

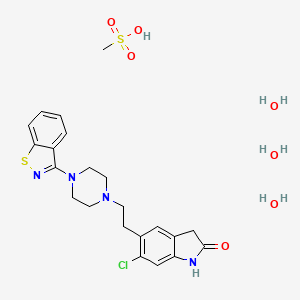

1. 5-(2-(4-(3-benzisothiazolyl)piperazinyl)ethyl)-6-chloro-1,3-dihydro-2h-indol-2-one
2. Cp 88059
3. Cp 88059-01
4. Cp-88,059
5. Cp-88,059-01
6. Cp-88,059-1
7. Ziprasidone
8. Ziprasidone Hydrochloride
9. Ziprasidone Hydrochloride, Monohydrate
10. Ziprazidone
1. Ziprasidone Mesylate
2. 199191-69-0
3. Ziprasidone Mesilate
4. Ziprasidone Mesylate Trihydrate
5. Ziprasidone Mesylate [usan]
6. Ziprasidone Mesilate Trihydrate
7. Ziprasidone Mesylate Hydrate
8. 3x6sax83jz
9. Ziprasidone (mesylate Hydrate)
10. Cp-88, 059-27
11. Nsc-760351
12. Cp-8805927
13. Geodon (tn)
14. Cp-88,059-27
15. Ziprasidone Mesylate (usan)
16. 5-[2-[4-(1,2-benzothiazol-3-yl)piperazin-1-yl]ethyl]-6-chloro-1,3-dihydroindol-2-one;methanesulfonic Acid;trihydrate
17. Cp-88059-27
18. 2h-indol-2-one, 5-(2-(4-(1,2-benzisothiazol-3-yl)-1-piperazinyl)ethyl)-6-chloro-1,3-dihydro-, Monomethanesulfonate, Trihydrate
19. 5-(2-(4-(1,2-benzisothiazol-3-yl)-1-piperazinyl)ethyl)-6-chloro-2-indolinone Monomethanesulfonate, Trihydrate
20. Unii-3x6sax83jz
21. Chembl3989833
22. Chebi:53757
23. Ziprasidone (mesylate Trihydrate)
24. Bcp12408
25. Ziprasidone Mesylate [vandf]
26. Hy-14542b
27. Ziprasidone Mesilate [mart.]
28. Cp88059
29. Nsc 760351
30. Bz164581
31. Ziprasidone Mesylate [orange Book]
32. D02100
33. 191z690
34. A814073
35. Q27124195
36. Ziprasidone Mesilate Trihydrate [ep Monograph]
37. 2h-indol-2-one, 5-(2-(4-(1,2-benzisothiazol-3-yl)-1-piperazinyl)ethyl)-6-chloro-1,3-dihydro-, Methanesulfonate, Hydrate (1:1:3)
38. 5-[2-[4-(1,2-benzothiazol-3-yl)-1-piperazinyl]ethyl]-6-chloro-1,3-dihydroindol-2-one; Methanesulfonic Acid; Trihydrate
39. 5-[2-[4-(1,2-benzothiazol-3-yl)piperazin-1-yl]ethyl]-6-chloranyl-1,3-dihydroindol-2-one; Methanesulfonic Acid; Trihydrate
| Molecular Weight | 563.1 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C22H31ClN4O7S2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 11 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 562.1322694 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 562.1322694 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 143 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 36 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 665 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 5 |
Antipsychotic Agents
Agents that control agitated psychotic behavior, alleviate acute psychotic states, reduce psychotic symptoms, and exert a quieting effect. They are used in SCHIZOPHRENIA; senile dementia; transient psychosis following surgery; or MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION; etc. These drugs are often referred to as neuroleptics alluding to the tendency to produce neurological side effects, but not all antipsychotics are likely to produce such effects. Many of these drugs may also be effective against nausea, emesis, and pruritus. (See all compounds classified as Antipsychotic Agents.)
Dopamine Antagonists
Drugs that bind to but do not activate DOPAMINE RECEPTORS, thereby blocking the actions of dopamine or exogenous agonists. Many drugs used in the treatment of psychotic disorders (ANTIPSYCHOTIC AGENTS) are dopamine antagonists, although their therapeutic effects may be due to long-term adjustments of the brain rather than to the acute effects of blocking dopamine receptors. Dopamine antagonists have been used for several other clinical purposes including as ANTIEMETICS, in the treatment of Tourette syndrome, and for hiccup. Dopamine receptor blockade is associated with NEUROLEPTIC MALIGNANT SYNDROME. (See all compounds classified as Dopamine Antagonists.)
Serotonin Antagonists
Drugs that bind to but do not activate serotonin receptors, thereby blocking the actions of serotonin or SEROTONIN RECEPTOR AGONISTS. (See all compounds classified as Serotonin Antagonists.)
