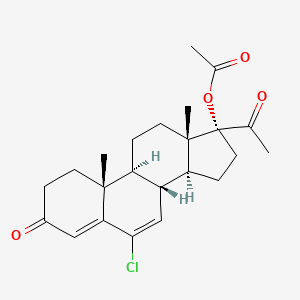

1. Chlormadinon Acetate
2. Chlormadinone
3. Chlormadinone Acetate, (9 Beta,10 Alpha)-isomer
4. Neo Eunomin
5. Neo-eunomin
6. Neoeunomin
7. Pregna-4,6-diene-3,20-dione, 17-(acetyloxy)-6-chloro-
1. 302-22-7
2. Gestafortin
3. Menstridyl
4. Normenon
5. Matrol
6. Cero
7. Chlormadinon Acetate
8. Pregna-4,6-diene-3,20-dione, 17-(acetyloxy)-6-chloro-
9. Nsc-92338
10. Bovisynchron
11. Chlordion
12. Clordion
13. Fertiletten
14. Minipill
15. Lutinyl
16. Skedule
17. Traslan
18. Retex
19. Synchrosyn P
20. Skedule Tm
21. Lutoral (syntex)
22. Chloramdinone Acetate
23. Synchrosyn
24. Chloromadinone Acetate
25. 17-(acetyloxy)-6-chloropregna-4,6-diene-3,20-dione
26. 17alpha-acetoxy-6-chloro-6-dehydroprogesterone
27. Chloromadinone 17-acetate
28. Chlormadinonu
29. Mls000028451
30. Mls001148653
31. 6-chloro-17-hydroxypregna-4,6-diene-3,20-dione Acetate
32. 6-chloro-17alpha-hydroxypregna-4,6-diene-3,20-dione Acetate
33. Chebi:31394
34. 0sy050l61n
35. Ay 13390-6
36. [(8r,9s,10r,13s,14s,17r)-17-acetyl-6-chloro-10,13-dimethyl-3-oxo-2,8,9,11,12,14,15,16-octahydro-1h-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl] Acetate
37. Ncgc00022680-04
38. Chlormadinone (acetate)
39. Smr000058325
40. 17-acetoxy-6-chloro-6-dehydroprogesterone
41. Dsstox_cid_274
42. Dsstox_rid_75478
43. 6-chloro-3,20-dioxopregna-4,6-dien-17-yl Acetate
44. 6-chloro-6-dehydro-17.alpha.-acetoxyprogesterone
45. Dsstox_gsid_20274
46. 6-chloro-6-dehydro-17.alpha.-hydroxyprogesterone Acetate
47. Chlormadinonu [polish]
48. Clormadinone Acetate
49. Progesterone, 6-chloro-6-dehydro-17-hydroxy-, Acetate
50. Pregna-4,6-diene-3,20-dione, 17-(acetoxy)-6-chloro-
51. (8r,9s,10r,13s,14s,17r)-17-acetyl-6-chloro-10,13-dimethyl-3-oxo-2,3,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-dodecahydro-1h-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl Acetate
52. Cas-302-22-7
53. Ccris 129
54. Hsdb 3591
55. Einecs 206-118-0
56. 6-chloro-delta6-17-acetoxyprogesterone
57. Nsc92338
58. Pregna-4,6-diene-3,20-dione, 6-chloro-17-hydroxy-, Acetate
59. Unii-0sy050l61n
60. 6-chloro-delta6-(17alpha)acetoxyprogesterone
61. 6-chloro-6-dehydro-17alpha-acetoxyprogesterone
62. 6-chloro-delta(sup 6)-17-acetoxyprogesterone
63. Chlormadinone Acetate [progestins]
64. 17-alpha-acetoxy-6-chloro-6-dehydroprogesterone
65. 6-chloro-6-dehydro-17-alpha-acetoxyprogesterone
66. 6-dehydro-6-chloro-17-alpha-acetoxyprogesterone
67. 17-alpha-acetoxy-6-chloro-6,7-dehydroprogesterone
68. 6-chloro-.delta.6-17-acetoxyprogesterone
69. Chlormadinone-acetate
70. Delta(sup 6)-6-chloro-17-alpha-acetoxyprogesterone
71. Delta(sup 6)-6-chloro-17alpha-acetoxyprogesterone
72. Lutoral (tn)
73. 6-chloro-delta-6-17alpha-hydroxyprogesterone Acetate
74. Chlormadinone Acetate [usan:jan:nf]
75. 6-chloro-6-dehydro-17alpha-hydroxyprogesterone Acetate
76. 6-chloro-delta(sup 6)-dehydro-17-acetoxyprogesterone
77. 17-alpha-acetoxy-6-chloro-4,6-pregnadiene-3,20-dione
78. 6-chloro-17-alpha-acetoxy-4,6-pregnadiene-3,20-dione
79. 6-chloro-6-dehydro-17-alpha-hydroxyprogesterone Acetate
80. 6-chloro-pregna-4,6-dien-17alpha-ol-3,20-dione Acetate
81. 6-chloro-17-alpha-hydroxy-delta(sup 6)-progesterone Acetate
82. 6-chloro-pregna-4,6-dien-17-alpha-ol-3,20-dione Acetate
83. Opera_id_343
84. 17.alpha.-acetoxy-6-chloro-6-dehydroprogesterone
85. 6-chloro-.delta.6-[17.alpha.]acetoxyprogesterone
86. Acetic Acid Chlormadinone
87. .delta.(sup 6)-6-chloro-17.alpha.-acetoxyprogesterone
88. 6-chloro-delta(sup 4,6)-pregnadiene-17-alpha-ol-3,20-dione 17-acetate
89. Schembl15046
90. Chembl110691
91. Chlormadinone Acetate, >=98%
92. Dtxsid6020274
93. Chlormadinone Acetate [mi]
94. Hms2231j04
95. Hms3715e19
96. Chlorinated Phenylmethylpolysiloxane
97. Chlormadinone Acetate [jan]
98. Bcp28307
99. Hy-b1095
100. Zinc3876041
101. Chlormadinone Acetate (jp17/usan)
102. Chlormadinone Acetate [hsdb]
103. Chlormadinone Acetate [usan]
104. Tox21_110881
105. Tox21_200665
106. Mfcd00056471
107. S4593
108. 6-chloro-pregna-4,20-dione Acetate
109. Chlormadinone Acetate [mart.]
110. Akos015955610
111. Chlormadinone Acetate [who-dd]
112. Tox21_110881_1
113. Ccg-220989
114. Cs-4683
115. Ks-5157
116. Rs-1280
117. Ay-13390-6
118. Ncgc00022680-05
119. Ncgc00258219-01
120. (1s,11s,15s,2r,10r,14r)-14-acetyl-8-chloro-2,15-dimethyl-5-oxotetracyclo[8.7.0 .0<2,7>.0<11,15>]heptadeca-6,8-dien-14-yl Acetate
121. 17.alpha.-acetoxy-6-chloro-4,20-dione
122. 6-chloro-17.alpha.-acetoxy-4,20-dione
123. Chlormadinone Acetate [ep Monograph]
124. Chlormadinone Acetate For System Suitability
125. 17.alpha.-acetoxy-6-chloropregna-4,20-dione
126. 6-chloro-.delta.(sup 4,20-dione 17-acetate
127. 6-chloro-17-hydroxypregna-4,20-dione Acetate
128. C74552
129. D01299
130. 6-chloro-.delta.(sup 6)-17-acetoxyprogesterone
131. Pregna-4,20-dione, 17-(acetyloxy)-6-chloro-
132. 302c227
133. Sr-01000003040
134. Pregna-4,20-dione, 6-chloro-17-hydroxy-, Acetate
135. Q-200829
136. Q5102980
137. Sr-01000003040-2
138. 6-chloro-17.alpha.-hydroxypregna-4,20-dione Acetate
139. 17alpha-acetoxy-6-chloropregna-4,6-diene-3,20-dione
140. 6-chloro-.delta.(sup 6)-dehydro-17-acetoxyprogesterone
141. 17.alpha.-acetoxy-6-chloro-6,7-dehydroprogesterone
142. 6-chloro-.delta.-6-17.alpha.-hydroxyprogesterone Acetate
143. Chloromadinone 17-acetate 100 Microg/ml In Methanol/water
144. Wln: L E5 B666 Ov Ku Mutj A1 E1 Fv1 Fov1 Lg
145. 6-chloro-17.alpha.-hydroxy-.delta.(sup 6)-progesterone Acetate
146. Chlormadinone Acetate, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
147. (8r,9s,10r,13s,14s,17r)-17-acetyl-6-chloro-10,13-dimethyl-3-oxo-2,3,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-dodecahydro-1h-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-ylacetate
| Molecular Weight | 404.9 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C23H29ClO4 |
| XLogP3 | 3.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 404.1754371 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 404.1754371 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 60.4 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 28 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 827 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 6 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Contraceptives, Oral, Synthetic; Progestational Hormones, Synthetic
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 2009)
Chlormadinone acetate has not been used in the United States since 1970, when the only product (an oral contraceptive) was removed from the market. Its use in the United Kingdom was suspended in the same year. Before suspension, chlormadinone acetate was used in oral contraceptives either together with mestranol as a "sequential" contraceptive or as a "progestogen only" oral contraceptive. Chlormadinone acetate has been used (frequently in combination with mestranol) for treatment of threatened abortion and dysmenorrhea.
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V72 584 (1999)
Ethinylestradiol/chlormadinone acetate 0.03/2mg (EE/CMA) is a combined monophasic contraceptive pill with anti-androgenic properties. In a large, non-comparative, multicentre trial (< or =24 cycles of treatment per woman) and two (6- and 12-cycle) post-marketing surveillance studies, EE/CMA was effective in preventing pregnancy. EE/CMA was significantly more effective than EE/levonorgestrel 0.03/0.15 mg/day in treating women with mild-to-moderate papulopustular acne of the face and related disorders in a randomized, single-blind, multicentre trial. EE/CMA was well tolerated in clinical trials and the post-marketing surveillance studies. Adverse events were those commonly reported with oral contraceptives. As expected, the most common menstrual disturbances were breakthrough bleeding, spotting and amenorrhea.
PMID:15025547 Curran MP, Wagstaff AJ; Drugs 64 (7): 751-62 (2004)
Orally active progestogen with antiandrogenic activity; has been used in combinations as an oral contraceptive.
O'Neil, M.J. (ed.). The Merck Index - An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals. Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck and Co., Inc., 2006., p. 348
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for CHLORMADINONE ACETATE (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Androgen Antagonists
Compounds which inhibit or antagonize the biosynthesis or actions of androgens. (See all compounds classified as Androgen Antagonists.)
Contraceptives, Oral, Synthetic
Oral contraceptives which owe their effectiveness to synthetic preparations. (See all compounds classified as Contraceptives, Oral, Synthetic.)
Contraceptives, Oral, Hormonal
Oral contraceptives which owe their effectiveness to hormonal preparations. (See all compounds classified as Contraceptives, Oral, Hormonal.)
... Pharmacokinetic studies have shown rapid and almost complete absorption after oral administration, and chlormadinone acetate is being bound to albumin rather than SHBG (Sex-Hormone-Binding-Globulin). Multiple dosing studies have demonstrated that steady state is reached by day 7 after oral administration with peak plasma concentrations in the region of 2 ng/mL. ...
PMID:16356876 Bouchard P; Eur J Contracept Reprod Health Care 10 Suppl 1: 7-11 (2005)
The half-life and metabolic clearance rate of chlormadinone acetate were computed after a single iv injection of 60 to 90 mcCi 1-alpha-tritiated-chlormadinone acetate (specific activity 222 mcCi/mg) into 7 women aged 34-52 years. Plasma was extracted with acetone:MeOH for total radioactivity; then extracted with water and ether for free steroid radioactivity; then with n-butanol for conjugated steroid radioactivity; and finally extracted with chloroform:MeOH and chromatographed on thin layer with ether:benzene for specific radioactivity due to chlormadinone acetate. Blood samples were taken at 0 .25, 0.5, 1, 8, 24 hours and every 24 hours for 5 days. ... All 4 curves, total radioactivity, conjugated steroids, free steroids, and specific activity had the same biphasic form: a rapid loss for about 24 hours, and an approaching equilibrium after 24 hours. The metabolic clearance rate was 42.61 liters per day... These data generate an estimate of the concentration of chlormadinone acetate in plasma of women taking 0.5 mg daily: about .45 ng/mL, i.e. about one-thirteenth the concentration of progesterone.
PMID:4134033 Dugwekar YG et al; Contraception 7 (1): 27-45 (1973)
Published data on pharmacokinetic parameters for chlormadinone acetate (CMA) are in part contradictory, especially with regard to terminal half-life (t(1/2,z)). Single and multiple doses of CMA (2 mg) and ethinylestradiol (EE; 0.03 mg) were administered to healthy female volunteers for six menstrual cycles. Plasma concentrations of CMA and EE were determined by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Single-dose and steady-state pharmacokinetic parameters were calculated. In a separate study, healthy female volunteers were given a single 2-mg dose of radiolabeled CMA. Concentrations of radioactivity in fecal and urine samples were determined via liquid scintillation. Excretion of total radioactivity was calculated as percentage of administered dose. Eighteen women completed the repeated-dose study. Peak plasma concentrations for CMA and EE were reached within 1 and 2 hr after taking the study drug. Peak plasma concentrations of CMA were approximately 1600 pg/mL after single-dose administration and 2000 pg/mL after multiple dosing. CMA and EE showed linear pharmacokinetics throughout six cycles, with constant trough values of approximately 400-500 pg/mL for CMA and 20-40 pg/mL for EE. Mass balance factors were 1.2-1.4 for CMA and 1.6-1.7 for EE, and accumulation factors were 1.7-2 for CMA and 1.7-1.8 for EE. Mean t(1/2,z) of CMA was approximately 25 hr after single dosing and 36-39 hr at steady state. In the excretion balance study, mean dose of CMA recovered was 87.3+/-6.4%, with urinary and fecal excretion accounting for 45% and 42%, respectively. The pharmacokinetics of CMA and EE is linear after multiple dosing and remains stable during long-term administration, once steady state is reached. The t(1/2,z) of CMA was 36-39 hr after multiple dosing, which is considerably shorter than the 80 hr often quoted in the literature.
PMID:16904418 Terlinden R et al; Contraception 74 (3): 239-44 (2006)
The bioavailability and bioequivalence of two different film coated tablets containing ethinylestradiol and chlormadinone acetate (Bellissima as test and the respective preparation from the originator as reference) were investigated in 20 healthy female volunteers after oral single-dose administration. The study was performed according to a single-center, randomised, single-dose, 2-way cross-over design with a wash-out phase of 28 days. Blood samples for pharmacokinetic profiling were taken up to 168 hr post-dose, and ethinylestradiol and chlormadinone acetate plasma concentrations were determined with a validated LC-MS/MS method. The observed mean maximum plasma concentrations (Cmax) of ethinylestradiol were 124.96 pg/mL (test) and 129.12 pg/mL (reference). In the case of chlormadinone acetate, Cmax averaged 6.9566 ng/mL (test) and 6.6663 ng/mL (reference). The geometric means of area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC(0-infinity)) of ethinylestradiol were 1292.35 pg/mL x hr (test) and 1380.49 pg/mL x hr (reference). For chlormadinone acetate, geometric means of AUC(0-infinity) were 53.322 ng/mL x hr (test) and 58.111 ng/mL x hr (reference). The median of tmax of ethinylestradiol was 1.5 hr for both test and reference and the median of tmax of chlormadinone acetate 1.0 hr (test) and 1.5 hr (reference). Plasma elimination half-lives (t1/2) of ethinylestradiol were 14.96 hr (test) and 15.41 hr (reference) and of chlormadinone acetate 56.63 hr (test) and 56.17 hr (reference), respectively. Both primary target parameters AUC(0-infinity) and Cmax were tested parametrically by analysis of variance (ANOVA). The point estimator and the 90% confidence intervals for the AUC(0-infinity) ratio (test/reference: 93.72% [86.62%-101.39%]) indicate high similarity of both formulations with respect to the extent of ethinylestradiol exposure. A high degree of similarity was also observed for Cmax of ethinylestradiol, as the point estimator and the 90% confidence interval for the Cmax ratio are 96.18% (90.82%-101.86%). Regarding the AUC(0-infinity) ratio of chlormadinone acetate, the point estimator is 91.60% and the 90% confidence interval 84.08%-99.79%. Furthermore, exchangeability of both formulations is also suggested by the point estimator and 90% confidence of Cmax of this active agent (104.72% [95.76%-114.53%]). Bioequivalence between test and reference formulation was demonstrated since for both ethinylestradiol and chlormadinone acetate all 90% confidence intervals of AUC(0-infinity) and Cmax fall into the generally accepted range of 80%-125%.
PMID:20108652 Bonn M et al; Arzneimittelforschung 59 (12): 651-8 (2009)
After intravenous injection of radiolabelled chlormadinone acetate, the steroid and its metabolites have an initial rapid half-life of 2.4 hours, followed by a slow half-life of 80.1 hours. The mean metabolic clearance rate is 126 L/day for chlormadinone acetate and 42.6 L/day for chlormadinone acetate and its metabolites. The long half-life and slow elimination rate are probably due to accumulation of the drug in fat tissue.
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V72 226 (1999)
The major metabolites of chlormadinone acetate are 2alpha- hydroxychlormadinone acetate and 3beta-hydroxychlormadinone acetate. Incubation of chlormadinone acetate with human or rat liver microsomes produces mainly the 3beta-hydroxy metabolite. In contrast, incubation with microsomes from phenobarbital-treated rats produces the 2alpha-hydroxy metabolite, indicating that the metabolite pattern is dependent on the hepatic monoxygenase state.
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V72 226 (1999)
... After a single dose of CMA the half-life time is around 34 hours and after multiple dose administration approximately 38 hours. ...
PMID:16356876 Bouchard P; Eur J Contracept Reprod Health Care 10 Suppl 1: 7-11 (2005)
Published data on pharmacokinetic parameters for chlormadinone acetate (CMA) are in part contradictory, especially with regard to terminal half-life (t(1/2,z)). Single and multiple doses of CMA (2 mg) and ethinylestradiol (EE; 0.03 mg) were administered to healthy female volunteers for six menstrual cycles. ... Mean t(1/2,z) of CMA was approximately 25 hr after single dosing and 36-39 hr at steady state. ... The t(1/2,z) of CMA was 36-39 hr after multiple dosing, which is considerably shorter than the 80 hr often quoted in the literature.
PMID:16904418 Terlinden R et al; Contraception 74 (3): 239-44 (2006)
The half-life and metabolic clearance rate of chlormadinone acetate were computed after a single iv injection of 60 to 90 mcCi 1-alpha-tritiated-chlormadinone acetate (specific activity 222 mcCi/mg) into 7 women aged 34-52 years. Plasma was extracted with acetone:MeOH for total radioactivity; then extracted with water and ether for free steroid radioactivity; then with n-butanol for conjugated steroid radioactivity; and finally extracted with chloroform:MeOH and chromatographed on thin layer with ether:benzene for specific radioactivity due to chlormadinone acetate. Blood samples were taken at .25, .5, 1, 8, 24 hours and every 24 hours for 5 days. The mean half-life of radioactivity specifically indentified as chlormadinone acetate for the first 24 hours was 2.6 hours, and after 24 hours was 81.8 hours, calculated by TAIT and BURSTEIN's method. ...
PMID:4134033 Dugwekar YG et al; Contraception 7 (1): 27-45 (1973)
After intravenous injection of radiolabelled chlormadinone acetate, the steroid and its metabolites have an initial rapid half-life of 2.4 hours, followed by a slow half-life of 80.1 hours.
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V72 226 (1999)
Chlormadinone acetate (CMA) is a derivative of naturally secreted progesterone that shows high affinity and activity at the progesterone receptor. It has an anti-estrogenic effect and, in contrast to natural progesterone, shows moderate anti-androgenic properties. CMA acts by blocking androgen receptors in target organs and by reducing the activity of skin 5alpha-reductase. It suppresses gonadotropin secretion and thereby reduces ovarian and adrenal androgen production. CMA shows high contraceptive efficacy by inhibiting ovulation due to its ability to suppress or disrupt endogenous gonadotropin secretion and, by this, inhibits follicular growth and maturation. In addition, it suppresses endometrial thickness and increases the viscosity of cervical mucus. ...
PMID:16356876 Bouchard P; Eur J Contracept Reprod Health Care 10 Suppl 1: 7-11 (2005)
The ovulation response to electrical stimulation of the median eminence, or to the intrapituitary infusion of median eminence extract, was observed in control rabbits and animals pre-treated with chlormadinone acetate. Chlormadinone acetate pre-treatment did not significantly reduce the proportion of rabbits ovulating in response to electrical stimulation. However, there was a significant reduction in the average number of ruptured follicles when compared with the animals in the control group. Chlormadinone acetate pre-treatment significantly reduced the proportion of animals ovulating in response to the intrapituitary infusion of median eminence extract as compared with the control series. However, there was no significant reduction in the average number of ruptured follicles (in those rabbits that ovulated) when compared with the control groups. Chlormadinone acetate pre-treatment produced no significant effect upon either the proportion of animals ovulating, or the average number of ruptured follicles, following i.v. injection of 50 ug LH.5. The conclusion drawn is that chlormadinone acetate blocks copulattion-induced ovulation in the rabbit by action at a site in the central nervous system located above the median eminence. The possible effects of chlormadinone acetate upon the secretion of FSH, the pituitary sensitivity to releasing factors and the ovarian sensitivity to LH are discussed.
PMID:4186126 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1351513 Harris GW, Sherratt RM et al; J Physiol 203 (1): 59-66 (1969)
Studies with the human breast cancer cell line ZR-75-1, which contains functional estrogen, progesterone and androgen receptors, suggest that chlormadinone acetate inhibited the growth of these cells by an interaction of androgen and progesterone receptor-mediated mechanisms.
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V72 240 (1999)
Groups of 8-12 male Sprague-Dawley Crl:CD(SD)Br rats were castrated and injected immediately thereafter twice daily for 14 days with one of a number of synthetic progestogens, including chlormadinone acetate, used in the treatment of prostate cancer. Controls received the vehicle, 1% gelatine in 0.9% saline... Dihydrotestosterone was injected at a dose of 150 ug twice daily for 14 days as a positive control. All animals were killed on the morning after the last day of treatment, and the ventral prostate and adrenals were removed and weighted; furthermore, the prostatic content of ornithine decarboxylase was measured, as it is consider to be a highly specific, sensitive of androgenic activity in the prostate. Dihydrotestosterone increased the ventral prostate weight to 43% above that of castrated controls. Chlormadinone acetate was less potent than dihydrotestosterone but caused significant increases in prostate weight, by about 22% at 3 mg and 36% at 10 mg per injection. Whereas dihydrotestosterone caused a 14-fold increase in ornithine decarboxylase activity in the prostate, chlormadinone acetate caused a 5.3-fold increase at 3 mg and an 11.8-fold increase at 10 mg. Chlormadinone acetate thus has weak but significant androgenic activity in the rat ventral prostate.
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V72 280-1 (1999)