


1. Caerulein
2. Cerulein
3. Ceruletid
4. Fi 6934
5. Fi-6934
6. Fi6934
7. Takus
1. Caerulein
2. 17650-98-5
3. Cerulein
4. Ceruletida
5. Ceruletidum
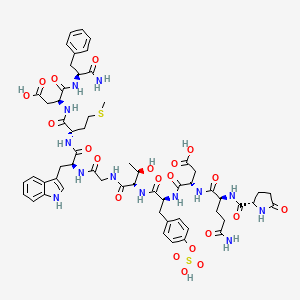
6. 5-oxo-l-prolyl-l-glutaminyl-l-alpha-aspartyl-o-sulfo-l-tyrosyl-l-threonylglycyl-l-tryptophyl-l-methionyl-l-alpha-aspartyl-l-phenylalaninamide
7. Fi-6934
8. 5-oxo-l-prolyl-l-glutaminyl-l-aspartyl-l-tyrosyl-l-threonylglycyl-l-tryptophyl-l-methionyl-l-aspartylphenyl-l-alaninamide 4-(hydrogen Sulfate) (ester)
9. Chebi:59219
10. 888y08971b
11. Ceruletidum [inn-latin]
12. Ceruletida [inn-spanish]
13. Ceruletide [usan:inn:ban]
14. 5-oxo-l-prolyl-l-glutaminyl-l-a-aspartyl-o-sulfo-l-tyrosyl-l-threonylglycyl-l-tryptophyl-l-methionyl-l-a-aspartyl-l-phenylalaninamide
15. Ccris 3063
16. Ceruletide (usan/inn)
17. Unii-888y08971b
18. Caerulein, Sulfated
19. Fi-6934caerulein
20. Ceruletide [mi]
21. Ceruletide [inn]
22. Ceruletide [usan]
23. Ceruletide [mart.]
24. Ceruletide [who-dd]
25. Schembl29520
26. Gtpl7589
27. Chembl1201355
28. Dtxsid8040434
29. Hy-a0190
30. Pyr-qd-tyr(so3h)-tgwmdf-nh2
31. Mfcd00076478
32. Cs-5876
33. Db00403
34. As-56061
35. C73362
36. D03442
37. Q5065299
38. Pglu-gln-asp-tyr(so3h)-thr-gly-trp-met-asp-phe-nh2
39. (3s)-3-{[(1s)-1-carbamoyl-2-phenylethyl]carbamoyl}-3-[(2s)-2-[(2s)-2-{2-[(2s,3r)-2-[(2s)-2-[(2s)-2-[(2s)-4-carbamoyl-2-{[(2s)-5-oxopyrrolidin-2-yl]formamido}butanamido]-3-carboxypropanamido]-3-[4-(sulfooxy)phenyl]propanamido]-3-hydroxybutanamido]acetamido}-3-(1h-indol-3-yl)propanamido]-4-(methylsulfanyl)butanamido]propanoic Acid
40. 5-oxo-l-prolyl-l-glutaminyl-l-a-aspartyl-o-sulfo-l-tyrosyl-l-threonylglycyl-l-tryptophyl-l-methionyl-l-.alpha.-aspartyl-l-phenylalaninamide
| Molecular Weight | 1352.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C58H73N13O21S2 |
| XLogP3 | -3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 17 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 22 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 38 |
| Exact Mass | 1351.44853874 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 1351.44853874 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 585 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 94 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 2840 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 10 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Caerulein is used in the treatment of paralytic ileus and as diagnostic aid in pancreatic malfunction.
Caerulein is a specific decapeptide similar in action and composition to the natural gastrointestinal peptide hormone cholecystokinin that stimulates gastric, biliary, and pancreatic secretion. It also exerts stimulatory actions on certain smooth muscles.
V - Various
V04 - Diagnostic agents
V04C - Other diagnostic agents
V04CC - Tests for bile duct patency
V04CC04 - Ceruletide
Absorption
Absorbed following intravenous administration.
Caerulein acts according to its similarity to the natural gastrointestinal peptide hormone cholecystokinin. Cholecystokinin is a peptide hormone of the gastrointestinal system responsible for stimulating the digestion of fat and protein. Cholecystokinin is secreted by the duodenum, the first segment of the small intestine. There it binds to CCK receptors, activating them and causing downstream effects. Specifically, it results in the release of digestive enzymes and bile from the pancreas and gall bladder, respectively. It also acts as a hunger suppresant. Cholecystokinin is secreted by the duodenum when fat- or protein-rich chyme leaves the stomach and enters the duodenum. The hormone acts on the pancreas to stimulate the secretion of the enzymes lipase, amylase, trypsin, and chymotrypsin. Together these pancreatic enzymes catalyze the digestion of fat and protein. Cholecystokinin also stimulates both the contraction of the gall bladder, and the relaxtion of the Sphincter of Oddi (Glisson's Sphinctor), which delivers, (not secretes) bile into the small intestine. Bile salts serve to emulsify fats, thereby increasing the effectiveness with which enzymes can digest them.
