
1. 58-94-6
2. Diuril
3. Chlorothiazid
4. Chlorthiazide
5. Chlotride
6. Thiazide
7. Chlortiazid
8. Chlorosal
9. Chlorurit
10. Saluretil
11. Warduzide
12. Alurene
13. Clotride
14. Diuresal
15. Diurilix
16. Diurite
17. Diutrid
18. Salisan
19. Salunil
20. Saluric
21. Yadalan
22. Flumen
23. Minzil
24. Urinex
25. Neo-dema
26. Sk-chlorothiazide
27. Chlorothiazidum
28. Clorotiazida
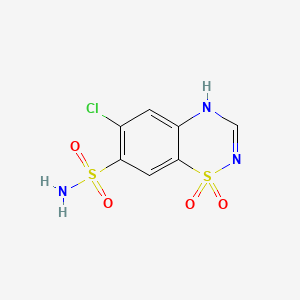
29. 6-chloro-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
30. 2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide, 6-chloro-, 1,1-dioxide
31. Component Of Aldoclor
32. 6-chloro-7-sulfamoyl-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine 1,1-dioxide
33. Nsc 25693
34. Nsc-25693
35. Diuril (tn)
36. Mls000028398
37. Chebi:3640
38. Chlorthiazid
39. Chlorthiazidum
40. Nsc25693
41. 77w477j15h
42. Cas-58-94-6
43. Ncgc00015242-04
44. Clorotiazide
45. Chloriazid
46. Chlrosal
47. Smr000058429
48. 6-chloro-4h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
49. Clorotiazide [dcit]
50. Diuril Boluses
51. 6-chloro-1,1-dioxo-2h-1$l^{6},2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
52. 6-chloro-1,1-dioxo-4h-1$l^{6},2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
53. Dsstox_cid_2800
54. Dsstox_rid_76733
55. Dsstox_gsid_22800
56. Diuril Boluses, Veterinary
57. Clorotiazida [inn-spanish]
58. Chlorothiazidum [inn-latin]
59. Ccris 5999
60. Hsdb 3030
61. Sr-01000075604
62. Einecs 200-404-9
63. Mfcd00058576
64. 6-chloro-1,1-dioxo-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
65. 6-chloro-1,1-dioxo-2h-1?^{6},2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
66. Chlorothiazide (jan/usp/inn)
67. Chlorothiazide [usp:inn:ban]
68. Unii-77w477j15h
69. Prestwick_56
70. Diupres (salt/mix)
71. Aldoclor (salt/mix)
72. Spectrum_000134
73. Prestwick0_000251
74. Prestwick1_000251
75. Prestwick2_000251
76. Prestwick3_000251
77. Spectrum2_000154
78. Spectrum3_000342
79. Spectrum4_000280
80. Spectrum5_001446
81. Lopac-c-4911
82. Chembl842
83. C 4911
84. Chlorothiazide [mi]
85. Cid_2720
86. Chlorothiazide [inn]
87. Chlorothiazide [jan]
88. Lopac0_000254
89. Schembl22329
90. Bspbio_000062
91. Bspbio_002003
92. Chlorothiazide [hsdb]
93. Kbiogr_000780
94. Kbioss_000594
95. Bidd:gt0635
96. Chlorothiazide [vandf]
97. Divk1c_000675
98. Spectrum1500180
99. Spbio_000288
100. Spbio_002281
101. Chlorothiazide [mart.]
102. Bpbio1_000070
103. Gtpl4835
104. Chlorothiazide [who-dd]
105. Chembl3392493
106. Dtxsid0022800
107. Bdbm39351
108. Chlorothiazide, Thiazide Diuretic
109. Hms502b17
110. Kbio1_000675
111. Kbio2_000594
112. Kbio2_003162
113. Kbio2_005730
114. Kbio3_001223
115. Ninds_000675
116. Hms1568d04
117. Hms1920k15
118. Hms2091c18
119. Hms2095d04
120. Hms2232n22
121. Hms3259k15
122. Hms3260d10
123. Hms3370a15
124. Hms3655m13
125. Hms3712d04
126. Pharmakon1600-01500180
127. Chlorothiazide [green Book]
128. Bcp24474
129. Hy-b0224
130. Zinc3872055
131. Chlorothiazide [ep Impurity]
132. Chlorothiazide [orange Book]
133. Tox21_110107
134. Tox21_200972
135. Tox21_500254
136. Wln: T66 Bswm Enj Hg Iszw
137. 6-chloro-1,1-dioxo-4h-1lambda6,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
138. 6-chloro-4h-benzo[e][1,2,4]thiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
139. Ccg-38953
140. Chlorothiazide [usp Impurity]
141. Nsc756682
142. S1641
143. Chlorothiazide [usp Monograph]
144. Akos015896601
145. Akos024319450
146. Tox21_110107_1
147. Db00880
148. Lp00254
149. Nc00500
150. Nsc-756682
151. Sdccgsbi-0050242.p005
152. Idi1_000675
153. Ncgc00015242-01
154. Ncgc00015242-02
155. Ncgc00015242-03
156. Ncgc00015242-05
157. Ncgc00015242-06
158. Ncgc00015242-07
159. Ncgc00015242-08
160. Ncgc00015242-09
161. Ncgc00015242-10
162. Ncgc00015242-12
163. Ncgc00015242-13
164. Ncgc00015242-19
165. Ncgc00091042-01
166. Ncgc00091042-02
167. Ncgc00091042-03
168. Ncgc00091042-04
169. Ncgc00091042-05
170. Ncgc00258525-01
171. Ncgc00260939-01
172. Ac-18732
173. As-11760
174. Sbi-0050242.p004
175. Eu-0100254
176. Ft-0664953
177. Hydrochlorothiazide Impurity, Chlorothiazide-
178. Sw219268-1
179. Chlorothiazide 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
180. C07461
181. D00519
182. D89501
183. Ab00051940-04
184. Ab00051940_05
185. Ab00051940_06
186. Hydrochlorothiazide Impurity A [ep Impurity]
187. Q2603363
188. Sr-01000075604-1
189. Sr-01000075604-3
190. Sr-01000075604-5
191. W-105353
192. Brd-k88682005-001-05-9
193. Brd-k88682005-001-07-5
194. Z1691545266
195. 6-chloro-7-sulfamoyl-2h-1,4-benzothiadiazine 1,1-dioxide
196. 6-chloro-2h-1,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
197. 6-chloro-4h-1,2,4-benzathiadiazine-7-sulfonamide-1,1-dioxide
198. Chlorothiazide, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
199. 2h-1,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide, 6-chloro-, 1,1-dioxide
200. 6-chloro-1,1-dioxo-2h-1lambda6,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
201. 6-chloro-1,1-dioxo-4h-1$l^{6,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
202. 6-chloro-2h-benzo[e][1,2,4]thiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
203. Chlorothiazide, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
204. Hydrochlorothiazide Impurity, Chlorothiazide- [usp Impurity]
205. 6-chloro-1,1-dioxo-1,2-dihydro-1lambda*6*-benzo[1,2,4]thiadiazine-7-sulfonic Acid Amide
206. Chlorothiazide, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
| Molecular Weight | 295.7 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C7H6ClN3O4S2 |
| XLogP3 | -0.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 294.9488257 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 294.9488257 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 135 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 17 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 532 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Chlorothiazide |
| PubMed Health | Chlorothiazide |
| Drug Classes | Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | Chlorothiazide is a diuretic and antihypertensive. It is 6-chloro-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide. Its empirical formula is C7H6CIN3O4S2 and its structural formula is:It is a white, or practically white crystalline compound with a... |
| Active Ingredient | Chlorothiazide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 250mg; 500mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mylan |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Diuril |
| PubMed Health | Chlorothiazide |
| Drug Classes | Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | DIURIL* (Chlorothiazide) is a diuretic and antihypertensive. It is 6-chloro-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide. Its empirical formula is C7H6ClN3O4S2and its structural formula is:It is a white, or practically white, crystalline pow... |
| Active Ingredient | Chlorothiazide; Chlorothiazide sodium |
| Dosage Form | Injectable; Suspension |
| Route | Injection; Oral |
| Strength | eq 500mg base/vial; 250mg/5ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Salix Pharms; Oak Pharms Akorn |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Chlorothiazide |
| PubMed Health | Chlorothiazide |
| Drug Classes | Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | Chlorothiazide is a diuretic and antihypertensive. It is 6-chloro-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide. Its empirical formula is C7H6CIN3O4S2 and its structural formula is:It is a white, or practically white crystalline compound with a... |
| Active Ingredient | Chlorothiazide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 250mg; 500mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mylan |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Diuril |
| PubMed Health | Chlorothiazide |
| Drug Classes | Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | DIURIL* (Chlorothiazide) is a diuretic and antihypertensive. It is 6-chloro-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide. Its empirical formula is C7H6ClN3O4S2and its structural formula is:It is a white, or practically white, crystalline pow... |
| Active Ingredient | Chlorothiazide; Chlorothiazide sodium |
| Dosage Form | Injectable; Suspension |
| Route | Injection; Oral |
| Strength | eq 500mg base/vial; 250mg/5ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Salix Pharms; Oak Pharms Akorn |
Antihypertensive Agents; Diuretics, Thiazide
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
THE THIAZIDES ARE DIURETICS OF CHOICE FOR MAINTENANCE THERAPY IN AMBULATORY PATIENTS WITH EDEMA CAUSED BY CHRONIC CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE BUT WITH NORMAL RENAL FUNCTION. ...LESS EFFECTIVE WHEN EDEMA IS ASSOCIATED WITH RENAL IMPAIRMENT. /THIAZIDES/
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs, AMA Drug Evaluations. 3rd ed. Littleton, Massachusetts: PSG Publishing Co., Inc., 1977., p. 81
THIAZIDES HAVE THEIR GREATEST USEFULNESS AS DIURETICS IN MGMNT OF EDEMA OF CHRONIC CARDIAC DECOMPENSATION. /THIAZIDES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 832
LESS COMMON USAGES OF THIAZIDES INCL TREATMENT OF DIABETES INSIPIDUS & MANAGEMENT OF HYPERCALCIURIA IN PT WITH RECURRENT URINARY CALCULI COMPOSED OF CALCIUM. /THIAZIDES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 832
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for CHLOROTHIAZIDE (15 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
WHEN CARDIAC DECOMPENSATION OR HYPERTENSION IS ACCOMPANIED BY SIGNIFICANT IMPAIRMENT OF RENAL FUNCTION, THIAZIDES SHOULD BE ADMIN WITH CAUTION BECAUSE OF THEIR CAPACITY TO AGGRAVATE RENAL INSUFFICIENCY. /THIAZIDES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 832
VET USE: AS WITH ANY POTENT DIURETIC, FLUID & ELECTROLYTE IMBALANCE MAY OCCUR ESP AFTER PROLONGED USE.
Rossoff, I.S. Handbook of Veterinary Drugs. New York: Springer Publishing Company, 1974., p. 107
PERIODIC SERUM ELECTROLYTE DETERMINATIONS SHOULD BE DONE ON ALL PATIENTS IN ORDER TO DETECT...HYPONATREMIA, HYPOCHLOREMIC ALKALOSIS, & HYPOKALEMIA. /THIAZIDES/
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 868
...CONTRAINDICATED IN ANURIA, PATIENTS HYPERSENSITIVE TO THESE & OTHER SULFONAMIDE DRUGS, & IN OTHERWISE HEALTHY PREGNANT WOMEN WITH OR WITHOUT EDEMA. ...SHOULD BE USED WITH CAUTION IN PATIENTS WITH RENAL DISEASE...ALSO... PATIENTS WITH IMPAIRED LIVER FUNCTION.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 868
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for CHLOROTHIAZIDE (18 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Chlorothiazide is indicated as adjunctive therapy in edema associated with congestive heart failure, hepatic cirrhosis, and corticosteroid and estrogen therapy. It is also indicated in the management of hypertension either as the sole therapeutic agent or to enhance the effectiveness of other antihypertensive drugs in the more severe forms of hypertension.
Like other thiazides, chlorothiazide promotes water loss from the body (diuretics). It inhibits Na+/Cl- reabsorption from the distal convoluted tubules in the kidneys. Thiazides also cause loss of potassium and an increase in serum uric acid. Thiazides are often used to treat hypertension, but their hypotensive effects are not necessarily due to their diuretic activity. Thiazides have been shown to prevent hypertension-related morbidity and mortality although the mechanism is not fully understood. Thiazides cause vasodilation by activating calcium-activated potassium channels (large conductance) in vascular smooth muscles and inhibiting various carbonic anhydrases in vascular tissue. Chlorothiazide affects the distal renal tubular mechanism of electrolyte reabsorption. At maximal therapeutic dosages, all thiazides are approximately equal in their diuretic efficacy. Chlorothiazide increases excretion of sodium and chloride in approximately equivalent amounts. Natriuresis may be accompanied by some loss of potassium and bicarbonate. After oral doses, 10-15 percent of the dose is excreted unchanged in the urine. Chlorothiazide crosses the placental but not the blood-brain barrier and is excreted in breast milk.
Antihypertensive Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of acute or chronic vascular HYPERTENSION regardless of pharmacological mechanism. Among the antihypertensive agents are DIURETICS; (especially DIURETICS, THIAZIDE); ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS; ADRENERGIC ALPHA-ANTAGONISTS; ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS; CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS; GANGLIONIC BLOCKERS; and VASODILATOR AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Antihypertensive Agents.)
Sodium Chloride Symporter Inhibitors
Agents that inhibit SODIUM CHLORIDE SYMPORTERS. They act as DIURETICS. Excess use is associated with HYPOKALEMIA. (See all compounds classified as Sodium Chloride Symporter Inhibitors.)
Diuretics
Agents that promote the excretion of urine through their effects on kidney function. (See all compounds classified as Diuretics.)
C - Cardiovascular system
C03 - Diuretics
C03A - Low-ceiling diuretics, thiazides
C03AA - Thiazides, plain
C03AA04 - Chlorothiazide
Absorption
Rapidly absorbed following oral administration.
Route of Elimination
Chlorothiazide is not metabolized but is eliminated rapidly by the kidney. After oral doses, 10 to 15 percent of the dose is excreted unchanged in the urine. Chlorothiazide crosses the placental but not the blood-brain barrier and is excreted in breast milk.
CHLOROTHIAZIDE IS DISTRIBUTED THROUGHOUT EXTRACELLULAR SPACE & DOES NOT ACCUMULATE IN TISSUES OTHER THAN THE KIDNEY.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 831
ALL OF THE THIAZIDE-LIKE DRUGS CROSS THROUGH THE PLACENTA.
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B. Molinoff, R.W. Ruddon, A.G. Goodman (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 9th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 1996., p. 784
IN NEPHRECTOMIZED ANIMAL, CHLOROTHIAZIDE MAY BE EXCRETED IN THE BILE; IT DOES NOT UNDERGO METABOLIC ALTERATION.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 831
CHLOROTHIAZIDE IN A 1.1 FETAL/MATERNAL CONCN RATIO REQUIRES 60 MIN TO APPEAR IN FETUS... /FROM TABLE/
LaDu, B.N., H.G. Mandel, and E.L. Way. Fundamentals of Drug Metabolism and Disposition. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1971., p. 102
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for CHLOROTHIAZIDE (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Chlorothiazide is not metabolized but is eliminated rapidly by the kidney.
...CHLOROTHIAZIDE...METABOLICALLY STABLE & FOLLOWING IV ADMIN TO...HUMANS...EXCRETED UNCHANGED IN URINE.
Parke, D. V. The Biochemistry of Foreign Compounds. Oxford: Pergamon Press, 1968., p. 183
45-120 minutes
Half-life is 1.5 hours. /From Table/
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B. Molinoff, R.W. Ruddon, A.G. Goodman (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 9th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 1996., p. 703
As a diuretic, chlorothiazide inhibits active chloride reabsorption at the early distal tubule via the Na-Cl cotransporter, resulting in an increase in the excretion of sodium, chloride, and water. Thiazides like chlorothiazide also inhibit sodium ion transport across the renal tubular epithelium through binding to the thiazide sensitive sodium-chloride transporter. This results in an increase in potassium excretion via the sodium-potassium exchange mechanism. The antihypertensive mechanism of chlorothiazide is less well understood although it may be mediated through its action on carbonic anhydrases in the smooth muscle or through its action on the large-conductance calcium-activated potassium (KCa) channel, also found in the smooth muscle.
THE MECHANISM BY WHICH THIAZIDE DIURETICS LOWER BLOOD PRESSURE HAS NOT BEEN FIRMLY ESTABLISHED. /THIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Evaluations of Drug Interactions. 2nd ed. and supplements. Washington, DC: American Pharmaceutical Assn., 1976, 1978., p. 89
...INDICATED THAT BENZOTHIADIAZIDES HAVE A DIRECT EFFECT ON RENAL TUBULAR TRANSPORT OF SODIUM & CHLORIDE INDEPENDENT OF CARBONIC ANHYDRASE INACTIVATION. /THIADIAZIDES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 712
IRRESPECTIVE OR ULTIMATE MECHANISM, IT APPEARS THAT DIURETIC THIAZIDES RELAX PERIPHERAL ARTERIOLAR SMOOTH MUSCLE. /THIAZIDES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 712
CARBONIC ANHYDRASE INHIBITOR WITHOUT EXCESSIVE BICARBONATE EXCRETION WITH RESULTANT ACIDOSIS.
Rossoff, I.S. Handbook of Veterinary Drugs. New York: Springer Publishing Company, 1974., p. 107
For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for CHLOROTHIAZIDE (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page.