
1. Altramet
2. Biomet
3. Biomet400
4. Cimetidine Hcl
5. Cimetidine Hydrochloride
6. Eureceptor
7. Hcl, Cimetidine
8. Histodil
9. Hydrochloride, Cimetidine
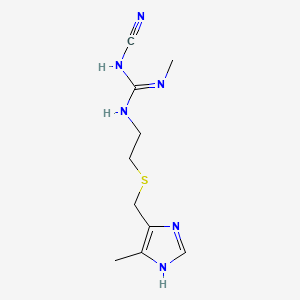
10. N-cyano-n'-methyl-n''-(2-(((5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-yl)methyl)thio)ethyl)guanidine
11. Sk And F 92334
12. Sk And F-92334
13. Sk And F92334
14. Skf 92334
15. Skf-92334
16. Skf92334
17. Tagamet
1. 51481-61-9
2. Tagamet
3. Acinil
4. Ulcedin
5. Eureceptor
6. Gastromet
7. Dyspamet
8. Tametin
9. Ulcimet
10. Cimal
11. Ulcedine
12. Ulcomedina
13. Cimetag
14. Tratul
15. Skf-92334
16. Acibilin
17. Cimetum
18. Edalene
19. Ulcomet
20. Ulhys
21. Tagamet Hb
22. Tagamet Hb 200
23. Cimetidina
24. Cimetidinum
25. Valmagen
26. Brumetidina
27. N-cyano-n'-methyl-n''-[2-[[(4-methyl-1h-imidazol-5-yl)methyl]thio]ethyl]guanidine
28. Skf 92334
29. 1-cyano-2-methyl-3-[2-[(5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-yl)methylsulfanyl]ethyl]guanidine
30. Stomedine
31. Aciloc
32. 2-cyano-1-methyl-3-(2-(((5-methylimidazol-4-yl)methyl)thio)ethyl)guanidine
33. 1-cyano-2-methyl-3-(2-(((5-methyl-4-imidazolyl)methyl)thio)ethyl)guanidine
34. Nsc-335308
35. Chebi:3699
36. N-cyano-n'-methyl-n''-(2-(((5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-yl)methyl)thio)ethyl)guanidine
37. Chembl30
38. Metracin
39. Brumetadina
40. 2-cyano-1-methyl-3-(2-{[(5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-yl)methyl]sulfanyl}ethyl)guanidine
41. Mls000069791
42. 76181-71-0
43. Gastrobitan
44. Ulcestop
45. Ulcofalk
46. Evicer
47. Peptol
48. 80061l1wgd
49. 51481-61-9 (free)
50. Guanidine, N-cyano-n'-methyl-n''-(2-(((5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-yl)methyl)thio)ethyl)-
51. Guanidine, N-cyano-n'-methyl-n''-[2-[[(5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-yl)methyl]thio]ethyl]-
52. Guanidine, N-cyano-n'-methyl-n''-[2-[[(5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-yl)methyl]thio]ethyl]-, (z)-
53. Nsc 335308
54. 2984-61-4
55. Ncgc00015240-06
56. Smr000038895
57. Cimetidine 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
58. Dsstox_cid_329
59. 2-cyano-1-methyl-3-(2-{[(5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-yl)methyl]thio}ethyl)guanidine
60. Dsstox_rid_75517
61. Guanidine, N''-cyano-n-methyl-n'-(2-(((5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-yl)methyl)thio)ethyl)-
62. N''-cyano-n-methyl-n'-(2-{[(5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-yl)methyl]thio}ethyl)guanidine
63. N-cyano-n'-methyl-n''-(2-([(5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-yl)methyl]sulfanyl)ethyl)guanidine
64. Cimetidinum [inn-latin]
65. Dsstox_gsid_20329
66. Cimetidina [inn-spanish]
67. Drg-0150
68. (e)-2-cyano-1-methyl-3-(2-(((5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-yl)methyl)thio)ethyl)guanidine
69. (z)-3-cyano-1-methyl-2-(2-{[(5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-yl)methyl]sulfanyl}ethyl)guanidine
70. 1-cyano-2-methyl-3-(2-{[(5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-yl)methyl]sulfanyl}ethyl)guanidine
71. 2-cyano-1-methyl-3-[2-[(5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-yl)methylsulfanyl]ethyl]guanidine
72. Guanidine, N''-cyano-n-methyl-n'-[2-[[(5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-yl)methyl]thio]ethyl]-
73. Tagamet (tn)
74. Ccris 3247
75. Equaline Acid Reducer
76. Hsdb 3917
77. Topcare Heartburn Relief
78. Sr-01000075260
79. Sr-05000001434
80. Fpf 1002
81. Einecs 257-232-2
82. Mfcd00133296
83. Cemitidine
84. Metidine
85. Unii-80061l1wgd
86. 1-cyano-2-methyl-3-(2-((5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-yl)methylthio)ethyl)guanidine
87. 1-cyano-2-methyl-3-[2-[(5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-yl)methylthio]ethyl]guanidine
88. Cimetidine,(s)
89. Prestwick_65
90. Cimetidine (tagamet)
91. Cimetidine [usan:usp:inn:ban:jan]
92. Cimetidine A
93. Spectrum_000495
94. Tocris-0902
95. Cimetidine [mi]
96. Opera_id_314
97. Cimetidine [inn]
98. Cimetidine [jan]
99. Prestwick3_000026
100. Spectrum2_000782
101. Spectrum3_001389
102. Spectrum4_000812
103. Spectrum5_001541
104. Cimetidine [hsdb]
105. Cimetidine [iarc]
106. Cimetidine [usan]
107. Lopac-c-4522
108. Cimetidine [vandf]
109. Upcmld-dp029
110. 2-cyano-1-methyl-3-[2-(5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-yl-methylthio)ethyl]guanidine
111. C 4522
112. Cimetidine [mart.]
113. Schembl1093
114. Schembl1094
115. Skf-92334; Tagamet
116. Cimetidine [usp-rs]
117. Cimetidine [who-dd]
118. Cimetidine [who-ip]
119. Guanidine, N-cyano-n'-methyl-n''-(2-(((5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-yl)methyl)thio) Ethyl)-
120. Lopac0_000293
121. Bspbio_000091
122. Bspbio_002978
123. Kbiogr_001323
124. Kbioss_000975
125. Us9138393, Cimetidine
126. Us9144538, Cimetidine
127. Mls001148596
128. Mls002153265
129. Mls002154178
130. Divk1c_000166
131. Spectrum1500684
132. Spbio_000884
133. Bpbio1_000101
134. Cimetidine (jp17/usp/inn)
135. Gtpl1231
136. Cimetidine [orange Book]
137. Dtxsid4020329
138. Schembl11282982
139. Upcmld-dp029:001
140. Bdbm22889
141. Cimetidine For System Suitability
142. Hms500i08
143. Kbio1_000166
144. Kbio2_000975
145. Kbio2_003543
146. Kbio2_006111
147. Kbio3_002198
148. Cimetidine [ep Monograph]
149. Cimetidine For Peak Identification
150. Ninds_000166
151. Bdbm181119
152. Cimetidine [usp Monograph]
153. Hms1921c14
154. Hms2089o03
155. Hms2092i14
156. Hms2095e13
157. Hms2232f16
158. Hms3259m15
159. Hms3260l08
160. Hms3267a03
161. Hms3369l10
162. Hms3414i17
163. Hms3651e21
164. Hms3678i17
165. Hms3712e13
166. Hms3750i05
167. Hms3884i12
168. Pharmakon1600-01500684
169. Cimetidine 1.0 Mg/ml In Methanol
170. Cimetidinum [who-ip Latin]
171. Ex-a1088
172. Tox21_110106
173. Tox21_201160
174. Tox21_500293
175. Bdbm50103595
176. Bdbm50403559
177. Ccg-40160
178. Nsc335308
179. Nsc757428
180. S1845
181. Stk528249
182. Zinc18115268
183. 1-cyano-2-methyl-3-[2-[[(5-methylimidazol-4-yl)methyl]thio]ethyl]guanidine
184. Akos005460997
185. Akos015900557
186. Akos015951369
187. Akos016003398
188. Akos016340377
189. Akos026749950
190. Akos032949548
191. Tox21_110106_1
192. Ab03708
193. Ac-8100
194. Ccg-204388
195. Ccg-220026
196. Ccg-221597
197. Db00501
198. Ks-5087
199. Lp00293
200. Nc00501
201. Nsc 757428
202. Nsc-757428
203. Sdccgsbi-0050281.p005
204. Idi1_000166
205. N''-cyano-n-methyl-n'-(2-{[(5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-yl)methyl]sulfanyl}ethyl)guanidine
206. N''-cyano-n-methyl-n'-[2-[(5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-yl)methylthio]ethyl]guanidine
207. N-cyano-n'-methyl-[2-[[[5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-yl]methyl]thio]ethyl]guanidine
208. Ncgc00015240-01
209. Ncgc00015240-02
210. Ncgc00015240-03
211. Ncgc00015240-04
212. Ncgc00015240-05
213. Ncgc00015240-07
214. Ncgc00024859-01
215. Ncgc00024859-02
216. Ncgc00024859-03
217. Ncgc00024859-04
218. Ncgc00024859-05
219. Ncgc00091439-01
220. Ncgc00091439-02
221. Ncgc00091439-03
222. Ncgc00091439-04
223. Ncgc00091439-05
224. Ncgc00091439-07
225. Ncgc00091439-10
226. Ncgc00185989-01
227. Ncgc00188961-01
228. Ncgc00258712-01
229. Ncgc00260978-01
230. Hy-14289
231. Nci60_002936
232. Sbi-0050281.p004
233. Db-051971
234. Eu-0100293
235. Ft-0602955
236. Sw196380-2
237. C06952
238. D00295
239. F16651
240. Ab00052157-03
241. Ab00052157_04
242. Ab00052157_05
243. 481c619
244. A828616
245. L000186
246. L003827
247. L013434
248. Q409492
249. Sr-05000001750
250. Q-200855
251. Q-200856
252. Sr-01000075260-1
253. Sr-01000075260-3
254. Sr-05000001434-1
255. Sr-05000001434-2
256. Sr-05000001750-1
257. Brd-k18618618-001-01-6
258. Brd-k34157611-001-04-6
259. Brd-k34157611-001-07-9
260. Z1259192068
261. Cimetidine, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
262. Cimetidine, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
263. 1-ethyl-2,3-dimethylimidazolium Tosylate, 98% [edimim] [tos]
264. 1-cyan-2-methyl-3-(2-{[(5-methylimidazol-4-yl)methyl]thio}ethyl)guanidin
265. Cimetidine, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
266. N"-cyano-n-methyl-n'-[2-(5-methylimidazol-4-ylmethylthio)ethyl]-guanidine
267. N"-cyano-n-methyl-n'-[2-(5-methylimidazol-4-ylmethylthio)ethyl]guanidine
268. N-cyano-n'-methyl-n"-[2-((4-methyl-5-imidazolyl)methylthio)ethyl]guanidine
269. N-cyano-n'-methyl-n"-[2-((5-methyl-4-imidazolyl)methylthio)ethyl]guanidine
270. N-cyano-n'-methyl-n"-[2-(5-methyl-4-imidazolylmethylthio)ethyl]guanidine
271. (z)-1-cyano-2-methyl-3-(2-{[(5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-yl)methyl]sulfanyl}ethyl)guanidine
272. (z)-n''-cyano-n-methyl-n'-(2-{[(5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-yl)methyl]sulfanyl}ethyl)guanidine
273. 2-chloro-5-(1-hydroxy-3-oxo-2,3-dihydro-1h-isoindol-1-yl)-benzenesulfonamide(cimetidine)
274. 2-cyano-1-methyl-3-(2-(((5-methylimidazol-4-yl)methyl)thio)ethyl)-guanidine
275. 2-methyl-8-phenethyl-imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-3-carboxylic Acid Methyl Ester(cimetidine)
276. 2-methylamino-2-[2-(4-methyl-1h-5-imidazolylmethylsulfanyl)ethylamino]-(e)-1-imino Cyanide
277. 3-cyano-2-methyl-1-[2-[(5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-yl)methylsulfanyl]ethyl]guanidine
278. 4-(((2-(((cyanoamino)(methylamino)methylene)amino)ethyl)thio)methyl)-5-methyl-1h-imidazole
279. Cimetidine For Peak Identification, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
280. Cimetidine For System Suitability, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
281. Guanidine, N-cyano-n'-methyl-n''-[2-[[5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-yl)methyl]thio]ethyl]-
282. N''-cyano-n-methyl-n'-(2-((5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-yl)-methylthio)ethyl)guanidine
283. N-cyano-n'-methyl-n"- [2-((5-methyl-4-imidazolyl)methylthio)ethyl]guanidine
284. N-cyano-n'-methyl-n"-[2-((4-methyl-5-imidazolyl) Methylthio)ethyl]guanidine
285. N-cyano-n'-methyl-n"-[2-((4-methyl-5-imidazolyl)- Methylthio)ethyl]guanidine
286. N-cyano-n'-methyl-n"-[2-((4-methyl-5-imidazolyl)-methylthio)ethyl]guanidine
287. N-cyano-n'-methyl-n"-[2-((4-methyl-5-imidazolyl)methyl-thio)ethyl]guanidine
288. N-cyano-n'-methyl-n"-[2-((4-methyl-5-imidazolyl)methylthio)ethyl) Guanidine
289. N-cyano-n'-methyl-n"-[2-((5-methyl-4-imidazolyl)methylthio)-ethyl]guanidine
290. N-cyano-n'-methyl-n"-[2-((5-methyl-4-imidazolyl)methylthio)ethyl]-guanidine
291. N-cyano-n'-methyl-n"-[2-{(5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-yl)methylthio}ethyl]guanidine
292. N-cyano-n'-methyl-n''-(2-([(5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-yl)methyl]sulfanyl)ethyl)guanidine #
293. N-cyano-n'-methyl-n''-[2-[(5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-yl)methyl]thio]ethyl]guanidine
294. N-cyano-n'-methyl-n''-[2-[[(5-methylimidazol-4-yl]methyl]thio]ethyl)guanidine
295. N-cyano-n'-methyl-n-"-[2-((4-methyl-5-imidazolyl)methylthio)ethyl]guanidine
296. N-methyl-n'-{2-[(5-methylimidazol-4-yl)-methylthio]-ethyl}-n"-cyanoguanidine
297. N-methyl-n-[2-(5-methyl-1h-4-imidazolylmethylsulfanyl)ethyl]-1-cyanoiminomethanediamine
298. N-methyl-n-[2-(5-methyl-1h-4-imidazolylmethylsulfanyl)ethyl]imino(-n-cyano)methanediaminem
299. N-tert-butyl-n''''''''-[4-(1h-imidazol-4-yl)-phenyl]-formamidine(cimetidine)
300. (cimetidine) N-methyl-n''''''''-[2-(5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-ylmethylsulfanyl)-ethyl]-guanidine,cyanide
301. (cimetidine) N-methyl-n-[2-(5-methyl-1h-4-imidazolylmethylsulfanyl)ethyl]cyanoiminomethanediamine
302. (cimetidine)n-methyl-n-[2-(5-methyl-1h-4-imidazolylmethylsulfanyl)ethyl]cyanomethyliminomethanediamine
303. 2-methylamino-2-[2-(5-methyl-1h-4-imidazolylmethylsulfanyl)ethylamino]-(z)-1-imino Cyanide(cimetidine)
304. Guanidine,n-cyano-n'-methyl-n''-[2-[[(5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-yl)methyl]thio]ethyl]-,(z)-
305. N''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''-cyano-n-methyl-n''''''''''''''''-(2-{[(5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-yl)methyl]thio}ethyl)guanidine
306. N''''''''''''''''-cyano-n-methyl-n''''''''-({[(5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-yl)methyl]thio}methyl)guanidine(cimetidine)
307. N''''''''''''''''-cyano-n-methyl-n''''''''-(2-{[(5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-yl)methyl]-lambda~4~-sulfanyl}ethyl)guanidine
308. N''''''''''''''''-cyano-n-methyl-n''''''''-(2-{[(5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-yl)methyl]thio}ethyl)guanidine
309. N''''''''''''''''-cyano-n-methyl-n''''''''-(2-{[(5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-yl)methyl]thio}ethyl)guanidine (cimetidine)
310. N''''''''''''''''-cyano-n-methyl-n''''''''-(2-{[(5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-yl)methyl]thio}ethyl)guanidine(cimetidine)
311. N-cyano-n''''''''-methyl-n''''''''''''''''-(2-(((5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-yl) Methyl)thio)ethyl)guanidine(cimetidine)
312. N-cyanomethyl-n''''''''-methyl-n''''''''''''''''-[2-(5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-ylmethylsulfanyl)-ethyl]-guanidine ( Cimetidine)
313. N-methyl-n''''''''-[2-(5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-ylmethylsulfanyl)-ethyl]-cyanoguanidine(cimetidine)
314. N-methyl-n''''''''-[2-(5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-ylmethylsulfanyl)-ethyl]-n''''''''''''''''-cyano-guanidine
315. N-methyl-n''''''''-[2-(5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-ylmethylsulfanyl)-ethyl]-n''''''''''''''''-cyano-guanidine(cimetidine)
316. N-methyl-n''''''''-cyano-n''''''''''''''''-[2-(5-methyl-1h-imidazol-4-ylmethylsulfanyl)-ethyl]-guanidine
317. N-methyl-n-[2-(5-methyl-1h-4-imidazolylmethylsulfanyl)ethyl]cyanoiminomethanediamine (cimetidine)
| Molecular Weight | 252.34 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C10H16N6S |
| XLogP3 | 0.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 252.11571571 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 252.11571571 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 114 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 17 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 296 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Cimetidine |
| PubMed Health | Cimetidine |
| Drug Classes | Antiulcer, Gastric Acid Secretion Inhibitor |
| Drug Label | Cimetidine is a histamine H2-receptor antagonist. Chemically it is N"-cyano-N-methyl-N'-[2-[[(5-methyl-1H-imidazol-4-yl)methyl]thio]-ethyl]guanidine. Its structural formula is:Cimetidine contains an imidazole ring, and is chemically related to h |
| Active Ingredient | Cimetidine |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 300mg; 200mg; 100mg; 800mg; 400mg |
| Market Status | Over the Counter; Prescription |
| Company | Ivax Sub Teva Pharms; Teva; Apotex; Perrigo; Contract Pharmacal; Pliva; Mylan; Dava Pharms |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Tagamet hb |
| Active Ingredient | Cimetidine |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 200mg |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Medtech Prods |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Cimetidine |
| PubMed Health | Cimetidine |
| Drug Classes | Antiulcer, Gastric Acid Secretion Inhibitor |
| Drug Label | Cimetidine is a histamine H2-receptor antagonist. Chemically it is N"-cyano-N-methyl-N'-[2-[[(5-methyl-1H-imidazol-4-yl)methyl]thio]-ethyl]guanidine. Its structural formula is:Cimetidine contains an imidazole ring, and is chemically related to h |
| Active Ingredient | Cimetidine |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 300mg; 200mg; 100mg; 800mg; 400mg |
| Market Status | Over the Counter; Prescription |
| Company | Ivax Sub Teva Pharms; Teva; Apotex; Perrigo; Contract Pharmacal; Pliva; Mylan; Dava Pharms |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Tagamet hb |
| Active Ingredient | Cimetidine |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 200mg |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Medtech Prods |
Adjuvants, Immunologic; Analgesics, Non-Narcotic; Anti-Ulcer Agents; Enzyme Inhibitors; Histamine H2 Antagonists
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
IN MAN, A SINGLE DOSE (300 MG) WILL INHIBIT BASAL (FASTING) SECRETION AND ALSO SECRETION INDUCED BY SOLID, LIQ, OR PEPTONE MEALS, SHAM FEEDING, FUNDIC DISTENTION, PENTAGASTRIN, BETHANECHOL, INSULIN, AND CAFFEINE, AS WELL AS THE PHYSIOLOGICAL STIMULUS PROVIDED BY EATING. ... THIS SPECTRUM INCL THE CEPHALIC OR VAGAL PHASE.
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 631
CIMETIDINE IS THE PREFERRED ALTERNATIVE FOR MANY PATIENTS WHO CANNOT OR WILL NOT TOLERATE AN INTENSIVE, PROLONGED ANTACID REGIMEN.
American Medical Association, Council on Drugs. AMA Drug Evaluations Annual 1994. Chicago, IL: American Medical Association, 1994., p. 899
Cimetidine is a useful alternative to antacids in preventing aspiration pneumonitis during childbirth and elective surgical procedures. It is less useful than antacids during emergency surgery because of its slow onset of action. This drug had been given to prevent alkalosis in patients subjected to prolonged nasogastric aspiration, especially those secreting large amounts of acid, and to decrease ileostomy/jejunostomy output in the short bowel syndrome.
American Medical Association, Council on Drugs. AMA Drug Evaluations Annual 1994. Chicago, IL: American Medical Association, 1994., p. 899
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for CIMETIDINE (21 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
DESPITE POOR PENETRATION TO THE CNS, NEURAL DYSFUNCTION HAS BEEN ENCOUNTERED, PARTICULARLY WITH HIGH DOSES IN ELDERLY PATIENTS AND IN ASSOCIATION WITH IMPAIRED RENAL EXCRETION. THE EFFECTS INCL CONFUSION, SLURRED SPEECH, DELIRIUM, HALLUCINATIONS, AND COMA.
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 631
IN SOME INSTANCES, WITHDRAWAL OF CIMETIDINE AFTER A PERIOD OF TREATMENT HAS BEEN FOLLOWED BY RELAPSES IN THE SYMPTOMS OF ULCER AND EVEN BY PERFORATION OF DUODENAL, ESOPHAGEAL, OR GASTRIC ULCERS.
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 632
... CIMETIDINE IS INEFFECTIVE IN ACUTE OR ALCOHOLIC PANCREATITIS AND IT MAY ACTUALLY INCR AND PROLONG HYPERAMYLASEMIA.
American Medical Association, Council on Drugs. AMA Drug Evaluations Annual 1994. Chicago, IL: American Medical Association, 1994., p. 899
... CLIN EXPERIENCE IN CHILDREN IS EXTREMELY LIMITED, AND THE BENEFIT/RISK RATIO SHOULD BE CONSIDERED CAREFULLY.
American Medical Association. AMA Drug Evaluations Annual 1991. Chicago, IL: American Medical Association, 1991., p. 771
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for CIMETIDINE (15 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Cimetidine is indicated to reduce gastric acid secretion and to treat the following disease states: duodenal ulcers, non-malignant gastric ulcers, gastroesophageal reflux disease, and pathological hypersecretion associated with Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome, systemic mastocytosis, and multiple endocrine adenomas. It is indicated for prophylaxis of recurrent gastric or duodenal ulcers, as adjunctive therapy in the management of cystic fibrosis in children, and to treat NSAID induced lesions and gastrointestinal symptoms.
Cimetidine is a histamine H2-receptor antagonist. It reduces basal and nocturnal gastric acid secretion and a reduction in gastric volume, acidity, and amount of gastric acid released in response to stimuli including food, caffeine, insulin, betazole, or pentagastrin. It is used to treat gastrointestinal disorders such as gastric or duodenal ulcer, gastroesophageal reflux disease, and pathological hypersecretory conditions. Cimetidine inhibits many of the isoenzymes of the hepatic CYP450 enzyme system. Other actions of Cimetidine include an increase in gastric bacterial flora such as nitrate-reducing organisms.
Cytochrome P-450 CYP1A2 Inhibitors
Drugs and compounds which inhibit or antagonize the biosynthesis or actions of CYTOCHROME P-450 CYP1A2. (See all compounds classified as Cytochrome P-450 CYP1A2 Inhibitors.)
Histamine H2 Antagonists
Drugs that selectively bind to but do not activate histamine H2 receptors, thereby blocking the actions of histamine. Their clinically most important action is the inhibition of acid secretion in the treatment of gastrointestinal ulcers. Smooth muscle may also be affected. Some drugs in this class have strong effects in the central nervous system, but these actions are not well understood. (See all compounds classified as Histamine H2 Antagonists.)
Anti-Ulcer Agents
Various agents with different action mechanisms used to treat or ameliorate PEPTIC ULCER or irritation of the gastrointestinal tract. This has included ANTIBIOTICS to treat HELICOBACTER INFECTIONS; HISTAMINE H2 ANTAGONISTS to reduce GASTRIC ACID secretion; and ANTACIDS for symptomatic relief. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Ulcer Agents.)
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A02 - Drugs for acid related disorders
A02B - Drugs for peptic ulcer and gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (gord)
A02BA - H2-receptor antagonists
A02BA01 - Cimetidine
Absorption
Two peak plasma concentrations are often observed after oral administration of cimetidine, likely as a result of discontinuous absorption in the gastrointestinal tract. In healthy patients, the absolute bioavailability of cimetidine is approximately 60%; however, the bioavailability can be as high as 70% in patients with peptic ulcer disease. Overall, rates of bioavailability are much more variable in patients with peptic ulcer disease.
Route of Elimination
Cimetidine is excreted primarily in the urine.
Volume of Distribution
The volume of distribution of cimetidine is reported to be 1 L/kg.
Clearance
Cimetidine's reported systemic clearance value is approximately 500-600 ml/min.
About 15% of cimetidine is metabolized in the liver. Seventy percent is excreted unchanged in the urine, with fecal losses accounting for approximately 10%.
Ellenhorn, M.J. and D.G. Barceloux. Medical Toxicology - Diagnosis and Treatment of Human Poisoning. New York, NY: Elsevier Science Publishing Co., Inc. 1988., p. 434
Given orally, cimetidine and ranitidine are almost completely absorbed. Because of first-pass metabolism in the liver, the bioavailability is 50-60%. Both drugs are little bound to plasma proteins (10-20%).
Haddad, L.M., Clinical Management of Poisoning and Drug Overdose. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: W.B. Saunders Co., 1990., p. 824
Both drugs are mainly excreted in urine - cimetidine up to 90% within 24 hr (50-75% unchanged) and ranitidine up to 60% within 24 hr (about 40% unchanged). The apparent volume of distribution is quite large, in the range of 1.5 l/kg bw, demonstrating that nearly all drug exists outside the intravascular space.
Haddad, L.M., Clinical Management of Poisoning and Drug Overdose. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: W.B. Saunders Co., 1990., p. 824
Cimetidine is widely distributed throughout the body and is 15-20% bound to plasma proteins. Animal studies indicate that the drug crosses the placenta. Cimetidine is distributed into milk.
McEvoy G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service-Drug Information 96. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1996 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2140
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for CIMETIDINE (14 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
After intravenous administration of cimetidine, the majority of the parent drug (58-77%) is eliminated unchanged in the urine. Cimetidines primary metabolite is cimetidine sulfoxide and represents an estimated 10-15% of total elimination. Researchers have also identified a minor cimetidine metabolite with a hydroxylated methyl group on the imidazole ring which represents only 4% of total elimination. Both cytochrome P450 enzymes and flavin-containing monooxygenases are implicated in the metabolism of cimetidine, although it is unclear which specific enzymes are involved. Cimetidine is a well known enzyme inhibitor and may impair the metabolism of certain co-administered medications.
About 50% to 80% of an intravenous dose is excreted as unchanged drug; 40% of an oral dose is excreted unchanged in the urine in patients with peptic ulcer disease. Most of the remainder of the drug appears in the urine as 5-hydroxymethyl or sulfoxide metabolites.
American Medical Association, Council on Drugs. AMA Drug Evaluations Annual 1994. Chicago, IL: American Medical Association, 1994., p. 900
Cimetidine is metabolized in the liver to sulfoxide and 5-hydroxymethyl derivatives, and possibly guanylurea, although this latter compound may result from in vitro degradation.
McEvoy G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service-Drug Information 96. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1996 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2140
Cimetidine's half-life is estimated to be around 2 hours.
ELEVEN PATIENTS WITH ASCITIC CIRRHOSIS & ELEVEN PATIENTS WITHOUT LIVER DISEASE RECEIVED 200 MG OF CIMETIDINE ORALLY AND IV. NO DIFFERENCES WERE OBSERVED IN CIMETIDINE T/2 BETWEEN THE 2 GROUPS. CIMETIDINE CLEARANCE WAS DIMINISHED IN CIRRHOTIC PATIENTS (0.426 + OR - 0.138 VERSUS 0.649 + OR - 0.163 L/HR/KG).
PMID:6852412 ALBIN H ET AL; GASTROENTEROL CLIN BIOL 7 (3): 251-5 (1983)
The elimination half-life in man is 1.9 to 2.2 hours.
Ellenhorn, M.J. and D.G. Barceloux. Medical Toxicology - Diagnosis and Treatment of Human Poisoning. New York, NY: Elsevier Science Publishing Co., Inc. 1988., p. 434
The plasma elimination half-life is about 2 hours.
American Medical Association, Council on Drugs. AMA Drug Evaluations Annual 1994. Chicago, IL: American Medical Association, 1994., p. 900
The half-time for elimination of cimetidine ... is 2 to 3 hours ... .
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 900
Cimetidine binds to an H2-receptor located on the basolateral membrane of the gastric parietal cell, blocking histamine effects. This competitive inhibition results in reduced gastric acid secretion and a reduction in gastric volume and acidity.
H2 antagonists inhibit gastric acid secretion elicited by histamine & other H2 agonists in a dose-dependent, competitive manner; the degree of inhibition parallels the concentration of the drug in plasma over a wide range. The H2 antagonists also inhibit acid secretion elicited by gastrin &, to a lesser extent, by muscarinic agonists. Importantly, these drugs inhibit basal (fasting) & nocturnal acid secretion & that stimulated by food, sham feeding, fundic distention, & various pharmacological agents; this property reflects the vital role of histamine in mediating the effects of diverse stimuli. The H2 antagonists reduce both the volume of gastric juice secreted & its H+ concentration. The output of pepsin, which is secreted by the chief cells of gastric glands (mainly under cholinergic control), generally falls in parallel with the reduction in volume of gastric juice. /H2 antagonists/
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 899
Cimetidine blocks H2-receptors, which in part are responsible for the inflammatory response, in the cutaneous blood vessels of humans.
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 16th ed. Volume I. Rockville, MD: U.S. Pharmaceutical Convention, Inc. 1996 (Plus updates)., p. 1612
The effects of cimetidine, omeprazole and atropine sulfate on the healing of acetic acid-induced gastric ulcers in rats with limited food intake time (9:00-10:00 am and 5:00-6:00 pm) were evaluated 15 days after the acid injection. Oral repeated admin of cimetidine (25-100 mg/kg twice daily) or omeprazole (10-50 mg/kg once daily) dose dependently accelerated ulcer healing. ... A single oral admin of omeprazole (50 mg/kg) or cimetidine (100 mg/kg) resulted in potent and long-lasting anti-acid secretory and gastrin-releasing actions. The degree and duration of anti-acid secretion by atropine sulfate were equal to those of cimetidine, but the elevation of gastrin release by atropine sulfate was weak and temporary. These results indicate that the gastric ulcers of rats with a limited food intake time are useful for evaluating the healing effects of cimetidine and omeprazole on gastric ulcers. In addition, the effects of both drugs may be related to the incr gastrin release rather than to the reduced acid secretion.
PMID:7843261 Ito M et al; Eur J Pharmacol 263 (3): 245-51 (1994)
Both KB-5492, a new anti-ulcer agent, and cimetidine, admin po at 25-200 mg/kg, dose-dependently prevented cysteamine (400 mg/kg, sc)-induced duodenal ulcers in rats with ED50 values of 63 and 40 mg/kg, respectively. Anti-ulcer doses of cimetidine, but not KB-5492, inhibited gastric acid hypersecretion induced by cysteamine (400 mg/kg, sc). In contrast, anti-ulcer doses of KB-5492, but not cimetidine, incr duodenal HC03- secretion in normal anesthetized rats. These findings suggest that KB-5492 prevents cysteamine-induced duodenal ulcers by stimulating duodenal HC03- secretion, whereas cimetidine does so by inhibiting cysteamine-induced gastric acid hypersecretion.
PMID:8022123 Morimoto Y et al; Jpn J Pharmacol 64 (3): 221-4 (1994)