

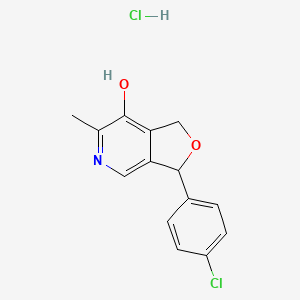

1. 1,3-dihydro-6-methyl-7-hydroxy-3-(4-chlorophenyl)furo(3,4-d)pyridine
2. Bn 1270
3. Bn-1270
4. Cicletanide
5. Cicletanine
6. Cycletanide
7. Justar
8. Tenstaten
1. 82747-56-6
2. Cicletanine Hcl
3. T0sy6373oq
4. 3-(4-chlorophenyl)-6-methyl-1,3-dihydrofuro[3,4-c]pyridin-7-ol;hydrochloride
5. Cicletanine Hydrochloride (jan)
6. Cicletanine Hydrochloride [jan]
7. Unii-t0sy6373oq
8. Tenstaten (tn)
9. Justar (tn)
10. Schembl387011
11. Win-90000 Hcl
12. Win 90,000 Hcl
13. Dtxsid801002869
14. Cicletanine Hydrochloride [mi]
15. Akos030255878
16. Cicletanine Hydrochloride [mart.]
17. Cicletanine Hydrochloride [who-dd]
18. Ft-0665030
19. D07697
20. Q27289519
21. 3-(4-chlorophenyl)-6-methyl-1h,3h-furo[3,4-c]pyridin-7-ol Hydrochloride
22. 3-(4-chlorophenyl)-6-methyl-1,3-dihydrofuro[3,4-c]pyridin-7-ol,hydrochloride
23. 3-(4-chlorophenyl)-6-methyl-1,3-dihydrofuro[3,4-c]pyridin-7-ol--hydrogen Chloride (1/1)
24. Furo(3,4-c)pyridin-7-ol, 3-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-6-methyl-, Hydrochloride
25. Furo(3,4-c)pyridin-7-ol, 3-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-6-methyl-, Hydrochloride, (+/-)-
| Molecular Weight | 298.2 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C14H13Cl2NO2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 297.0323340 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 297.0323340 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 42.4 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 19 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 294 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
Diuretics
Agents that promote the excretion of urine through their effects on kidney function. (See all compounds classified as Diuretics.)
Antihypertensive Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of acute or chronic vascular HYPERTENSION regardless of pharmacological mechanism. Among the antihypertensive agents are DIURETICS; (especially DIURETICS, THIAZIDE); ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS; ADRENERGIC ALPHA-ANTAGONISTS; ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS; CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS; GANGLIONIC BLOCKERS; and VASODILATOR AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Antihypertensive Agents.)
Anti-Arrhythmia Agents
Agents used for the treatment or prevention of cardiac arrhythmias. They may affect the polarization-repolarization phase of the action potential, its excitability or refractoriness, or impulse conduction or membrane responsiveness within cardiac fibers. Anti-arrhythmia agents are often classed into four main groups according to their mechanism of action: sodium channel blockade, beta-adrenergic blockade, repolarization prolongation, or calcium channel blockade. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Arrhythmia Agents.)