

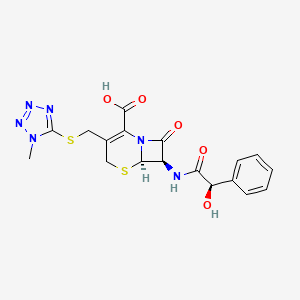

1. Cephamandole
2. Compound 83405
1. Cefadole
2. 34444-01-4
3. Cephamandole
4. Cefamandol
5. Cephadole
6. Cefamandolum
7. L-cefamandole
8. Compound 83405
9. Chebi:3480
10. (6r,7r)-7-(r)-mandelamido-3-(((1-methyl-1h-tetrazol-5-yl)thio)methyl)-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo(4.2.0)oct-2-ene-carboxylic Acid
11. 5ckp8c2lli
12. (6r,7r)-7-{[(2r)-2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetyl]amino}-3-{[(1-methyl-1h-tetrazol-5-yl)sulfanyl]methyl}-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
13. Compound-83405
14. (6r,7r)-7-[[(2r)-2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetyl]amino]-3-[(1-methyltetrazol-5-yl)sulfanylmethyl]-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
15. J01dc03
16. Kefdole
17. 7-d-mandelamido-3-(((1-methyl-1h-tetrazol-5-yl)thio)methyl)-3-cephem-4-carboxylic Acid
18. Kefamandol
19. Mancef
20. (6r,7r)-7-((r)-2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetamido)-3-(((1-methyl-1h-tetrazol-5-yl)thio)methyl)-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
21. 7-[(2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetyl)amino]-3-[(1-methyltetrazol-5-yl)sulfanylmethyl]-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
22. 30034-03-8
23. Unii-5ckp8c2lli
24. Cefamandol [inn-spanish]
25. Cefamandole (usan/inn)
26. Cefamandolum [inn-latin]
27. Free Form
28. Cefamandole [usan:inn:ban]
29. Einecs 252-030-0
30. Brn 0598510
31. Cefamandole [mi]
32. Prestwick0_000747
33. Prestwick1_000747
34. Prestwick2_000747
35. Prestwick3_000747
36. Cefamandole [inn]
37. Cefamandole [usan]
38. Epitope Id:141490
39. Cefamandole [vandf]
40. Cefamandole [mart.]
41. Chembl1146
42. Schembl37287
43. Bspbio_000734
44. Cefamandole [who-dd]
45. Spbio_002673
46. Bpbio1_000808
47. Dtxsid7022750
48. Gtpl12210
49. Hy-b1128
50. Zinc3830394
51. Bdbm50350468
52. Akos025401365
53. Ac-1294
54. Cs-4724
55. Db01326
56. (6r,7r)-7-[[(2r)-2-hydroxy-2-phenyl-acetyl]amino]-3-[(1-methyltetrazol-5-yl)sulfanylmethyl]-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
57. (6r,7r)-7-{[(2r)-2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetyl]amino}-3-{[(1-methyl-1h-tetrazol-5-yl)thio]methyl}-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
58. 5-thia-1-azabicyclo(4.2.0)oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid, 7-((hydroxyphenylacetyl)amino)-3-(((1-methyl-1h-tetrazol-5-yl)thio)methyl)-8-oxo-, (6r-(6alpha,7beta(r*)))-
59. 7beta-[(2r)-2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetamido]-3-{[(1-methyl-1h-tetrazol-5-yl)sulfanyl]methyl}ceph-3-em-4-carboxylic Acid
60. C06879
61. D02344
62. 444c014
63. Cefamandole, Antibiotic For Culture Media Use Only
64. Q2601530
65. W-106736
66. Brd-k27130738-236-03-4
67. (6r,7r)-7-((r)-2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetamido)-3-((1-methyl-1h-tetrazol-5-ylthio)methyl)-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
68. (6r,7r)-7-[(2r)-2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetamido]-3-{[(1-methyl-1h-1,2,3,4-tetrazol-5-yl)sulfanyl]methyl}-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
69. 5-thia-1-azabicyclo(4.2.0)oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid, 7-((hydroxyphenylacetyl)amino)-3-(((1-methyl-1h-tetrazol-5-yl)thio)methyl)-8-oxo-, (6r-(6.alpha.,7.beta.(r*)))-
70. 5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid, 7-[[(2r)-2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetyl]amino]-3-[[(1-methyl-1h-tetrazol-5-yl)thio]methyl]-8-oxo-, (6r,7r)-
71. 5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid, 7-[[(2r)-2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetyl]amino]-3-[[(1-methyl-1h-tetrazol-5-yl)thio]methyl]-8-oxo-, 6r,7r)-
| Molecular Weight | 462.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C18H18N6O5S2 |
| XLogP3 | -0.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 10 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 462.07801004 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 462.07801004 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 201 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 31 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 777 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 3 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
For the treatment of serious infections caused by susceptible strains of microorganisms.
The parenteral prodrug formate ester cefamandole nafate is a broad-spectrum cephalosporin antibiotic. The bactericidal action of cefamandole results from inhibition of cell-wall synthesis. Cephalosporins have in vitro activity against a wide range of gram-positive and gram-negative organisms.
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Substances that inhibit the growth or reproduction of BACTERIA. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Bacterial Agents.)
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J01 - Antibacterials for systemic use
J01D - Other beta-lactam antibacterials
J01DC - Second-generation cephalosporins
J01DC03 - Cefamandole
The half-life after an intravenous dose is 32 minutes; after intramuscular administration, the half-life is 60 minutes.
Like all beta-lactam antibiotics, cefamandole binds to specific penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) located inside the bacterial cell wall, causing the inhibition of the third and last stage of bacterial cell wall synthesis. Cell lysis is then mediated by bacterial cell wall autolytic enzymes such as autolysins; it is possible that cefamandole interferes with an autolysin inhibitor.
