
1. Chlorphthalidolone
2. Chlortalidone
3. Hygroton
4. Oxodoline
5. Phthalamudine
6. Thalitone
1. 77-36-1
2. Chlortalidone
3. Phthalamudine
4. Chlorphthalidolone
5. Hygroton
6. Chlorthalidon
7. Phthalamodine
8. Natriuran
9. Thalitone
10. Chlorothalidone
11. Chlorphthalidone
12. Saluretin
13. Zambesil
14. Igroton
15. Isoren
16. Oradil
17. Renon
18. Hydro-long
19. Chlortalidonum
20. Oxodolin
21. Oksodolin (oxodolin)
22. Racemic Chlorthalidone
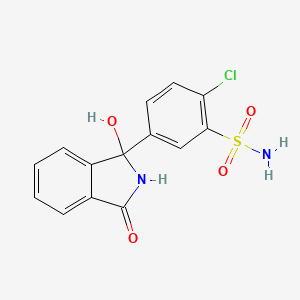
23. 2-chloro-5-(1-hydroxy-3-oxoisoindolin-1-yl)benzenesulfonamide
24. Demi-regroton
25. G-33182
26. 2-chloro-5-(1-hydroxy-3-oxo-1-isoindolinyl)benzenesulfonamide
27. 1-keto-3-(3'-sulfamyl-4'-chlorophenyl)-3-hydroxyisoindoline
28. 3-hydroxy-3-(4-chloro-3-sulfamylphenyl)phthalimidine
29. 2-chloro-5-(1-hydroxy-3-oxo-2h-isoindol-1-yl)benzenesulfonamide
30. 3-(4'-chloro-3'-sulfamoylphenyl)-3-hydroxyphthalimidine
31. 1-oxo-3-(3-sulfamyl-4-chlorophenyl)-3-hydroxyisoindoline
32. G 33182
33. Nsc-69200
34. Benzenesulfonamide, 2-chloro-5-(2,3-dihydro-1-hydroxy-3-oxo-1h-isoindol-1-yl)-
35. Chlortalidone [inn]
36. Benzenesulfonamide, 2-chloro-5-(1-hydroxy-3-oxo-1-isoindolinyl)-
37. 2-chloro-5-(1-hydroxy-3-oxo-2,3-dihydro-1h-isoindol-1-yl)benzenesulfonamide
38. Mls000069531
39. Chebi:3654
40. Q0mqd1073q
41. Clortalidone
42. Famolin
43. Higroton
44. Urolin
45. 2-chloro-5-(2,3-dihydro-1-hydroxy-3-oxo-1h-isoindol-1-yl)benzenesulfonamide
46. Clortalidona
47. Smr000058635
48. (+-)-hygroton
49. Clortalidone [dcit]
50. (+-)-chlorthalidone
51. Dsstox_cid_2812
52. 2-chloro-5-(1-hydroxy-3-oxo-2,3-dihydro-1h-isoindol-1-yl)benzene-1-sulfonamide
53. Dsstox_rid_76738
54. Dsstox_gsid_22812
55. Chlortalidonum [inn-latin]
56. Clortalidona [inn-spanish]
57. Thalitone (tn)
58. Hygroton (tn)
59. Chlorthalidone (usp)
60. Hsdb 3035
61. Sr-01000721929
62. Einecs 201-022-5
63. Nsc 69200
64. Chlortalidone (jan/inn)
65. Brn 0312295
66. Chlorthalidone [usan:usp]
67. Unii-q0mqd1073q
68. Oksodolin
69. Cas-77-36-1
70. Ncgc00016317-01
71. Prestwick_759
72. Regroton (salt/mix)
73. Combipres (salt/mix)
74. Spectrum_000146
75. Opera_id_138
76. (.+/-.)-hygroton
77. Prestwick0_000351
78. Prestwick1_000351
79. Prestwick2_000351
80. Prestwick3_000351
81. Spectrum2_000099
82. Spectrum3_000349
83. Spectrum4_000957
84. Spectrum5_000743
85. (.+/-.)-chlorthalidone
86. Chlortalidone [jan]
87. Chlorthalidone [mi]
88. Chembl1055
89. Schembl26234
90. Bspbio_000441
91. Bspbio_002017
92. Chlorthalidone [hsdb]
93. Chlorthalidone [usan]
94. Kbiogr_001574
95. Kbioss_000626
96. 5-22-07-00602 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
97. Chlortalidone [mart.]
98. Chlorthalidone (chlortalidone)
99. Chlorthalidone [vandf]
100. Divk1c_000731
101. Spectrum1500187
102. Spbio_000058
103. Spbio_002362
104. Chlortalidone [who-dd]
105. Chlortalidone [who-ip]
106. Bpbio1_000487
107. Gtpl7147
108. Chlorthalidone [usp-rs]
109. Dtxsid4022812
110. Bdbm25900
111. Hms502e13
112. Kbio1_000731
113. Kbio2_000626
114. Kbio2_003194
115. Kbio2_005762
116. Kbio3_001237
117. Ninds_000731
118. Hms1569g03
119. Hms1920m09
120. Hms2091e12
121. Hms2096g03
122. Hms2236d07
123. Hms3259h04
124. Hms3372a07
125. Hms3713g03
126. Pharmakon1600-01500187
127. Chlortalidone [ep Impurity]
128. Bcp27835
129. Nsc69200
130. Chlortalidone [ep Monograph]
131. Chlorthalidone [orange Book]
132. Tox21_110369
133. Ccg-38917
134. Mfcd00036257
135. Nsc756692
136. S3074
137. Stk686335
138. Chlortalidone 1.0 Mg/ml In Methanol
139. Chlortalidonum [who-ip Latin]
140. Chlorthalidone [usp Monograph]
141. Akos005599810
142. Tox21_110369_1
143. Db00310
144. Ks-1342
145. Nc00690
146. Nsc-756692
147. Clorpres Component Chlorthalidone
148. Idi1_000731
149. Kerledex Component Chlorthalidone
150. Regroton Component Chlorthalidone
151. Combipres Component Chlorthalidone
152. Ncgc00094616-01
153. Ncgc00094616-02
154. Ncgc00094616-03
155. Ncgc00094616-04
156. Ncgc00094616-07
157. Tenoretic Component Chlorthalidone
158. Ac-11367
159. Hy-15833
160. Chlorthalidone Component Of Clorpres
161. Chlorthalidone Component Of Kerledex
162. Chlorthalidone Component Of Regroton
163. Sbi-0051313.p003
164. Chlorthalidone Component Of Combipres
165. Chlorthalidone Component Of Tenoretic
166. Db-056211
167. Lopressidone Component Chlorthalidone
168. [(3,5-difluorophenyl)amino](oxo)aceticacid
169. Ab00051946
170. Demi-regroton Component Chlorthalidone
171. C76474
172. Chlorthalidone Component Of Lopressidone
173. D00272
174. Ab00051946_12
175. Chlorthalidone Component Of Demi-regroton
176. 036c257
177. A839067
178. Q425289
179. Sr-01000721929-2
180. Sr-01000721929-3
181. W-104322
182. Brd-a26384407-001-05-3
183. Brd-a26384407-001-15-2
184. 2-chloro-5-(1-hydroxy-3-oxo-1h-isoindolinyl)benzenesulfonamide
185. Chlorthalidone, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
186. 2-chloro-5-(1,3-dihydroxy-1h-isoindol-1-yl)benzene-1-sulfonamide
187. Benzenesulfonamide,3-dihydro-1-hydroxy-3-oxo-1h-isoindol-1-yl)-
188. Chlorthalidone, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
189. 2-chloro-5-(1-hydroxy-3-oxo-2,3-dihydro-1h-isoindol-1-yl)benzenesulfonamide #
190. 2-chloro-5-[(1s)-1-hydroxy-3-oxo-isoindolin-1-yl]benzenesulfonamide;chlorthalidone
191. Chlortalidone For Peak Identification, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
192. 74658-80-3
| Molecular Weight | 338.8 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C14H11ClN2O4S |
| XLogP3 | 0.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 338.0128057 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 338.0128057 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 118 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 22 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 564 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Chlorthalidone |
| PubMed Health | Chlorthalidone (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | Chlorthalidone is an oral antihypertensive/diuretic. It is a monosulfamyl diuretic that differs chemically from thiazide diuretics in that a double-ring system is incorporated in its structure. It is 2-chloro-5(1-hydroxy-3-oxo-1- isoindolinyl) benzen... |
| Active Ingredient | Chlorthalidone |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 25mg; 50mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mylan |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Thalitone |
| PubMed Health | Chlorthalidone (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | Thalitone (chlorthalidone USP) is an antihypertensive/diuretic supplied as 15 mg tablets for oral use. It is a monosulfamyl diuretic that differs chemically from thiazide diuretics in that a double ring system is incorporated in its structure. It i... |
| Active Ingredient | Chlorthalidone |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 15mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Citron Pharma |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Chlorthalidone |
| PubMed Health | Chlorthalidone (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | Chlorthalidone is an oral antihypertensive/diuretic. It is a monosulfamyl diuretic that differs chemically from thiazide diuretics in that a double-ring system is incorporated in its structure. It is 2-chloro-5(1-hydroxy-3-oxo-1- isoindolinyl) benzen... |
| Active Ingredient | Chlorthalidone |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 25mg; 50mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mylan |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Thalitone |
| PubMed Health | Chlorthalidone (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | Thalitone (chlorthalidone USP) is an antihypertensive/diuretic supplied as 15 mg tablets for oral use. It is a monosulfamyl diuretic that differs chemically from thiazide diuretics in that a double ring system is incorporated in its structure. It i... |
| Active Ingredient | Chlorthalidone |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 15mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Citron Pharma |
Antihypertensive Agents; Diuretics, Sulfamyl
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
...ORALLY EFFECTIVE DIURETIC USEFUL IN TREATMENT OF EDEMA ASSOC WITH CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE, RENAL DISEASE, HEPATIC CIRRHOSIS, PREGNANCY, OBESITY, & PREMENSTRUAL SYNDROME. DIURETIC EFFECTS START WITHIN 2 HR AFTER ADMIN, REACH PEAK IN 6 HR, & PERSIST FOR 48 TO 72 HR.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 871
MOST OF THIAZIDES ARE GIVEN IN DIVIDED DAILY DOSES FOR TREATMENT OF HYPERTENSION, BUT SINGLE DAILY DOSE MAY BE PREFERABLE FOR MOBILIZATION OF EDEMA FLUID. ...CHLORTHALIDONE...SHOULD BE GIVEN LESS FREQUENTLY, SINCE.../IT HAS/ DURATION OF ACTION LONGER THAN 24 HR.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 832
CHLORTHALIDONE ALSO EXERTS ANTIHYPERTENSIVE EFFECT & MAY BE ADMIN WITH OTHER AGENTS, SUCH AS RESERPINE, GANGLIONIC BLOCKING AGENTS, HYDRALAZINE, & GUANETHIDINE. SINCE.../IT/ CONTAINS SULFONAMIDE GROUP, ITS PHARMACOLOGICAL ACTIONS & MANY OF ITS UNTOWARD EFFECTS ARE SIMILAR TO THOSE OF OTHER ORALLY ADMIN DIURETICS.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 871
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for CHLORTHALIDONE (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
CHLORTHALIDONE IS CONTRAINDICATED IN PT WITH SEVERE RENAL OR HEPATIC DISEASE. PT ON THIS DRUG SHOULD BE WATCHED CLOSELY FOR SYMPTOMS OF RENAL DAMAGE OR OF ELECTROLYTE DISTURBANCE.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 871
May suppress lactation ... /Thiazide diuretics; from table/
Young, L.Y., M.A. Koda-Kimble (eds.). Applied Therapeutics. The Clinical Use of Drugs. 6th ed. Vancouver, WA., Applied Therapeutics, Inc. 1995., p. 45-29
Many experts consider diuretics contraindicated in pregnancy except for patients with heart disease, since they do not prevent or alter course of toxemia and may decrease placental perfusion. /Chlorothiazide; from table/
Young, L.Y., M.A. Koda-Kimble (eds.). Applied Therapeutics. The Clinical Use of Drugs. 6th ed. Vancouver, WA., Applied Therapeutics, Inc. 1995., p. 45-9
Maternal Medication usually Compatible with Breast-Feeding: Chlorthalidone: Reported Sign or Symptom in Infant or Effect on Lactation: Excreted slowly. /from Table 6/
Report of the American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Drugs in Pediatrics 93 (1): 140 (1994)
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for CHLORTHALIDONE (14 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
3. 3= MODERATELY TOXIC: PROBABLE ORAL LETHAL DOSE (HUMAN) 0.5-5 G/KG, BETWEEN 1 OZ & 1 PINT (OR 1 LB) FOR 70 KG PERSON (150 LB).
Gosselin, R.E., H.C. Hodge, R.P. Smith, and M.N. Gleason. Clinical Toxicology of Commercial Products. 4th ed. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1976., p. II-239
Chlorthalidone is indicated in the management of hypertension either as the sole therapeutic agent or to enhance the effect of other antihypertensive drugs in the more severe forms of hypertension. Chlorthalidone is indicated as adjunctive therapy in edema associated with congestive heart failure, hepatic cirrhosis, and corticosteroid and estrogen therapy. Chlorthalidone has also been found useful in edema due to various forms of renal dysfunction, such as nephrotic syndrome, acute glomerulonephritis, and chronic renal failure.
FDA Label
Sodium Chloride Symporter Inhibitors
Agents that inhibit SODIUM CHLORIDE SYMPORTERS. They act as DIURETICS. Excess use is associated with HYPOKALEMIA. (See all compounds classified as Sodium Chloride Symporter Inhibitors.)
Diuretics
Agents that promote the excretion of urine through their effects on kidney function. (See all compounds classified as Diuretics.)
Antihypertensive Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of acute or chronic vascular HYPERTENSION regardless of pharmacological mechanism. Among the antihypertensive agents are DIURETICS; (especially DIURETICS, THIAZIDE); ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS; ADRENERGIC ALPHA-ANTAGONISTS; ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS; CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS; GANGLIONIC BLOCKERS; and VASODILATOR AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Antihypertensive Agents.)
C - Cardiovascular system
C03 - Diuretics
C03B - Low-ceiling diuretics, excl. thiazides
C03BA - Sulfonamides, plain
C03BA04 - Chlortalidone
Route of Elimination
Approximately 50% of the administered dose is excreted unmetabolized through the kidney, and excretion is characterized by biphasic elimination with a rapid phase followed by a slow secretory phase.
Volume of Distribution
Chlorthalidone has been shown to rapidly concentrate within erythrocytes and subsequently equilibrate via a slow diffusion back into the serum compartment, resulting in a large volume of distribution.
BIOCHEM STUDIES SUGGEST THAT PROLONGED DURATION OF ACTION IS DUE TO SLOW GI ABSORPTION & ENTEROHEPATIC RECIRCULATION. DRUG IS EXCRETED UNCHANGED BY KIDNEY.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 871
MOST /THIAZIDE/ COMPD ARE RAPIDLY EXCRETED WITHIN 3 TO 6 HR. /THIAZIDE COMPD/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 831
STUDY OF DOSE-DEPENDENT URINARY EXCRETION OF CHLORTHALIDONE.
FLEUREN HLJ ET AL; DOSE-DEPENDENT URINARY EXCRETION OF CHLORTHALIDONE; CLIN PHARMACOL THER 25(6) 806-812 (1979)
Liver
40-50 hours
Chlorthalidone prevents reabsorption of sodium and chloride through inhibition of the Na+/Cl- symporter in the cortical diluting segment of the ascending limb of the loop of Henle. Reduction of sodium reabsorption subsequently reduces extracellular fluid and plasma volume via an osmotic, sodium-driven diuresis. By increasing the delivery of sodium to the distal renal tubule, Chlorthalidone indirectly increases potassium excretion via the sodium-potassium exchange mechanism. The exact mechanism of chlorthalidone's anti-hypertensive effect is under debate, however, it is thought that increased diuresis results in decreased plasma and extracellular fluid volume which therefore requires decreased cardiac output and overall lowers blood pressure. Chlorthalidone has also been shown to decrease platelet aggregation and vascular permeability, as well as promote angiogenesis in vitro, which is thought to be partly the result of reductions in carbonic anhydrasedependent pathways. These pathways may play a role in chlorthalidone's cardiovascular risk reduction effects.
...ACT BY INHIBITING RENAL TUBULAR TRANSPORT OF VARIOUS IONS.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 871
Decreased plasma volume and decreased extracellular fluid volume; decreased cardiac output initially, followed by decreased total peripheral resistance with normalization of cardiac output ... /from table/
Ellenhorn, M.J., S. Schonwald, G. Ordog, J. Wasserberger. Ellenhorn's Medical Toxicology: Diagnosis and Treatment of Human Poisoning. 2nd ed. Baltimore, MD: Williams and Wilkins, 1997., p. 552
...ANTIHYPERTENSIVE EFFECT OF CHLORTHALIDONE IS THOUGHT TO BE DUE TO DECR CARDIAC OUTPUT.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 862
The exact mechanism for reduction of arterial blood pressure by diuretics is not certain. Initially the drugs decrease extracellular volume and cardiac output. However, the hypotensive effect is maintained during long-term therapy because of reduced vascular resistance ... /Diuretics/
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B. Molinoff, R.W. Ruddon, A.G. Goodman (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 9th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 1996., p. 781
For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for CHLORTHALIDONE (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.