
1. Cefalotin
2. Cefalotina Normon
3. Cefalotina Sodica Spaly
4. Ceftina
5. Cephalothin Monosodium Salt
6. Cephalothin, Sodium
7. Keflin
8. Monosodium Salt, Cephalothin
9. Salt, Cephalothin Monosodium
10. Seffin
11. Sodium Cephalothin
1. Cefalotin
2. 153-61-7
3. Cephalotin
4. Cefalothin
5. Cephalothinum
6. Cefalotina
7. Cefalotine
8. Cefalotinum
9. (6r,7r)-3-(acetoxymethyl)-8-oxo-7-(2-(thiophen-2-yl)acetamido)-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
10. Cemastin
11. 7-(2-thienylacetamido)cephalosporanic Acid
12. Coaxin
13. Keflin
14. Cefalotine [inn-french]
15. Cefalotinum [inn-latin]
16. Cefalotina [inn-spanish]
17. Averon-1
18. Cephalotin Acid
19. 7-(thiophene-2-acetamido)cephalosporin
20. (6r,7r)-3-(acetyloxymethyl)-8-oxo-7-[(2-thiophen-2-ylacetyl)amino]-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
21. 3-acetoxymethyl-7-(2-thienylacetamido)-3-cephem-4-carboxylic Acid
22. Cefalotin [inn]
23. (6r,7r)-3-[(acetyloxy)methyl]-8-oxo-7-[2-(thiophen-2-yl)acetamido]-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
24. Chebi:124991
25. Mls001048966
26. 7-(2'-thienylacetamido)cephalosporanic Acid
27. R72lw146e6
28. 5-thia-1-azabicyclo(4.2.0)oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid, 3-((acetyloxy)methyl)-8-oxo-7-((2-thienylacetyl)amino)-, (6r-trans)-
29. Ncgc00159332-02
30. Smr000386987
31. Dsstox_cid_2783
32. Dsstox_rid_76728
33. Dsstox_gsid_22783
34. Cefalotin (ban)
35. 7-(thiophene-2-acetamido)cephalosporanic Acid
36. (6r,7r)-3-(acetoxymethyl)-8-oxo-7-[[2-(2-thienyl)acetyl]amino]-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
37. Cas-153-61-7
38. 7-(2-(2-thienyl)acetylamido)cephalosporanic Acid
39. Hsdb 3024
40. Cefalotina Fabra (tn)
41. 58-71-9
42. Einecs 205-815-7
43. Brn 0945586
44. Unii-r72lw146e6
45. 6r-trans-3-((acetyloxy)methyl)-8-oxo-7-((2-thienylacetyl)amino)-5-thia-1-azabicyclo(4.2.0)-oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
46. 4kox
47. 5-thia-1-azabicyclo(4.2.0)oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid, 3-((acetyloxy)methyl)-8-oxo-7-((2-thienylacetyl)amino)-, (6r,7r)-
48. 5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid, 3-[(acetyloxy)methyl]-8-oxo-7-[(2-thienylacetyl)amino]-, (6r,7r)-
49. (+-)-cephalothin
50. 3-(acetoxymethyl)-8-oxo-7-(2-(2-thienyl)acetamido)-5-thia-1-azabicyclo(4.2.0)oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
51. 3-(hydroxymethyl)-8-oxo-7-(2-(2-thienyl)acetamido)-5-thia-1-azabicyclo(4.2.0)oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid Acetate
52. Spectrum_000110
53. Cephalothin [mi]
54. Prestwick0_000719
55. Prestwick1_000719
56. Prestwick2_000719
57. Prestwick3_000719
58. Spectrum2_000121
59. Spectrum3_000332
60. Spectrum4_000269
61. Spectrum5_000669
62. Cephalothin [hsdb]
63. Chembl617
64. Epitope Id:116207
65. Cephalothin [vandf]
66. Cefalotin [who-dd]
67. Cid_6024
68. Schembl2990
69. Lopac0_000283
70. Bspbio_000937
71. Bspbio_001963
72. Kbiogr_000738
73. Kbioss_000550
74. 3-acetoxymethyl-8-oxo-7-(2-thiophen-2-yl-acetylamino)-5-thia-1-aza-bicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
75. 5-thia-1-azabicyclo(4.2.0)oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid, 3-(hydroxymethyl)-8-oxo-7-(2-(2-thienyl)acetamido)-, Acetate (ester)
76. Divk1c_000097
77. Spbio_000162
78. Spbio_002858
79. Bpbio1_001031
80. Gtpl8798
81. Cephalothin [green Book]
82. Dtxsid4022783
83. Schembl20477170
84. Bdbm82898
85. Hy-b1275a
86. Kbio1_000097
87. Kbio2_000550
88. Kbio2_003118
89. Kbio2_005686
90. Kbio3_001183
91. Ninds_000097
92. Hms2267p23
93. Zinc3830507
94. Tox21_111579
95. Mfcd00242614
96. S5294
97. Akos015920120
98. Tox21_111579_1
99. Ccg-268605
100. Cs-w008776
101. Db00456
102. Gs-3577
103. Sdccgsbi-0050271.p005
104. 7beta-(thiophen-2-ylacetamido)-3-acetoxymethyl-3,4-didehydrocepham-4-carboxylic Acid
105. Idi1_000097
106. Ncgc00023699-09
107. (6r,7r)-3-(acetoxymethyl)-8-oxo-7-(2-(thiophen-2-yl)acetamido)-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylicacid
108. (6r,7r)-3-[(acetyloxy)methyl]-8-oxo-7-[(2-thienylacetyl)amino]-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
109. Sbi-0050271.p004
110. 7-(2-thienylacetamido) Cephalosporanic Acid
111. 7-(2-thienylacetamido)-cephalosporanic Acid
112. C-2484
113. C07761
114. D07635
115. 153c617
116. A809447
117. Cephalothin, Antibiotic For Culture Media Use Only
118. Sr-01000003118
119. Q2736126
120. Sr-01000003118-3
121. Brd-k28210218-236-05-7
122. Z1741977144
123. Cephalothin 7-(2-thienylacetamido)cephalosporanic Acid
124. 3-acetoxymethyl-7beta-(2-thienylacetamido) Ceph-3-em-4-carboxylic Acid
125. 3-acetoxymethyl-7beta-(2-thienylacetamido)-3-cephem-4-carboxylic Acid
126. 3-acetoxymethyl-7beta-(2-thienylacetamido)ceph-3-em-4-carboxylic Acid
127. (6r,7r)-3-(acetoxymethyl)-8-keto-7-[[2-(2-thienyl)acetyl]amino]-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
128. (6r,7r)-3-(acetoxymethyl)-8-oxo-7-(2-(thiophen-2-yl)acetamido)-5-thia-1-aza-bicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
129. (6r,7r)-3-(acetyloxymethyl)-8-oxidanylidene-7-(2-thiophen-2-ylethanoylamino)-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
130. (6r,7r)-3-(acetyloxymethyl)-8-oxo-7-[(1-oxo-2-thiophen-2-ylethyl)amino]-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
131. (6r,7r)-3-[(acetyloxy)methyl]-8-oxo-7-[(thiophen-2-ylacetyl)amino]-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
132. 51098-29-4
| Molecular Weight | 396.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C16H16N2O6S2 |
| XLogP3 | -0.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 396.04497858 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 396.04497858 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 167 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 26 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 680 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Since, among the cephalosporins, cephalothin is the most impervious to attack by Staphylococcal beta-lactamase, it is very effective in severe Staphylococcal infections, such as endocarditis.
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B., A.G. Gilman. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2001., p. 1210
Mesh Heading: anti-bacterial agents
National Library of Medicine, SIS; ChemIDplus Record for Cephalothin (153-61-7). Available from, as of April 13, 2006: https://chem.sis.nlm.nih.gov/chemidplus/chemidlite.jsp
Use should be restricted to treatment of serious infections caused by susceptible organisms, most commonly when patient is hypersensitive to penicillins. /Sodium/
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs, AMA Drug Evaluations. 3rd ed. Littleton, Massachusetts: PSG Publishing Co., Inc., 1977., p. 715
... Cephalosporin is ... drug of first choice ... for Klebsiella infections ... They are useful as alternative choices to penicillin. /Cephalosporins/
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B. Molinoff, R.W. Ruddon, A.G. Goodman (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 9th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 1996., p. 1096
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for CEPHALOTHIN (28 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Excretion is delayed in presence of decr renal function, and intervals between doses must be lengthened when renal failure is severe.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1160
Cephalothin should not be used to treat bacterial meningitis.
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B. Molinoff, R.W. Ruddon, A.G. Goodman (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 9th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 1996., p. 1093
Infections due to Enterococci are usually unaffected by these cmpd ... Enterococcal endocarditis cannot be cured with cephalosporin even when it is given concurrently with gentamicin or streptomycin. /Cephalosporins/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1163
Patients with a history of a mild or a temporally distant reaction to penicillin appear to be at low risk of rash or other allergic reaction following the admin of a cephalosporin ... Patients who have had a recent severe, immediate reaction to a penicillin should be given a cephalosporin with great caution, if at all. /Cephalosporin/
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B., A.G. Gilman. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2001., p. 1212
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for CEPHALOTHIN (21 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Used to prevent infection during surgery and to treat many kinds of infections of the blood, bone or joints, respiratory tract, skin, and urinary tract.
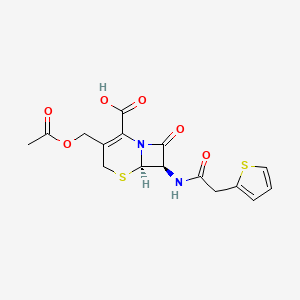
Cefalotin (INN) or cephalothin (USAN) is a semisynthetic first generation cephalosporin having a broad spectrum of antibiotic activity that is administered parenterally.
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Substances that inhibit the growth or reproduction of BACTERIA. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Bacterial Agents.)
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J01 - Antibacterials for systemic use
J01D - Other beta-lactam antibacterials
J01DB - First-generation cephalosporins
J01DB03 - Cefalotin
CEPHALOTHIN ENTERS AQUEOUS HUMOR AFTER SUBCONJUNCTIVAL INJECTIONS YIELDING PEAK LEVELS CA 1-2 HR AFTER DOSING. RATIO OF AQ HUMOR:SERUM ANTIBIOTIC LEVELS RANGES FROM 4.0 TO 67.0 DURING 5 HR AFTER DOSING, & LOSS OF ANTIBIOTIC FROM AQ HUMOR OCCURS BY BIPHASIC PROCESS.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals Volume 3. London: The Chemical Society, 1975., p. 177
...CEPHALOTHIN...WERE SHOWN...TO PENETRATE INTO BONE TO VERY LIMITED EXTENT AFTER SC OR ORAL DOSES TO RATS. RATIOS OF BONE TO SERUM CONCN AVG 1:4 FOR CEPHALOTHIN... DESPITE DIFFERENCES IN CONCN, T/2 IN BONE & SERUM WERE SIMILAR.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals. Volume 2: A Review of the Literature Published Between 1970 and 1971. London: The Chemical Society, 1972., p. 452
DRUGS RECENTLY SHOWN TO ACTIVELY CROSS HUMAN PLACENTA INCL...CEPHALOTHIN...
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals. Volume 2: A Review of the Literature Published Between 1970 and 1971. London: The Chemical Society, 1972., p. 433
Concn of cephalothin present in urine after admin of 1 g range from 0.7 to 5 mg/mL. Excretion is delayed in presence of decr renal function ...
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1160
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for CEPHALOTHIN (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Metabolized to a less active desacetyl metabolite, although 50-75% of the drug is eliminated unchanged in the urine.
Approx 25% of cephalothin dose admin was eliminated in urine as deacetylcephalothin.
PMID:411623 ROLEWICZ TF ET AL; CLIN PHARMACOL THER 22 (DEC): 928-35 (1977)
Cephalothin ... /is/ deacetylated in vivo, and these metabolites have less antimicrobial activity than the parent cmpd ... The deacetylated metabolites also are excreted by the kidneys.
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B., A.G. Gilman. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2001., p. 1210
30 minutes
Half-life = 0.6 hr /by/ injection /From table/
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B., A.G. Gilman. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2001., p. 1206
The bactericidal activity of cefalotin results from the inhibition of cell wall synthesis via affinity for penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs). The PBPs are transpeptidases which are vital in peptidoglycan biosynthesis. Therefore, their inhibition prevents this vital cell wall compenent from being properly synthesized.
Bactericidal; action depends on ability to reach and bind penicillin-binding proteins located in bacterial cytoplasmic membranes. Cephalosporins inhibit bacterial septum and cell wall synthesis, probably by action of membrane-bound transpeptidase enzymes. This prevents cross-linkage of peptidoglycan chains, which is necessary for bacterial cell wall strength and rigidity. Also, cell division and growth are inhibited, and elongation of susceptible bacteria and lysis frequently occur. Rapidly dividing bacteria are those most susceptible to the actin of cephalosporins. /Cephalosporins/
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006., p. 822