


1. 2-(4-benzylpiperidino)-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-methyl-1-ethanol
2. 4-benzyl-alpha-(p-hydroxyphenyl)-beta-methyl-1-piperidineethanol
3. 61 91 Rc
4. Alpha-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-beta-methyl-4-(phenylmethyl)-1-piperidine Ethanol
5. Ifenprodil
6. Ifenprodil Hydrochloride
7. Ifenprodil Hydrochloride, (+-)-isomer
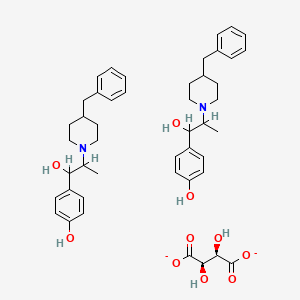
8. Ifenprodil Tartrate
9. Ifenprodil Tartrate (1:1), (r*,s*)-(+-)-(r-(r*,r*))-isomer
10. Ifenprodil Tartrate (1:1), (r-(r*,r*))-isomer
11. Ifenprodil Tartrate (2:1), (r-(r*,r*))-isomer
12. Ifenprodil, (r*,s*)-(+-)-isomer
13. Ifenprodil, Tartrate(r-(r*,r*))-isomer
1. Dilvax
2. Ifenprodil Tartrate
3. Ifenprodil L-(+)-tartrate
4. 66157-43-5
5. Cerocral
6. Validex
7. 4-[2-(4-benzylpiperidin-1-yl)-1-hydroxypropyl]phenol;(2r,3r)-2,3-dihydroxybutanedioate
8. Ifenprodil Tartrate (2:1)
9. Ifenprodil L-(+)-tartrate (2:1)
10. 2-(4-benzyl-piperidino)-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-propanol Tartrate (2:1)
11. 4-benzyl-alpha-(p-hydroxyphenyl)-beta-methyl-1-piperidineethanol Tartrate
12. 4-benzyl-alpha-(p-hydroxyphenyl)-beta-methyl-1-piperidine-ethanol-(l)-(+)-tartrate
13. Piperidineethanol, Alpha-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-beta-methyl-4-(phenylmethyl)-, Tartrate (2:1)
14. 1-piperidineethanol, 4-benzyl-alpha-(p-hydroxyphenyl)-beta-methyl-, Tartrate (salt) (2:1)
| Molecular Weight | 799.0 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C46H58N2O10-2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 12 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 11 |
| Exact Mass | 798.40914605 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 798.40914605 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 208 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 58 |
| Formal Charge | -2 |
| Complexity | 476 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 4 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 3 |
Excitatory Amino Acid Antagonists
Drugs that bind to but do not activate excitatory amino acid receptors, thereby blocking the actions of agonists. (See all compounds classified as Excitatory Amino Acid Antagonists.)
Adrenergic alpha-Antagonists
Drugs that bind to but do not activate alpha-adrenergic receptors thereby blocking the actions of endogenous or exogenous adrenergic agonists. Adrenergic alpha-antagonists are used in the treatment of hypertension, vasospasm, peripheral vascular disease, shock, and pheochromocytoma. (See all compounds classified as Adrenergic alpha-Antagonists.)
Vasodilator Agents
Drugs used to cause dilation of the blood vessels. (See all compounds classified as Vasodilator Agents.)