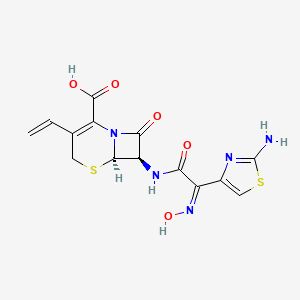

1. 7-(2 (2-aminothiazol-4-yl)-2-hydroxyiminoacetamido)-3-vinyl-3-cephem-4-carboxylic Acid
2. Ci 983
3. Ci-983
4. Ci983
5. Fk 482
6. Fk-482
7. Fk482
8. Omnicef
9. Pd 134393
10. Pd-134393
1. Omnicef
2. 91832-40-5
3. Cefzon
4. Cfdn
5. Cefdinirum
6. Ci-983
7. Fk-482
8. Fk 482
9. Cefdinir Anhydrous
10. Bmy-28488
11. Cefdinir (omnicef)
12. Chebi:3485
13. Cefdinyl
14. Ci0fao63wc
15. (6r,7r)-7-[[(2z)-2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-hydroxyiminoacetyl]amino]-3-ethenyl-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
16. Nsc-758926
17. Cefdinir 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
18. Pd 134393
19. Cefdirnir
20. Cefdinirum [inn-latin]
21. (6r,7r)-7-((z)-2-(2-aminothiazol-4-yl)-2-(hydroxyimino)acetamido)-8-oxo-3-vinyl-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
22. (6r,7r)-7-[(2z)-2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-(n-hydroxyimino)acetamido]-3-ethenyl-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
23. Ceftinex
24. (e)-cefdinir
25. Bmy 28488
26. Ci 983
27. (6r,7r)-7-{2-(2-amino-thiazol-4-yl)-2-[(z)-hydroxyimino]-acetylamino}-8-oxo-3-vinyl-5-thia-1-aza-bicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
28. (6r,7r,z)-7-(2-(2-aminothiazol-4-yl)-2-(hydroxyimino)acetamido)-8-oxo-3-vinyl-5-thia-1-aza-bicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
29. Omnicef (tn)
30. Cefzon (tn)
31. Pd-134393
32. Sr-05000001991
33. Unii-ci0fao63wc
34. Cefdinir [usan:usp:inn:ban]
35. Ci983
36. Fk482
37. Cefdinir, 97%
38. (-)-(6r,7r)-7-(2-(2-amino-4-thiazolyl)glyoxylamido)-8-oxo-3-vinyl-5-thia-1-azabicyclo(4.2.0)oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid, 7(sup 2)-(z)-oxime
39. Fr-80482
40. Cefdinir [usan]
41. Cefdinir [inn]
42. Cefdinir [jan]
43. Cefdinir [mi]
44. Cefdinir [vandf]
45. Spectrum5_001560
46. Cefdinir [mart.]
47. Cefdinir [usp-rs]
48. Cefdinir [who-dd]
49. Chembl927
50. Schembl36995
51. Bspbio_002735
52. Mls001304703
53. Mls001424233
54. Bidd:gt0827
55. Spectrum1505208
56. Cefdinir (jp17/usp/inn)
57. Cefdinir [orange Book]
58. Cefdinir [usp Monograph]
59. Dtxsid8046084
60. Cid_6915944
61. Bcpp000293
62. Hms1922l19
63. Hms2093k20
64. Hms3715f07
65. Pharmakon1600-01505208
66. Amy22139
67. Hy-b0136
68. Bdbm50248190
69. Ccg-39455
70. Mfcd00865030
71. Nsc758926
72. S1605
73. Zinc13119676
74. Akos015951262
75. Akos032960348
76. Bcp9000503
77. Cs-1925
78. Db00535
79. Nsc 758926
80. Ncgc00178499-01
81. Ncgc00178499-02
82. Ncgc00178499-08
83. (6r,7r)-7-{[(2z)-2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-(hydroxyimino)acetyl]amino}-3-ethenyl-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
84. 5-thia-1-azabicyclo(4.2.0)oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid, 7-(((2-amino-4-thiazolyl) (hydroxyimino)acetyl)amino)-3-ethenyl-8-oxo-, (6r-(6alpha,7beta(z)))-
85. 5-thia-1-azabicyclo(4.2.0)oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid, 7-(((2-amino-4-thiazolyl)(hydroxyiminoacetyl)amino)-3-ethenyl-8-oxo-, (6r-(6-alpha,7-beta(z)))-
86. 5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid,7-[[(2z)-(2-amino-4-thiazolyl)(hydroxyimino)acetyl]amino]-3-ethenyl-8-oxo-, (6r,7r)-
87. 7beta-[(2z)-2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-(hydroxyimino)acetamido]-3-ethenyl-3,4-didehydrocepham-4-carboxylic Acid
88. As-35316
89. Pd134393
90. Sbi-0206739.p001
91. C-2466
92. C08110
93. D00917
94. Ab01274720-01
95. Ab01274720_02
96. Ab01274720_03
97. Cefdinir, Antibiotic For Culture Media Use Only
98. 832c405
99. A844075
100. Sr-05000001991-1
101. Sr-05000001991-2
102. Brd-k15766189-001-05-6
103. Q27263344
104. (-)-(6r,7r)-7-(2-(2-amino-4-thiazolyl)glyoxylamido)-8-oxo-3-vinyl-5-thia-1-azabicyclo(4.2.0)oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid, 72-(z)-oxime
105. (6r,7r)-7-(((2z)-(2-amino-4-thiazolyl)(hydroxyimino)acetyl)amino)-3-ethenyl-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo(4.2.0)oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
106. (6r,7r)-7-[[(2z)-2-(2-aminothiazol-4-yl)-2-hydroxyimino-acetyl]amino]-8-oxo-3-vinyl-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid;cefdinir
107. (7r)-3-vinyl-7-[[(2-amino-4-thiazolyl)[(e)-hydroxyimino]acetyl]amino]cepham-3-ene-4-carboxylic Acid
108. 5-thia-1-azabicyclo(4.2.0)oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid, 7-(((2-amino-4-thiazolyl) (hydroxyimino)acetyl)amino)-3-ethenyl-8-oxo-, (6r-(6.alpha.,7.beta.(z)))-
109. 5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid, 7-[[(2z)-2-(2-amino-4-thiazolyl)-2-(hydroxyimino)acetyl]amino]-3-ethenyl-8-oxo-, (6r,7r)-
110. Syn-7-(2-(2-amino-4-thiazolyl)-2-hydroxyiminoacetamido)-3-vinyl-3-cephem-4-carboxylic Acid
| Molecular Weight | 395.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C14H13N5O5S2 |
| XLogP3 | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 10 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 395.03581088 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 395.03581088 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 212 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 26 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 739 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Cefdinir |
| PubMed Health | Cefdinir (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antibiotic |
| Drug Label | Cefdinir for oral suspension, USPcontains the active ingredient cefdinir USP, an extended-spectrum, semisynthetic cephalosporin, for oral administration. Chemically, cefdinir is [6R-[6,7 (Z)]]-7-[[(2-amino-4-thiazolyl)(hydroxyimino)acetyl]amino... |
| Active Ingredient | Cefdinir |
| Dosage Form | Capsule; For suspension |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 300mg; 125mg/5ml; 250mg/5ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Teva Pharms; Aurobindo Pharma; Lupin; Sandoz; Orchid Hlthcare |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Cefdinir |
| PubMed Health | Cefdinir (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antibiotic |
| Drug Label | Cefdinir for oral suspension, USPcontains the active ingredient cefdinir USP, an extended-spectrum, semisynthetic cephalosporin, for oral administration. Chemically, cefdinir is [6R-[6,7 (Z)]]-7-[[(2-amino-4-thiazolyl)(hydroxyimino)acetyl]amino... |
| Active Ingredient | Cefdinir |
| Dosage Form | Capsule; For suspension |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 300mg; 125mg/5ml; 250mg/5ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Teva Pharms; Aurobindo Pharma; Lupin; Sandoz; Orchid Hlthcare |
Cefdinir is indicated to treat acute bacterial otitis media, acute maxillary sinusitis, community-acquired (CA) pneumonia, acute bacterial exacerbations of chronic bronchitis, pharyngitis/tonsillitis, and uncomplicated skin and skin structure infections in children and adults. The organisms susceptible to cefdinir have been listed below in addition to their associated clinical condition that may be treated with cefdinir. Various beta-lactamase producing organisms may be treated, as indicated in certain sections below. **Respiratory** Acute bacterial exacerbations of chronic bronchitis caused by Haemophilus influenzae, Haemophilus parainfluenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae (penicillin-susceptible only), and Moraxella catarrhalis Community-acquired pneumonia caused by Haemophilus influenzae, Haemophilus parainfluenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae (penicillin-susceptible only), and Moraxella catarrhalis **Ear, nose, and throat** Acute bacterial otitis media caused by Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, and Streptococcus pneumoniae (penicillin-susceptible only) Tonsillitis caused by Streptococcus pyogenes Pharyngitis caused by Streptococcus pyogenes Acute maxillary sinusitis caused by Haemophilus pneumoniae and Streptococcus pneumoniae (penicillin-susceptible only), and Moraxella catarrhalis **Skin and skin structure infections** Uncomplicated skin and skin structure infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes
Cefdinir is a bactericidal agent that treats bacterial infections by interfering with cell wall synthesis. Cefdinir exerts broad-spectrum activity against a variety of gram-positive and gram-negative bacterial infections. It is effective against several beta-lactamase enzyme producing bacteria. As a result, many organisms that are resistant to other cephalosporins may be susceptible to cefdinir.
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Substances that inhibit the growth or reproduction of BACTERIA. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Bacterial Agents.)
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J01 - Antibacterials for systemic use
J01D - Other beta-lactam antibacterials
J01DD - Third-generation cephalosporins
J01DD15 - Cefdinir
Absorption
Maximal plasma cefdinir concentration can be attained between 2-4 hours after an ingested dose. The bioavailability of cefdinir depends on the formulation used. The estimated bioavailability of cefdinir in the capsule form is approximately 16%-21%, depending on the dose. Absolute bioavailability after the administration of a suspension of cefdinir is 25%.. The Cmax of cefdinir is 1.60 g/mL after a 300 mg dose with an AUC of 7.05. Cmax is 2.87 g/mL after a 600 mg dose with an AUC of 11. A meal high in fat can reduce the absorption of cefdinir by up to 15%, however, this is not a cause for clinically significant changes, therefore cefdinir may be taken with or without food. When given with aluminum or magnesium-containing antacids or iron, cefdinir absorption may decrease. It is recommended to allow 2 hours between cefdinir administration and the administration of these agents.
Route of Elimination
This drug is mainly excreted by the kidneys. Dose adjustments may be required for patients with renal impairment or patients on dialysis. Approximately 18.4% of a 300 mg dose of cefdinir was found unchanged in the urine after a 300 mg dose was administered during a pharmacokinetic study of 21 individuals. A large proportion of the administered dose is excreted in the feces, although the majority is found in the urine.
Volume of Distribution
The average volume of distribution of cefdinir in adults is about 0.35 L/kg and 0.67 L/kg in children. Another resource estimates the volume of distribution in adults at 1.562.09 L/kg. Cefdinir is found to be distributed in various tissues at clinically effective concentrations. It may be found in the epithelial lining fluid, bronchial mucosa, tonsils, sinuses, skin blister fluid, as well as the middle ear fluid. Third-generation cephalosporins such as cefdinir cross the blood-brain barrier and are found in high concentrations in the cerebrospinal fluid, unlike their first and second generation counterparts. The wide tissue distribution of cefdinir allows it to treat a variety of infections throughout the body.
Clearance
The renal clearance in healthy adults in a pharmacokinetic study was 2.0 ( 1.0) mL/min/kg and the clearance in patients with renal failure was lower, decreasing in proportion to the degree of renal impairment. Dose adjustment is required in patients with renal impairment.
This drug is not significantly metabolized and its pharmacological actions are mainly attributed to the parent drug.
The average plasma elimination half-life is about 1.7 hours in adults. In children and healthy infants, plasma elimination half-life ranges from 1.21.5 hours.
Five-member thiazolidine rings that make up penicillins are replaced in cephalosporins by a six-member dihydrothiazine ring, conferring greater bactericidal activity. This This 6-member ring enables cefdinir and other cephalosporins to resist inactivation by certain bacterial enzymes. With a mechanism similar to other beta-lactam antibiotics, the bactericidal activity of cefdinir is caused by the inhibition of cell wall synthesis via binding to penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs). Cefdinir, like other cephalosporins, penetrates the bacterial cell wall, combats inactivation by beta-lactamase enzymes, and inactivates penicillin-binding proteins. This interferes with the final step of transpeptidation in cell walls, eventually leading to cell lysis, which eventually leads to the death of bacteria that are susceptible to this drug. Cefdinir has shown affinity to penicillin protein binding proteins 2 and 3. It has also been shown to inhibit transpeptidase enzymes of various bacteria, which may play a role in its bactericidal action. One in vitro study suggests that cefdinir inhibits myeloperoxidase release extracellularly. The impact of this potential drug target in relation to its mechanism of action is unknown.