1. 537-55-3
2. Ac-tyr-oh
3. N-acetyl-tyrosine
4. Acetyl Tyrosine
5. Acetyl-l-tyrosine
6. L-tyrosine, N-acetyl-
7. L-n-acetyltyrosine
8. N-acetyltyrosin
9. Melanowhite-a
10. (2s)-2-acetamido-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoic Acid
11. Tyrosine, N-acetyl-
12. Chembl65543
13. Da8g610zo5
14. Chebi:21563
15. (s)-2-acetamido-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoic Acid
16. (2s)-2-acetylamino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoic Acid
17. N-acetyltyrosine (n-acetyl-l-tyrosine)
18. Ncgc00159393-02
19. Ncgc00159393-03
20. Dsstox_cid_26045
21. Dsstox_rid_81305
22. Dsstox_gsid_46045
23. (+)-(2s)-2-(acetylamino)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoic Acid
24. Mfcd00037190
25. Cas-537-55-3
26. N-aceyl-l-tyrosine
27. L-tyrosine, Acetyl-
28. Tyrosine, N-acetyl-, L-
29. N-acetyltyrosine (van)
30. Unii-da8g610zo5
31. Nsc-10853
32. N-acetyl Tyrosine
33. Einecs 208-671-3
34. Nsc 10853
35. L-n-acetyl-tyrosine
36. Tanogen Hb
37. Tyr-excel
38. Acetyl L-tyrosine
39. N-acetyl-l-tyrosine,(s)
40. L-tyrosine, N-acetyl
41. Schembl321220
42. Acetyl Tyrosine [inci]
43. (2s)-2-(acetylamino)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoic Acid
44. Dtxsid7046045
45. N-acetyltyrosin [who-dd]
46. Zinc156395
47. Tox21_111630
48. Ac7826
49. Bdbm50043802
50. S6316
51. Akos010396311
52. Akos015841008
53. N-acetyl-l-tyrosine [usp-rs]
54. N-acetyl-l-tyrosine, >99% (tlc)
55. Tox21_111630_1
56. Am82306
57. Cs-w013098
58. Db11102
59. Hy-w012382
60. N-acetyltyrosine [ep Monograph]
61. Ac-13390
62. Ds-15166
63. (2s)-2-acetylamino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoate
64. (s)-2-acetamido-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoicacid
65. 537a553
66. A829762
67. J-300276
68. N-acetyl-l-tyrosine 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
69. Q-201443
70. A53ee723-a216-4295-8abe-c8c9ee26bbfc
71. Q27109405
72. (s)-2-acetylamino-3-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-propionic Acid
73. 2-(s)-acetylamino-3-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-propionic Acid
74. N-acetyltyrosine, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
75. N-acetyl-l-tyrosine, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
76. N-acetyl-l-tyrosine, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
77. 3nf
78. N-acetyl-l-tyrosine, Pharmagrade, Ajinomoto, Ep, Manufactured Under Appropriate Gmp Controls For Pharma Or Biopharmaceutical Production, Suitable For Cell Culture
| Molecular Weight | 223.22 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C11H13NO4 |
| XLogP3 | -0.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 223.08445790 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 223.08445790 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 86.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 16 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 259 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
N-acetyltyrosine is indicated, in combination with several other amino acids and dextrose, as a peripherally administered source of nitrogen for nutritional support in patients with adequate stores of body fat in whom, for short periods, oral administration cannot be tolerated, is undesirable, or inadequate. It is also indicated, with other amino acids, 5-10% dextrose, and fat emulsion, for parenteral nutrition to preserve protein and reduce catabolism in stress conditions where oral administration is inadequate. When administered with other amino acids and concentrated dextrose, it is indicated for central vein infusion to prevent or reverse negative nitrogen balance in patients where the alimentary tract by the oral, gastrostomy, or jejestomy routes cannot or should not be used or in patients in which gastrointestinal absorption of protein is impaired, metabolic requirements for protein are substantially increased, or morbidity and mortality may be reduced by replacing amino acids lost from tissue breakdown
FDA Label
N-acetyltyrosine is used as a high solubility precursor to [DB00135] used due to [DB00135]'s poor solubility. It is deacetylated to form [DB00135].
Route of Elimination
N-acetyltyrosine is eliminated in the urine. The extent of urinary elimination versus utilization in the tissues appears to be related to the rapidity of infusion. When infused slowly in standard doses as in the clinical setting, about 35% is excreted unchanged in the urine. When larger doses are infused rapidly, much higher amounts are excreted reaching values up to 56%. In rat studies it was found that of the drug eliminated in the urine about 74% is present as unchanged N-acetyltyrosine and 23% is present as tyrosine.
Used as a source of [DB00135]. See [DB00135] for more information on its role and pharmacology.