

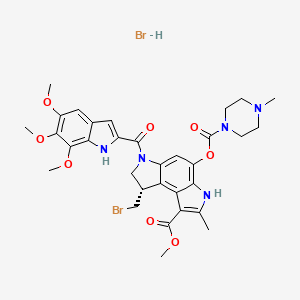

1. Benzo(1,2-b:4,3-b')dipyrrole-1-carboxylic Acid, 8-(bromomethyl)-3,6,7,8-tetrahydro-2-methyl-4-(((4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)carbonyl)oxy)-6-((5,6,7-trimethoxy-1h-indol-2-yl)carbonyl)-, Methyl Ester, (s)-
2. Kw 2189
3. Kw-2189
4. Methyl(1s)-1-bromomethyl-7-methyl-5-((4-methylpiperazinyl)carbonyloxy)-3-((5,6,7-trimethoxy-2-indolyl)carbonyl)-1,2-dihydro-3h-pyrrolo(3,2-e)indole-8-carboxylate Hydrobromide
1. Kw-2189
2. Pibrozelesin Hbr
3. Pibrozelesin Hydrobromide [usan]
4. 148778-32-9
5. 0481jcc90t
6. Pibrozelesin Hydrobromide (usan)
7. Methyl (8s)-8-(bromomethyl)-2-methyl-4-(4-methylpiperazine-1-carbonyl)oxy-6-(5,6,7-trimethoxy-1h-indole-2-carbonyl)-7,8-dihydro-3h-pyrrolo[3,2-e]indole-1-carboxylate;hydrobromide
8. Methyl (s)-8-(bromomethyl)-3,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4-hydroxy-2-methyl-6-((5,6,7-trimethoxyindol-2-yl)carbonyl)benzo(1,2-b:4,3-b')dipyrrole-1-carboxylate, 4-methyl-1-piperazinecarboxylate (ester), Monohydrobromide
9. Unii-0481jcc90t
10. Chembl2106438
11. Pibrozelesin Hydrobromide [who-dd]
12. D05472
13. Q27247636
14. 8-(bromomethyl)-3,6,7,8-tetrahydro-2-methyl-4-(((4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)carbonyl)oxy)-6-((1,6,7-trimethoxy-1h-indol-2-yl)carbonyl)benzo(1,2-b:4,3-b')dipyrrole-1-carboxylic Acid, Methyl Ester, Monohydrobromide
15. 8-(bromomethyl)-3,6,7,8-tetrahydro-2-methyl-4-(((4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)carbonyl)oxy)-6-((1,6,7-trimethoxy-1h-indol-2-yl)carbonyl)benzo(1,2-b:4,3-b')dipyrrole-1-carboxylic Acid,-, Methyl Ester, Monohydrobromide
16. Benzo(1,2-b:4,3-b')dipyrrole-1-carboxylic Acid, 8-(bromomethyl)-3,6,7,8-tetrahydro-2-methyl-4-(((4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)carbonyl)oxy)-6-((5,6,7-trimethoxy-1h-indol-2-yl)carbonyl)-, Methyl Ester, Hydrobromide (1:1)
| Molecular Weight | 779.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C32H37Br2N5O8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 9 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 9 |
| Exact Mass | 779.09884 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 777.10089 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 139 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 47 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 1130 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
Antibiotics, Antineoplastic
Chemical substances, produced by microorganisms, inhibiting or preventing the proliferation of neoplasms. (See all compounds classified as Antibiotics, Antineoplastic.)
Antineoplastic Agents, Alkylating
A class of drugs that differs from other alkylating agents used clinically in that they are monofunctional and thus unable to cross-link cellular macromolecules. Among their common properties are a requirement for metabolic activation to intermediates with antitumor efficacy and the presence in their chemical structures of N-methyl groups, that after metabolism, can covalently modify cellular DNA. The precise mechanisms by which each of these drugs acts to kill tumor cells are not completely understood. (From AMA, Drug Evaluations Annual, 1994, p2026) (See all compounds classified as Antineoplastic Agents, Alkylating.)
Antineoplastic Agents, Hormonal
Antineoplastic agents that are used to treat hormone-sensitive tumors. Hormone-sensitive tumors may be hormone-dependent, hormone-responsive, or both. A hormone-dependent tumor regresses on removal of the hormonal stimulus, by surgery or pharmacological block. Hormone-responsive tumors may regress when pharmacologic amounts of hormones are administered regardless of whether previous signs of hormone sensitivity were observed. The major hormone-responsive cancers include carcinomas of the breast, prostate, and endometrium; lymphomas; and certain leukemias. (From AMA Drug Evaluations Annual 1994, p2079) (See all compounds classified as Antineoplastic Agents, Hormonal.)