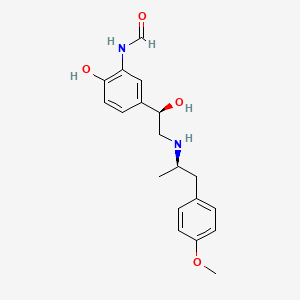

1. 3-formylamino-4-hydroxy-alpha-(n-1-methyl-2-p-methoxyphenethylaminomethyl)benzyl Alcohol.hemifumarate
2. Bd 40a
3. Eformoterol
4. Foradil
5. Formoterol
6. Formoterol Fumarate
7. Formoterol Fumarate, ((r*,r*)-(+-))-isomer
8. Formoterol, ((r*,r*)-(+-))-isomer
9. Oxis
1. (r,r)-formoterol
2. Formoterol
3. 67346-49-0
4. (-)-formoterol
5. Oxis
6. 73573-87-2
7. Arformoterol [inn]
8. N-[2-hydroxy-5-[(1r)-1-hydroxy-2-[[(2r)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)propan-2-yl]amino]ethyl]phenyl]formamide
9. Eformoterol
10. Atimos
11. Arformoterol (inn)
12. Foradil
13. 5zz84gcw8b
14. Chembl1363
15. F91h02ebwt
16. Chebi:408174
17. N-{2-hydroxy-5-[(1r)-1-hydroxy-2-{[(2r)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)propan-2-yl]amino}ethyl]phenyl}formamide
18. Formoterolum [inn-latin]
19. Formoterol Fumarate
20. Formoterolum
21. Innovair
22. Fluir
23. Racemic Formoterol
24. (+-)-formoterol
25. Formoterol [inn]
26. 1254575-18-2
27. Ym-08316
28. Unii-5zz84gcw8b
29. Unii-f91h02ebwt
30. Formoterol [usan:inn:ban]
31. Hsdb 7287
32. H98
33. Formoterol R,r-form
34. Formoterol [mi]
35. Formoterol [hsdb]
36. Formoterol [vandf]
37. Schembl4247
38. Arformoterol [vandf]
39. Formoterol [who-dd]
40. Arformoterol [who-dd]
41. Gtpl7479
42. Cid_9912089
43. Hy-b0010a
44. Dtxsid40110071
45. Formoterol R,r-form [mi]
46. Zinc2599970
47. Bdbm50151720
48. Akos015969668
49. Cs-1413
50. Db01274
51. N-{2-hydroxy-5-[(1r)-1-hydroxy-2-({(1r)-1-methyl-2-[4-(methyloxy)phenyl]ethyl}amino)ethyl]phenyl}formamide
52. (-)-formoterol;arformoterol;(r,r)-formoterol
53. 73f872
54. D07463
55. D87655
56. Q4789167
57. (+-)-2'-hydroxy-5'-((rs)-1-hydroxy-2-(((rs)-p-methoxy-alpha-methylphenethyl)amino)ethyl)formanilide
58. (-)-n-(2-hydroxy-5-((1r)-1-hydroxy-2-(((1r)-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-methylethyl)amino)ethyl)phenyl)formamide Hydrogen (2r,3r)-2,3-dihydroxybutanedioate
59. Formamide, N-(2-hydroxy-5-((1r)-1-hydroxy-2-(((1r)-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-methylethyl)amino)ethyl)phenyl)-
60. Formamide, N-(2-hydroxy-5-(1-hydroxy-2-((2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-methylethyl)amino)ethyl)phenyl)-
61. Formamide, N-(2-hydroxy-5-(1-hydroxy-2-((2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-methylethyl)amino)ethyl)phenyl)-, (r-(r*,r*))-
62. N-(2-hydroxy-5-((r)-1-hydroxy-2-((r)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)propan-2-ylamino)ethyl)phenyl)formamide
63. N-(2-hydroxy-5-{1-hydroxy-2-[2-(4-methoxy-phenyl)-1-methyl-ethylamino]-ethyl}-phenyl)-formamide
| Molecular Weight | 344.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C19H24N2O4 |
| XLogP3 | 1.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 8 |
| Exact Mass | 344.17360725 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 344.17360725 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 90.8 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 25 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 388 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Antiasthmatic
O'Neil, M.J. (ed.). The Merck Index - An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals. 13th Edition, Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck and Co., Inc., 2001., p. 753
Formoterol is indicated to treat asthma concomitantly with short-acting beta2-agonists, inhaled or systemic corticosteroids and theophylline therapy. /Included in US product labeling/
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 1432
Formoterol is indicated for long-term maintenance treatment of asthma in adult and children 5 years of age and older with reversible obstructive airway disease, including patients with symptoms of nocturnal asthma. /Included in US product labeling/
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 1432
Formoterol is indicated as long-term, twice-daily administration in the treatment of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease including chronic bronchitis and emphysema. /Included in US product labeling/
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 1432
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for FORMOTEROL (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
FDA Pregnancy Risk Category: C /RISK CANNOT BE RULED OUT. Adequate, well controlled human studies are lacking, and animal studies have shown risk to the fetus or are lacking as well. There is a chance of fetal harm if the drug is given during pregnancy; but the potential benefits may outweigh the potential risk./
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 1433
Anaphylactic reactions, urticaria, angioedema, rash, and bronchospasm have been reported rarely with formoterol oral inhalation therapy.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2004. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2004 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1258
Formoterol oral inhalation powder should not be initiated in patients with substantially worsening or acutely deteriorating asthma, which may be a life-threatening condition. Failure to respond to a previously effective dosage of formoterol may indicated substantially worsening asthma that requires reevaluation. If inadequate control of symptoms persists with supplemental beta2-agonist bronchodilator therapy (i.e., if there is a need to increase the dose or frequency of administration of the short-acting, inhaled bronchodilator), prompt reevaluation of asthma therapy is required, with special consideration given to the possible need for anti-inflammatory treatment (e.g., corticosteroids); however, extra/increased doses of formoterol should not be used in such situations.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2004. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2004 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1257
Although uncommon at recommended dosages, clinically important changes in systolic and/or diastolic blood pressure, heart rate, and ECG (e.g. flattening of the T wave, prolongation of the QTc interval, ST-segment depression) have been associated with formoterol oral inhalation therapy and may necessitate discontinuance of the drug. Cardiovascular effects generally have resolved within a few hours. Like other sympathomimetic amines, formoterol should be used with caution in patients with cardiovascular disorders, especially coronary insufficiency, cardiac arrhythmias, or hypertension; in patient s withe seizure disorders or thyrotoxicosis; and in those who are unusually responsive to sympathomimetic amines.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2004. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2004 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1258
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for FORMOTEROL (19 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
A bronchodilator used for the long term, symptomatic treatment of reversible bronchoconstriction in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), including chronic bronchitis and emphysema.
Arformoterol, the active (R,R)-enantiomer of formoterol, is a selective long-acting 2-adrenergic receptor agonist (beta2-agonist) that has two-fold greater potency than racemic formoterol (which contains both the (S,S) and (R,R)-enantiomers). The (S,S)-enantiomer is about 1,000-fold less potent as a 2-agonist than the (R,R)-enantiomer. Arformoterol seems to have little or no effect on 1-adrenergic receptors.
Adrenergic beta-2 Receptor Agonists
Compounds bind to and activate ADRENERGIC BETA-2 RECEPTORS. (See all compounds classified as Adrenergic beta-2 Receptor Agonists.)
Bronchodilator Agents
Agents that cause an increase in the expansion of a bronchus or bronchial tubes. (See all compounds classified as Bronchodilator Agents.)
R03AC13
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
R - Respiratory system
R03 - Drugs for obstructive airway diseases
R03A - Adrenergics, inhalants
R03AC - Selective beta-2-adrenoreceptor agonists
R03AC13 - Formoterol
R - Respiratory system
R03 - Drugs for obstructive airway diseases
R03C - Adrenergics for systemic use
R03CC - Selective beta-2-adrenoreceptor agonists
R03CC15 - Formoterol
Route of Elimination
After administration of a single oral dose of radiolabeled arformoterol to eight healthy male subjects, 63% of the total radioactive dose was recovered in urine and 11% in feces within 48 hours. Direct glucuronidation of arformoterol is mediated by several UGT enzymes and is the primary elimination route.
Clearance
renal cl=8.9 L/hr [Healthy male subjects]
Protein binding: Moderate 61-64%. Serum albumin binding was 31% to 38% over a range of 5 to 500 ng/mL.
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 1433
Bioavailability: Pulmonary: 21-37%; Total systemic: 46%.
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 1432
It is not known whether formoterol is distributed in human breast milk. However, it is distributed in rat milk after oral administration.
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 1433
In asthma patients following a 12 or 24 ug dose: 10% and 15 to 18% excreted unchanged in the urine, respectively. In chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) patients following a 12 or 24 ug dose: 7% and 6 to 9% excreted unchanged in the urine; respectively.
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 1433
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for FORMOTEROL (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Arformoterol was almost entirely metabolized following oral administration of 35 mcg of radiolabeled arformoterol in eight healthy subjects. Direct conjugation of arformoterol with glucuronic acid was the major metabolic pathway. O-Desmethylation is a secondary route catalyzed by the CYP enzymes CYP2D6 and CYP2C19.
Formoterol is metabolized primarily by direct glucuronidation at either the phenolic or aliphatic hydroxyl group and O-demethylation followed by glucuronide conjugation at either phenolic hydroxyl groups. Minor pathways involve sulfate conjugation of formoterol and deformylation followed by sulfate conjugation. The most prominent pathway involves direct conjugation at the phenolic hydroxyl group. The second major pathway involves O-demethylation followed by conjugation at the phenolic 2'-hydroxyl group. Four cytochrome P450 isozymes (CYP2D6, CYP2C19, CYP2C9 and CYP2A6) are involved in the O-demethylation of formoterol. Formoterol did not inhibit CYP450 enzymes at therapeutically relevant concentrations. Some patients may be deficient in CYP2D6 or 2C19 or both. Whether a deficiency in one or both of these isozymes results in elevated systemic exposure to formoterol or systemic adverse effects has not been adequately explored.
PDR; Physicians' Desk Reference 57th ed 2003. Montvale,NJ: Medical Economics Co. p. 2275 (2003)
Formoterol was conjugated to inactive glucuronides and a previously unidentified sulfate. The phenol glucuronide of formoterol was the main metabolite in urine. Formoterol was also O-demethylated and deformylated. Plasma exposure to these pharmacologically active metabolites was low. O-demethylated formoterol was seen mainly as inactive glucuronide conjugates and deformylated formoterol only as an inactive sulfate conjugate. Intact formoterol and O-demethylated formoterol dominated recovery in feces. Mean recovery of unidentified metabolites was 7. 0% in urine and 2.0% in feces.
PMID:10497135 Rosenborg J et al; Drug Metab Dispos 27 (10): 1104-16 (1999)
In COPD patients given 15 mcg inhaled arformoterol twice a day for 14 days, the mean terminal half-life of arformoterol was 26 hours.
Mean terminal: 10 hours
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 1432
While it is recognized that 2-receptors are the predominant adrenergic receptors in bronchial smooth muscle and 1-receptors are the predominant receptors in the heart, data indicate that there are also 2-receptors in the human heart comprising 10% to 50% of the total beta-adrenergic receptors. The precise function of these receptors has not been established, but they raise the possibility that even highly selective 2-agonists may have cardiac effects. The pharmacologic effects of 2-adrenoceptor agonist drugs, including arformoterol, are at least in part attributable to stimulation of intracellular adenyl cyclase, the enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to cyclic-3′,5′-adenosine monophosphate (cyclic AMP). Increased intracellular cyclic AMP levels cause relaxation of bronchial smooth muscle and inhibition of release of proinflammatory mediators from cells, especially from mast cells. In vitro tests show that arformoterol is an inhibitor of the release of mast cell mediators, such as histamine and leukotrienes, from the human lung. Arformoterol also inhibits histamine-induced plasma albumin extravasation in anesthetized guinea pigs and inhibits allergen-induced eosinophil influx in dogs with airway hyper-response.
Formoterol is a long-acting selective stimulator of the beta2-adrenergic receptors in bronchial smooth muscle. This stimulation causes relaxation of smooth muscle fibers and produces bronchodilation.
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 1432
Formoterol stimulates beta2-adrenergic receptors and apparently has little or no effect on beta1- or alpha-adrenergic receptors. The drug's beta-adrenergic effects appear to result from stimulation of the production of cyclic adeno-3'-5'-monophosphate (cAMP)by activation of adenyl cyclase. Cyclic AMP mediate numerous cellular responses, increased concentrations of cAMP are associated with relaxation of bronchial smooth muscle and suppression of some aspects of inflammation, such as inhibition of release proinflammatory mast cell mediators(eg histamine, leukotrienes).
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2004. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2004 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1258