
1. Aller-chlor
2. Antihistaminico Llorens
3. Chlo-amine
4. Chlor-100
5. Chlor-trimeton
6. Chlor-tripolon
7. Chlorphenamine
8. Chlorpheniramine Maleate
9. Chlorpheniramine Tannate
10. Chlorpro
11. Chlorprophenpyridamine
12. Chlorspan 12
13. Chlortab-4
14. Cloro-trimeton
15. Efidac 24
16. Kloromin
17. Maleate, Chlorpheniramine
18. Piriton
19. Tannate, Chlorpheniramine
20. Teldrin
1. Chlorphenamine
2. 132-22-9
3. Teldrin
4. Chlorophenylpyridamine
5. Chlor-trimeton
6. Clorfeniramina
7. Phenetron
8. Haynon
9. Clorfenamina
10. Chloropheniramine-d4
11. Chlorpheniraminum
12. Polaronil
13. Chlorphenaminum
14. Chlorpheniramine Polistirex
15. Clofeniramina
16. 3-(4-chlorophenyl)-n,n-dimethyl-3-(pyridin-2-yl)propan-1-amine
17. 1-(p-chlorophenyl)-1-(2-pyridyl)-3-dimethylaminopropane
18. 3-(p-chlorophenyl)-3-(2-pyridyl)-n,n-dimethylpropylamine
19. Gamma-(4-chlorophenyl)-gamma-(2-pyridyl)propyldimethylamine
20. Gamma-(4-chlorophenyl)-n,n-dimethyl-2-pyridinepropanamine
21. 1-(p-chlorophenyl)-1-(2-pyridyl)-3-n,n-dimethylpropylamine
22. Chlo-amine
23. 3-(4-chlorophenyl)-n,n-dimethyl-3-pyridin-2-ylpropan-1-amine
24. Chlorphenamine [inn]
25. D-chlorpheniramine
26. 2-pyridinepropanamine, Gamma-(4-chlorophenyl)-n,n-dimethyl-
27. Chembl505
28. Chloropheniramine
29. Chlorprophenpyridamine
30. Dexchlorpheniramine Free Base
31. Allergican
32. Allergisan
33. Chloropiril
34. Cloropiril
35. Histadur
36. Chebi:52010
37. Chloroprophenpyridamine
38. 3u6io1965u
39. 25523-97-1 (free Base)
40. Chlorphenamine (inn)
41. 2-(p-chloro-alpha-(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)benzyl)pyridine
42. 3-(4-chlorophenyl)-n,n-dimethyl-3-(2-pyridyl)propan-1-amine
43. Aller-chlor
44. 4-chloropheniramine
45. 2-[p-chloro-alpha-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]benzyl]pyridine
46. Chlorphenamin
47. Telachlor
48. Clorfeniramina [italian]
49. Clorfenamina [inn-spanish]
50. Chlorphenaminum [inn-latin]
51. Pyridine, 2-(p-chloro-alpha-(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)benzyl)-
52. Hsdb 3032
53. 113-92-8
54. Einecs 205-054-0
55. Chlorphenamine [inn:ban]
56. Piriiton
57. Unii-3u6io1965u
58. Chlor-pro
59. [3h]chlorphenamine
60. Clofeniramina (tn)
61. [3h]chlorpheniramine
62. Chlorpheniramine-[d6]
63. S-(+)-chlorpheniramine
64. Prestwick0_000117
65. Prestwick1_000117
66. Prestwick2_000117
67. Prestwick3_000117
68. Ncgc00015227-04
69. 5-ht,n-acetyl
70. Schembl4219
71. Lopac0_000261
72. Oprea1_779072
73. Bspbio_000134
74. Chlorpheniramine [mi]
75. Divk1c_000596
76. Chlorpheniramine Maleate B.p.
77. Spbio_002073
78. Chlorpheniramine [hsdb]
79. Bpbio1_000148
80. Gtpl6976
81. Chlorphenamine [who-dd]
82. Chlorpheniramine [vandf]
83. Dtxsid0022804
84. Bdbm35938
85. Kbio1_000596
86. Chlorpheniramine-d6see C424303
87. Ninds_000596
88. 783ahi015x
89. Hms2090m21
90. Hms3428j07
91. Chlorpheniramine Polistirex [usan]
92. 2-pyridinepropanamine, .gamma.-(4-chlorophenyl)-n,n-dimethyl-
93. Hy-b0286
94. Bbl012285
95. Stk736174
96. Akos001650136
97. Ccg-108982
98. Db01114
99. Sb19135
100. Sdccgsbi-0050249.p002
101. Idi1_000596
102. Ncgc00015227-03
103. Ncgc00015227-05
104. Ncgc00015227-06
105. Ncgc00015227-09
106. Ncgc00015227-19
107. Ncgc00162108-01
108. Ncgc00162108-02
109. Chlorpheniramine Component Of Tuzistra
110. Cs-0009285
111. Ft-0665002
112. Ft-0772034
113. Tuzistra Componenet Of Chlorpheniramine
114. C06905
115. D07398
116. L000003
117. Q420133
118. W-108317
119. Brd-a04553218-050-03-0
120. Brd-a04553218-050-08-9
121. .gamma.-(4-chlorophenyl)-n,n-dimethyl-2-pyridinepropanamine
122. 2-(p-chloro-.alpha.-(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)benzyl)pyridine
123. N-[3-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-(2-pyridinyl)propyl]-n,n-dimethylamine #
124. N.-propanamine, 3-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-(2-pyridyl)-n,n-dimethyl-
125. (?)-3-(4-chlorophenyl)-n,n-dimethyl-3-(2-pyridinyl)propan-1-amine
126. 2-pyridinepropanamine, .gamma.-(4-chlorophenyl)-n,n-dimethyl-, (s)-
127. Pyridine, 2-[p-chloro-.alpha.-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]benzyl]-, (s)-(+)-
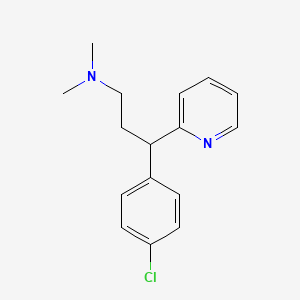
| Molecular Weight | 274.79 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C16H19ClN2 |
| XLogP3 | 3.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 274.1236763 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 274.1236763 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 16.1 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 19 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 249 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Chlorpheniramine maleate |
| Drug Label | Ed Chlortan Tablets are yellow, round, plain bottom, debossed "PH above 012" on top.... |
| Active Ingredient | Chlorpheniramine maleate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 12mg |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Avanthi |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Chlor-trimeton |
| Active Ingredient | Chlorpheniramine maleate; pseudoephedrine sulfate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 12mg; 8mg; 120mg |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Schering Plough |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Chlorpheniramine maleate |
| Drug Label | Ed Chlortan Tablets are yellow, round, plain bottom, debossed "PH above 012" on top.... |
| Active Ingredient | Chlorpheniramine maleate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 12mg |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Avanthi |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Chlor-trimeton |
| Active Ingredient | Chlorpheniramine maleate; pseudoephedrine sulfate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 12mg; 8mg; 120mg |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Schering Plough |
Anti-Allergic Agents; Antipruritics; Histamine H1 Antagonists
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
Antihistamines are indicated in the prophylactic and symptomatic treatment of perennial and seasonal allergic rhinitis, vasomotor rhinitis, and allergic conjunctivitis due to inhalant allergens and foods. /Antihistamines; Included in US product labeling/
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 15 th ed. Volume 1. Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., 1995. (Plus updates.), p. 303
Antihistamines are indicated for the symptomatic treatment of pruritus associated with allergic reactions and of mild, uncomplicated allergic skin manifestations of urticaria and angioedema, in dermatographism, and in urticaria associated with transfusions. /Antihistamines; Included in US product labeling/
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 15 th ed. Volume 1. Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., 1995. (Plus updates.), p. 303
Antihistamines are also used in the treatment of pruritus associated with pityriasis rosea. /Antihistamines; NOT included in US product labeling/
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 15 th ed. Volume 1. Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., 1995. (Plus updates.), p. 303
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for CHLORPHENIRAMINE (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Use is not recommended in newborn or premature infants because this age group has an increased susceptibility to anticholinergic side effects, such as central nervous system excitation, and an increased tendency toward convulsions. A paradoxical reaction characterized by hyperexcitability may occur in children taking antihistamines. /Antihistamines/
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 15 th ed. Volume 1. Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., 1995. (Plus updates.), p. 306
Dizziness, sedation, confusion, and hypotension may be more likely to occur in geriatric patients taking antihistamines. Geriatric patients are especially susceptible to the anticholinergic side effects, such as dryness of mouth and urinary retention (especially in males), of the antihistamines. If these side effects occur and continue or are severe, medication should probably be discontinued. /Antihistamines/
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 15 th ed. Volume 1. Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., 1995. (Plus updates.), p. 306
Prolonged use of antihistamines ... may decrease or inhibit salivary flow, thus contributing to the development of caries, periodontal disease, oral candidiasis, and discomfort. /Antihistamines/
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 15 th ed. Volume 1. Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., 1995. (Plus updates.), p. 306
ANTIHISTAMINE DRUGS MAY BE OF SOME USE IN MINIMIZING SERUM REACTIONS BUT ARE OF NO THERAPEUTIC VALUE...& MAY EVEN POTENTIATE TOXIC ACTION OF VENOM... /ANTIHISTAMINES/
Garner's Veterinary Toxicology. 3rd ed., rev. by E.G.C. Clarke and M.L. Clarke. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1967., p. 445
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for CHLORPHENIRAMINE (14 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
5. 5= EXTREMELY TOXIC: PROBABLE ORAL LETHAL DOSE (HUMAN) 5-50 MG/KG, BETWEEN 7 DROPS & 1 TEASPOONFUL FOR 70 KG PERSON (150 LB). /ANTIHISTAMINICS/
Gosselin, R.E., R.P. Smith, H.C. Hodge. Clinical Toxicology of Commercial Products. 5th ed. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1984., p. II-15
For the treatment of rhinitis, urticaria, allergy, common cold, asthma and hay fever.
In allergic reactions an allergen interacts with and cross-links surface IgE antibodies on mast cells and basophils. Once the mast cell-antibody-antigen complex is formed, a complex series of events occurs that eventually leads to cell-degranulation and the release of histamine (and other chemical mediators) from the mast cell or basophil. Once released, histamine can react with local or widespread tissues through histamine receptors. Histamine, acting on H1-receptors, produces pruritis, vasodilatation, hypotension, flushing, headache, tachycardia, and bronchoconstriction. Histamine also increases vascular permeability and potentiates pain. Chlorpheniramine, is a histamine H1 antagonist (or more correctly, an inverse histamine agonist) of the alkylamine class. It competes with histamine for the normal H1-receptor sites on effector cells of the gastrointestinal tract, blood vessels and respiratory tract. It provides effective, temporary relief of sneezing, watery and itchy eyes, and runny nose due to hay fever and other upper respiratory allergies.
Histamine H1 Antagonists
Drugs that selectively bind to but do not activate histamine H1 receptors, thereby blocking the actions of endogenous histamine. Included here are the classical antihistaminics that antagonize or prevent the action of histamine mainly in immediate hypersensitivity. They act in the bronchi, capillaries, and some other smooth muscles, and are used to prevent or allay motion sickness, seasonal rhinitis, and allergic dermatitis and to induce somnolence. The effects of blocking central nervous system H1 receptors are not as well understood. (See all compounds classified as Histamine H1 Antagonists.)
Anti-Allergic Agents
Agents that are used to treat allergic reactions. Most of these drugs act by preventing the release of inflammatory mediators or inhibiting the actions of released mediators on their target cells. (From AMA Drug Evaluations Annual, 1994, p475) (See all compounds classified as Anti-Allergic Agents.)
Antipruritics
Agents, usually topical, that relieve itching (pruritus). (See all compounds classified as Antipruritics.)
R06AB54
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
R - Respiratory system
R06 - Antihistamines for systemic use
R06A - Antihistamines for systemic use
R06AB - Substituted alkylamines
R06AB04 - Chlorphenamine
Absorption
Well absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract.
STUDIES IN MAN & EXPTL ANIMALS INDICATE THAT (3)H-CHLORPHENIRAMINE MALEATE IS RAPIDLY & QUANT ABSORBED FROM GUT. ALTHOUGH PLASMA LEVELS OF TOTAL RADIOACTIVITY ARE PROLONGED, PLASMA T/2 OF CHLORPHENIRAMINE IS ONLY 12-15 HR IN MAN & 3 HR IN DOG. T/2 IN MAN IS ABOUT 3 TIMES LONGER THAN THERAPEUTIC EFFECT...
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals Volume 3. London: The Chemical Society, 1975., p. 194
The H1 antagonists are well absorbed from the GI tract. Following oral administration, peak plasma concn are achieved in 2 to 3 hr and effects usually last 4 to 6 hr; however, some of the drugs are much longer acting ... . /Histamine Antagonists: H1 Antagonists/
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 584
H1 blockers are among the many drugs that induce hepatic microsomal enzymes, and they may facilitate their own metabolism. /Histamine Antagonists: H1 Antagonists/
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 584
Primarily hepatic via Cytochrome P450 (CYP450) enzymes.
MAIN SITE OF METABOLIC TRANSFORMATION IS LIVER. /ANTIHISTAMINES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 607
21-27 hours
IN MAN...PLASMA T/2 OF CHLORPHENIRAMINE IS...12-15 HR...ALTHOUGH PLASMA LEVELS OF TOTAL RADIOACTIVITY ARE PROLONGED...
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals Volume 3. London: The Chemical Society, 1975., p. 194
Elimination: 14 to 25 hours
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 15 th ed. Volume 1. Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., 1995. (Plus updates.), p. 305
Chlorpheniramine binds to the histamine H1 receptor. This blocks the action of endogenous histamine, which subsequently leads to temporary relief of the negative symptoms brought on by histamine.
Antihistamines used in the treatment of allergy act by competing with histamine for H1-receptor sites on effector cells. They thereby prevent, but do not reverse, responses mediated by histamine alone. Antihistamines antagonize, in varying degrees, most of the pharmacological effects of histamine, including urticaria and pruritus. Also, the anticholinergic actions of most antihistamines provide a drying effect on the nasal mucosa. /Antihistamines/
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 15 th ed. Volume 1. Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., 1995. (Plus updates.), p. 304
H1 antagonists inhibit most responses of smooth muscle to histamine. Antagonism of the constrictor action of histamine on respiratory smooth muscle is easily shown in vivo and in vitro. /Histamine Antagonists: H1 Antagonists/
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 582
H1 antagonists strongly block the action of histamine that results in increased permeability and formation of edema and wheal. /Histamine Antagonists: H1 Antagonists/
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 583
Within the vascular tree, the H1 antagonists inhibit both the vasoconstrictor effects of histamine and, to a degree, the more rapid vasodilator effects that are mediated by H1 receptors on endothelial cells. Residual vasodilatation reflects the involvement of H2 receptors on smooth muscle and can be suppressed only by the concurrent administration of an H2 antagonist. Effects of the histamine antagonists on histamine induced changes in systemic blood pressure parallel these vascular effects. /Histamine Antagonists: H1 Antagonists/
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 583
Many of the H1 antagonists tend to inhibit responses to acetylcholine that are mediated by muscarinic receptors. These atropine like actions are sufficiently prominent in some of the drugs to be manifest during clinical usage ... . /Histamine Antagonists: H1 Antagonists/
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 584