
1. Anhydrous, Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride
2. Bay 09867
3. Bay-09867
4. Bay09867
5. Ciprinol
6. Cipro
7. Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride
8. Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride Anhydrous
9. Ciprofloxacin Monohydrochloride Monohydrate
10. Hydrochloride Anhydrous, Ciprofloxacin
11. Hydrochloride, Ciprofloxacin
12. Monohydrate, Ciprofloxacin Monohydrochloride
13. Monohydrochloride Monohydrate, Ciprofloxacin
1. 85721-33-1
2. Ciprofloxacine
3. Ciprobay
4. Cipro
5. Ciproxan
6. Ciprofloxacina
7. Cipro Iv
8. Ciprofloxacinum
9. Bay Q 3939
10. Ciprofloxacino
11. Ciproflox
12. Ciproxina
13. Otiprio
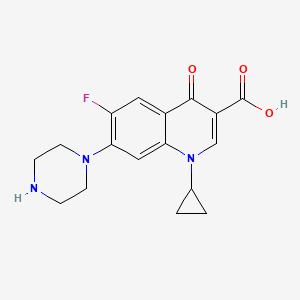
14. 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(piperazin-1-yl)-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
15. 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-3-quinolinecarboxylic Acid
16. Cetraxal
17. Cipro Xr
18. Bay-09867
19. Cpfx
20. 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-1,4-dihydro-3-quinolinecarboxylic Acid
21. Bayq3939
22. 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-piperazin-1-ylquinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
23. Ciproxin
24. Ciflox
25. Ciprofloxacin (cipro)
26. Chembl8
27. Bay O 9867
28. 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-piperazin-1-yl-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
29. 3-quinolinecarboxylic Acid, 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-
30. Nsc-758467
31. 5e8k9i0o4u
32. Ciprocinol
33. Cipromycin
34. Ciproquinol
35. Bacquinor
36. Bernoflox
37. Cifloxin
38. Ciprinol
39. Ciprodar
40. Septicide
41. Bay O 9867 Free Base
42. Bay-o-9867 Free Base
43. Chebi:100241
44. Bay-q-3939
45. Velmonit
46. Ciprofloxacin Monohydrochloride
47. Ciprecu
48. Ciprogis
49. Ciprolin
50. Ciprolon
51. Ciprowin
52. Ciproxine
53. Citopcin
54. Corsacin
55. Fimoflox
56. Ipiflox
57. Italnik
58. Probiox
59. Proflaxin
60. Quinolid
61. Quintor
62. Roxytal
63. Spitacin
64. Superocin
65. Zumaflox
66. Baflox
67. Ciplus
68. Ciriax
69. Rancif
70. Cilab
71. Cixan
72. Cycin
73. Loxan
74. Unex
75. Sophixin Ofteno
76. Ciprobay Uro
77. Alcon Cilox
78. Bi-cipro
79. Cipro (tn)
80. 3-quinolinecarboxylic Acid, 1,4-dihydro-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-
81. Proksi 250
82. Proksi 500
83. Cyprobay
84. Auripro
85. Eni
86. 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-3-quinoline-carboxylic Acid
87. 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-piperazin-1-yl-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
88. 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-7-hexahydro-1-pyrazinyl-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-3-quinolinecarboxylic Acid
89. Bay-o 9867
90. Ciprofloxacine [inn-french]
91. Ciprofloxacinum [inn-latin]
92. 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-7-(4-methyl-piperazin-1-yl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
93. Smr000471901
94. Ciprofloxacino [inn-spanish]
95. Ccris 5241
96. Nsc620634
97. Hsdb 6987
98. Sr-05000001863
99. Ciprofloxacin 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
100. Ncgc00016959-01
101. Cas-93107-08-5
102. Cipro In Dextrose 5% In Plastic Container
103. Brn 3568352
104. Rubrum
105. Unii-5e8k9i0o4u
106. Ciprine
107. Linhaliq
108. Bay 09867
109. Cipro In Sodium Chloride 0.9% In Plastic Container
110. Ciprofloxacin,(s)
111. Ciprofloxacin [usan:usp:inn:ban]
112. Mfcd00185755
113. Spectrum_000162
114. 3-quinolinecarboxylic Acid, 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-, Hydrochloride
115. Prestwick0_000113
116. Prestwick1_000113
117. Prestwick2_000113
118. Prestwick3_000113
119. Spectrum2_001567
120. Spectrum3_001872
121. Spectrum4_000874
122. Spectrum5_001089
123. Cipro (*hydrochloride*)
124. Cbmicro_048498
125. Ciprofloxacin [mi]
126. Ciloxan (*hydrochloride*)
127. Ciprofloxacin [inn]
128. Ciprofloxacin [jan]
129. Schembl2900
130. Ciprofloxacin [hsdb]
131. Ciprofloxacin [usan]
132. Oprea1_008239
133. Oprea1_313572
134. Bspbio_000126
135. Bspbio_003344
136. Ciprofloxacin [vandf]
137. Kbiogr_001567
138. Kbioss_000642
139. Anhydrous Ciprofloxacin
140. Mls001336035
141. Mls006011837
142. Bidd:gt0205
143. Ciprofloxacin [mart.]
144. Divk1c_000095
145. Spectrum1503614
146. Spbio_001474
147. Spbio_002065
148. Ciprofloxacin [usp-rs]
149. Ciprofloxacin [who-dd]
150. Ciprofloxacin [who-ip]
151. Bpbio1_000140
152. Dtxsid8022824
153. Bay-o9867
154. Bdbm21690
155. Gtpl10902
156. Hms500e17
157. Kbio1_000095
158. Kbio2_000642
159. Kbio2_003210
160. Kbio2_005778
161. Kbio3_002846
162. Linhaliq [liposomal Formulation]
163. Zinc20220
164. Ciprofloxacin (jp17/usp/inn)
165. Ninds_000095
166. Bay O 9867 (*hydrochloride*)
167. Hms1922e18
168. Hms2090o07
169. Hms2093i03
170. Pharmakon1600-01503614
171. Ciprofloxacin [orange Book]
172. Albb-015909
173. Bcp28586
174. Hy-b0356
175. Rkl10073
176. Ciprofloxacin [ep Monograph]
177. Bbl005612
178. Ccg-39345
179. Ciprofloxacin [usp Monograph]
180. Ciprofloxacin Extended Release
181. Ciprofloxacin, >=98.0% (hplc)
182. Nsc758467
183. Nsc759028
184. S2027
185. Stk021082
186. 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-piperazin-1-yl-quinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
187. 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-piperazinylhydroquinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
188. Akos000269653
189. Ciprodex Component Ciprofloxacin
190. Ciprofloxacinum [who-ip Latin]
191. Ac-7613
192. Db00537
193. Ks-5006
194. Nsc 758467
195. Nsc-759028
196. Idi1_000095
197. Smp1_000125
198. Ncgc00016959-02
199. Ncgc00016959-03
200. Ncgc00016959-04
201. Ncgc00016959-05
202. Ncgc00016959-07
203. Ncgc00095058-01
204. Ncgc00095058-02
205. Ncgc00178128-01
206. Ciprofloxacin Component Of Ciprodex
207. Sbi-0048462.p003
208. Ft-0601635
209. C-6350
210. C05349
211. Ciprofloxacin 100 Microg/ml In Methanol:water
212. D00186
213. 721c331
214. A841426
215. Ciprofloxacin, Vetranal(tm), Analytical Standard
216. Q256602
217. Ciprofloxacin, Antibiotic For Culture Media Use Only
218. Sr-05000001863-1
219. Sr-05000001863-3
220. Brd-k04804440-311-02-3
221. Z56933707
222. Ciprofloxacin, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
223. Enrofloxacin For Veterinary Use Impurity B [ep Impurity]
224. Ciprofloxacin, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
225. 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro 4-oxo-7-[1-piperazinyl)-quinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
226. 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7- (1-piperazinyl)-3-quinoline-carboxylic Acid
227. 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-quinoline -3-carboxylic Acid
228. 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-quinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
229. 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)quinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
230. 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1piperazinyl)-3quinolinecarboxylic Acid
231. 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(piperazin-1-yl)-quinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
232. 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-7-(1-piperazinyl)-4-oxo-3-quinoline Carboxylic Acid
233. 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(piperazin-1-yl)-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylicacid
234. 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-piperazin-4-ium-1-yl-quinoline-3-carboxylate;ciprofloxacin
235. 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-7-(piperazin-1-yl)-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
236. Ciprofloxacin, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
237. 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-piperazin-1-yl-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic Acid Hydrochloride
| Molecular Weight | 331.34 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H18FN3O3 |
| XLogP3 | -1.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 331.13321961 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 331.13321961 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 72.9 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 24 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 571 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 14 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Cetraxal |
| PubMed Health | Ciprofloxacin (Into the ear) |
| Drug Classes | Antibacterial |
| Drug Label | CETRAXAL (ciprofloxacin otic solution) 0.2% contains the synthetic antimicrobial agent ciprofloxacin hydrochloride. CETRAXAL is a sterile, preservative-free solution for otic use. Each single use container of CETRAXAL delivers 0.25 mL of solution equ... |
| Active Ingredient | Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Solution/drops |
| Route | Otic |
| Strength | eq 0.2% base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Wraser Pharms |
| 2 of 14 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Ciloxan |
| PubMed Health | Ciprofloxacin (Into the eye) |
| Drug Classes | Antibiotic |
| Drug Label | CILOXAN (ciprofloxacin HCl ophthalmic solution) is a synthetic, sterile, multiple dose, antimicrobial for topical ophthalmic use. Ciprofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibacterial active against a broad spectrum of gram-positive and gram-negative oc... |
| Active Ingredient | Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Solution/drops; Ointment |
| Route | Ophthalmic |
| Strength | eq 0.3% base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Alcon Pharms |
| 3 of 14 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Cipro |
| PubMed Health | Ciprofloxacin/Dexamethasone (Into the ear) |
| Drug Classes | Anti-Infective/Anti-Inflammatory Combination, Antibacterial |
| Drug Label | Ciprofloxacin Tablets, USPis a synthetic broad spectrum antimicrobial agent for oral administration. Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride, USP, a fluoroquinolone, is the monohydrochloride monohydrate salt of 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-pip... |
| Active Ingredient | Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride; Ciprofloxacin |
| Dosage Form | Injectable; Tablet; For suspension |
| Route | Injection; Oral |
| Strength | eq 750mg base; eq 100mg base; 400mg/40ml (10mg/ml); 200mg/20ml (10mg/ml); 500mg/5ml; eq 500mg base; eq 250mg base; 250mg/5ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Bayer Hlthcare |
| 4 of 14 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Cipro xr |
| PubMed Health | Ciprofloxacin Betaine/Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antibacterial |
| Drug Label | Ciprofloxacin Tablets, USPis a synthetic broad spectrum antimicrobial agent for oral administration. Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride, USP, a fluoroquinolone, is the monohydrochloride monohydrate salt of 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-pip... |
| Active Ingredient | Ciprofloxacin; ciprofloxacin hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release |
| Route | oral |
| Strength | eq 287.5mg base; 425.2mg; eq 574.9mg base; 212.6mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Bayer Pharms |
| 5 of 14 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Ciprofloxacin |
| PubMed Health | Ciprofloxacin |
| Drug Classes | Antibacterial, Antibiotic, Antitubercular |
| Active Ingredient | Ciprofloxacin |
| Dosage Form | Injectable; Tablet; For suspension |
| Route | oral; Injection; Oral |
| Strength | 400mg/40ml (10mg/ml); 200mg/20ml (10mg/ml); 250mg; 500mg/5ml; 100mg; 250mg/5ml |
| Market Status | Tentative Approval; Prescription |
| Company | Ivax Sub Teva Pharms; Hospira; Claris Lifesciences; Hikma Farmaceutica; Lupin; Sandoz; Carlsbad; Hikma |
| 6 of 14 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Ciprofloxacin extended release |
| PubMed Health | Ciprofloxacin Betaine/Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antibacterial |
| Drug Label | Ciprofloxacin Tablets, USPis a synthetic broad spectrum antimicrobial agent for oral administration. Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride, USP, a fluoroquinolone, is the monohydrochloride monohydrate salt of 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-pip... |
| Active Ingredient | Ciprofloxacin; ciprofloxacin hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 425.2mg; eq 287.5mg base; 212.6mg; eq 574.9mg base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mylan Pharms; Anchen Pharms; Actavis Labs Fl; Dr Reddys Labs |
| 7 of 14 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride |
| Active Ingredient | Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Solution/drops; Tablet |
| Route | Ophthalmic; Oral |
| Strength | eq 100mg base; eq 750mg base; eq 500mg base; eq 0.3% base; eq 250mg base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Watson Labs; Nexus Pharms; Ranbaxy; Ivax Sub Teva Pharms; Apotex; Bausch And Lomb; Aurobindo Pharma; Taro; Dr Reddys Labs; Unique Pharm Labs; Carlsbad; Pharmaforce; Fdc; Mylan; Hikma; Akorn |
| 8 of 14 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Cetraxal |
| PubMed Health | Ciprofloxacin (Into the ear) |
| Drug Classes | Antibacterial |
| Drug Label | CETRAXAL (ciprofloxacin otic solution) 0.2% contains the synthetic antimicrobial agent ciprofloxacin hydrochloride. CETRAXAL is a sterile, preservative-free solution for otic use. Each single use container of CETRAXAL delivers 0.25 mL of solution equ... |
| Active Ingredient | Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Solution/drops |
| Route | Otic |
| Strength | eq 0.2% base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Wraser Pharms |
| 9 of 14 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Ciloxan |
| PubMed Health | Ciprofloxacin (Into the eye) |
| Drug Classes | Antibiotic |
| Drug Label | CILOXAN (ciprofloxacin HCl ophthalmic solution) is a synthetic, sterile, multiple dose, antimicrobial for topical ophthalmic use. Ciprofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibacterial active against a broad spectrum of gram-positive and gram-negative oc... |
| Active Ingredient | Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Solution/drops; Ointment |
| Route | Ophthalmic |
| Strength | eq 0.3% base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Alcon Pharms |
| 10 of 14 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Cipro |
| PubMed Health | Ciprofloxacin/Dexamethasone (Into the ear) |
| Drug Classes | Anti-Infective/Anti-Inflammatory Combination, Antibacterial |
| Drug Label | Ciprofloxacin Tablets, USPis a synthetic broad spectrum antimicrobial agent for oral administration. Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride, USP, a fluoroquinolone, is the monohydrochloride monohydrate salt of 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-pip... |
| Active Ingredient | Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride; Ciprofloxacin |
| Dosage Form | Injectable; Tablet; For suspension |
| Route | Injection; Oral |
| Strength | eq 750mg base; eq 100mg base; 400mg/40ml (10mg/ml); 200mg/20ml (10mg/ml); 500mg/5ml; eq 500mg base; eq 250mg base; 250mg/5ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Bayer Hlthcare |
| 11 of 14 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Cipro xr |
| PubMed Health | Ciprofloxacin Betaine/Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antibacterial |
| Drug Label | Ciprofloxacin Tablets, USPis a synthetic broad spectrum antimicrobial agent for oral administration. Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride, USP, a fluoroquinolone, is the monohydrochloride monohydrate salt of 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-pip... |
| Active Ingredient | Ciprofloxacin; ciprofloxacin hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release |
| Route | oral |
| Strength | eq 287.5mg base; 425.2mg; eq 574.9mg base; 212.6mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Bayer Pharms |
| 12 of 14 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Ciprofloxacin |
| PubMed Health | Ciprofloxacin |
| Drug Classes | Antibacterial, Antibiotic, Antitubercular |
| Active Ingredient | Ciprofloxacin |
| Dosage Form | Injectable; Tablet; For suspension |
| Route | oral; Injection; Oral |
| Strength | 400mg/40ml (10mg/ml); 200mg/20ml (10mg/ml); 250mg; 500mg/5ml; 100mg; 250mg/5ml |
| Market Status | Tentative Approval; Prescription |
| Company | Ivax Sub Teva Pharms; Hospira; Claris Lifesciences; Hikma Farmaceutica; Lupin; Sandoz; Carlsbad; Hikma |
| 13 of 14 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Ciprofloxacin extended release |
| PubMed Health | Ciprofloxacin Betaine/Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antibacterial |
| Drug Label | Ciprofloxacin Tablets, USPis a synthetic broad spectrum antimicrobial agent for oral administration. Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride, USP, a fluoroquinolone, is the monohydrochloride monohydrate salt of 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-pip... |
| Active Ingredient | Ciprofloxacin; ciprofloxacin hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 425.2mg; eq 287.5mg base; 212.6mg; eq 574.9mg base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mylan Pharms; Anchen Pharms; Actavis Labs Fl; Dr Reddys Labs |
| 14 of 14 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride |
| Active Ingredient | Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Solution/drops; Tablet |
| Route | Ophthalmic; Oral |
| Strength | eq 100mg base; eq 750mg base; eq 500mg base; eq 0.3% base; eq 250mg base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Watson Labs; Nexus Pharms; Ranbaxy; Ivax Sub Teva Pharms; Apotex; Bausch And Lomb; Aurobindo Pharma; Taro; Dr Reddys Labs; Unique Pharm Labs; Carlsbad; Pharmaforce; Fdc; Mylan; Hikma; Akorn |
Anti-Infective Agents; Nucleic Acid Synthesis Inhibitors
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 2012)
Ciprofloxacin (IV, conventional tablets, oral suspension) is used in adults for the treatment of bone and joint infections, including osteomyelitis, caused by susceptible E. cloacae, ... Ps. aeruginosa, or S. marcescens. ... /Included in US product label/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 358
Ciprofloxacin (IV, conventional tablets, oral suspension) is used in adults for the treatment of bone and joint infections, including osteomyelitis, caused by susceptible E. aerogenes, ... E. coli, K. pneumoniae, M. morganii, P. mirabilis, ... . The drug also has been used in adults for the treatment of bone and joint infections caused by susceptible S. aureus, S. epidermidis, other coagulase-negative staphylococci, or Enterococcus faecalis (formerly S. faecalis), but other anti-infectives generally are preferred for these infections. Although resistance to ciprofloxacin has been reported in some strains of oxacillin-resistant S. aureus, oral ciprofloxacin may be a useful alternative to parenteral anti-infectives for the treatment of infections caused by susceptible oxacillin-resistant staphylococci. /NOT included in US product label/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 358
Although only limited experience is available to date, ciprofloxacin is recommended by the American Heart Association (AHA) and Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) as an alternative agent for the treatment of native or prosthetic valve endocarditis caused by fastidious gram-negative bacilli known as the HACEK group (Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans, Cardiobacterium hominis, Eikenella corrodens, Haemophilus aphrophilus, H. influenzae, H. parainfluenzae, H. paraphrophilus, Kingella denitrificans, K. kingae). /NOT included in US product label/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 358
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for CIPROFLOXACIN (53 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
/BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: Fluoroquinolones, including Cipro, are associated with an increased risk of tendinitis and tendon rupture in all ages. This risk is further increased in older patients usually over 60 years of age, in patients taking corticosteroid drugs, and in patients with kidney, heart or lung transplants.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for CIPRO (ciprofloxacin hydrochloride) tablet, film coated CIPRO (ciprofloxacin) kit (November 2011). Available from, as of February 28, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=888dc7f9-ad9c-4c00-8d50-8ddfd9bd27c0
/BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: Fluoroquinolones, including Cipro, may exacerbate muscle weakness in persons with myasthenia gravis. Avoid Cipro in patients with known history of myasthenia gravis.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for CIPRO (ciprofloxacin hydrochloride) tablet, film coated CIPRO (ciprofloxacin) kit (November 2011). Available from, as of February 28, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=888dc7f9-ad9c-4c00-8d50-8ddfd9bd27c0
In 4 corneal transplantation patients treated preoperatively with ciprofloxacin ophthalmic drops, microprecipitates associated with damaged corneal epithelium were noted in 2 patients. Another patient developed a large macroprecipitate in a corneal ulcer. All specimens were examined by electron microscopy & high-pressure liquid chromatography. The crystalline precipitates were pure ciprofloxacin. The macroprecipitate demonstrated a large zone of inhibition on agar plates seeded with a susceptible organism at 24 & 48 hr. It was bioactive & bioavailable in vitro.
PMID:11687375 Eiferman RA et al; J Cataract Refract Surg 27 (10): 1701-1702 (2001)
Serious and occasionally fatal hypersensitivity (anaphylactic) reactions, some following the first dose, have been reported in patients receiving quinolone therapy. Some reactions were accompanied by cardiovascular collapse, loss of consciousness, tingling, pharyngeal or facial edema, dyspnea, urticaria, and itching. Only a few patients had a history of hypersensitivity reactions. Serious anaphylactic reactions require immediate emergency treatment with epinephrine. Oxygen, intravenous steroids, and airway management, including intubation, should be administered as indicated.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for CIPRO (ciprofloxacin hydrochloride) tablet, film coated CIPRO (ciprofloxacin) kit (November 2011). Available from, as of February 28, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=888dc7f9-ad9c-4c00-8d50-8ddfd9bd27c0
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for CIPROFLOXACIN (41 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Ciprofloxacin is only indicated in infections caused by susceptible bacteria. Ciprofloxacin immediate release tablets, oral suspensions, and intravenous injections are indicated for the treatment of skin and skin structure infections, bone and joint infections, complicated intra-abdominal infections, nosocomial pneumonia, febrile neutropenia, adults who have inhaled anthrax, plague, chronic bacterial prostatitis, lower respiratory tract infections including acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis, urinary tract infections, complicated urinary tract infections in pediatrics, complicated pyelonephritis in pediatrics, and acute sinusitis. A ciprofloxacin otic solution and otic suspension with hydrocortisone are indicated for acute otitis externa. Ciprofloxacin suspension with dexamethasone is indicated for acute otitis media in pediatric patients with tympanostomy tubes or acute otitis externa. A ciprofloxacin intratympanic injection is indicated for pediatric patients with bilateral otitis media with effusion who are having tympanostomy tubes placed or pediatric patients 6 months or older with acute otitis externa. A ciprofloxacin eye drop is indicated for bacterial corneal ulcers and conjunctivitis. A ciprofloxacin eye ointment is indicated for bacterial conjunctivitis. A ciprofloxacin extended release tablet is indicated for uncomplicated urinary tract infections, complicated urinary tract infections, and acute uncomplicated pyelonephritis.
FDA Label
Ciprofloxacin is a second generation fluoroquinolone that is active against many Gram negative and Gram positive bacteria. It produces its action through inhibition of bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV. Ciprofloxacin binds to bacterial DNA gyrase with 100 times the affinity of mammalian DNA gyrase. There is no cross resistance between fluoroquinolones and other classes of antibiotics, so it may be of clinical value when other antibiotics are no longer effective. Ciprofloxain and its derivatives are also being investigated for its action against malaria, cancers, and AIDS.
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Substances that inhibit the growth or reproduction of BACTERIA. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Bacterial Agents.)
Topoisomerase II Inhibitors
Compounds that inhibit the activity of DNA TOPOISOMERASE II. Included in this category are a variety of ANTINEOPLASTIC AGENTS which target the eukaryotic form of topoisomerase II and ANTIBACTERIAL AGENTS which target the prokaryotic form of topoisomerase II. (See all compounds classified as Topoisomerase II Inhibitors.)
Cytochrome P-450 CYP1A2 Inhibitors
Drugs and compounds which inhibit or antagonize the biosynthesis or actions of CYTOCHROME P-450 CYP1A2. (See all compounds classified as Cytochrome P-450 CYP1A2 Inhibitors.)
S01AE03
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J01 - Antibacterials for systemic use
J01M - Quinolone antibacterials
J01MA - Fluoroquinolones
J01MA02 - Ciprofloxacin
S - Sensory organs
S01 - Ophthalmologicals
S01A - Antiinfectives
S01AE - Fluoroquinolones
S01AE03 - Ciprofloxacin
S - Sensory organs
S02 - Otologicals
S02A - Antiinfectives
S02AA - Antiinfectives
S02AA15 - Ciprofloxacin
S - Sensory organs
S03 - Ophthalmological and otological preparations
S03A - Antiinfectives
S03AA - Antiinfectives
S03AA07 - Ciprofloxacin
Absorption
A 250mg oral dose of ciprofloxacin reaches an average maximum concentration of 0.94mg/L in 0.81 hours with an average area under the curve of 1.013L/h\*kg. The FDA reports an oral bioavailability of 70-80% while other studies report it to be approximately 60%. An early review of ciprofloxacin reported an oral bioavailability of 64-85% but recommends 70% for all practical uses.
Route of Elimination
27% of an oral dose was recovered unmetabolized in urine compared to 46% of an intravenous dose. Collection of radiolabelled ciprofloxacin resulted in 45% recovery in urine and 62% recovery in feces.
Volume of Distribution
Cirpofloxacin follws a 3 compartment distribution model with a central compartment volume of 0.161L/kg and a total volume of distribution of 2.00-3.04L/kg.
Clearance
The average renal clearance after a 250mg oral dose is 5.08mL/min\*kg. Following a 100mg intravenous dose, the average total clearance is 9.62mL/min\*kg, average renal clearance is 4.42mL/min\*kg, and average non renal clearance is 5.21mL/min\*kg.
Based on population pharmacokinetics, bioavailability of ciprofloxacin oral suspension in children is approximately 60%. Following a single oral dose of 10 mg/kg of ciprofloxacin given as the oral suspension to children 4 months to 7 years of age, the mean peak plasma concentration was 2.4 ug/mL. There was no apparent age dependence and no increase in peak plasma concentrations following multiple doses.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 379
When extended-release tablets containing ciprofloxacin hydrochloride (ProQuin XR) are administered with food, approximately 87% of the drug is gradually released from the tablet over a 6- hour period. When administered following a meal, peak plasma concentrations are attained approximately 4.5-7 hours after the dose. Bioavailability is substantially lower if ProQuin XR tablets are given while fasting. In healthy adults receiving ProQuin XR extended-release tablets in a dosage of 500 mg once daily given following a standardized meal, peak plasma concentrations at steady state (day 3) average 0.82 mcg/mL and are attained 6.1 hours after the dose. /Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 379
Following oral administration of extended-release tablets containing ciprofloxacin hydrochloride and base (Cipro XR), peak plasma concentrations of ciprofloxacin are attained within 1-4 hours. Cipro XR tablets contain approximately 35% of the dose within an immediate-release component; the remaining 65% of the dose is contained in a slow-release matrix. Oral administration of ciprofloxacin 500 mg daily as Cipro XR extended-release tablets or 250 mg twice daily as conventional tablets results in steady-state mean peak plasma concentrations of 1.59 or 1.14 ug/mL, respectively; however, the area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) is similar with both regimens. /Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 379
Peak serum concentrations of ciprofloxacin and AUCs of the drug are slightly higher in geriatric patients than in younger adults; this may occur because of increased bioavailability, reduced volume of distribution, and/or reduced renal clearance in these patients. Single-dose oral studies using ciprofloxacin conventional tablets and single- and multiple-dose IV studies indicate that, compared with younger adults, peak plasma concentrations are 16-40% higher, mean AUC is approximately 30% higher, and elimination half-life is prolonged approximately 20% in individuals older than 65 years of age. These differences can be at least partially attributed to decreased renal clearance in this age group and are not clinically important.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 379
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for CIPROFLOXACIN (18 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Ciprofloxacin is primarily metabolized by CYP1A2. The primary metabolites oxociprofloxacin and sulociprofloxacin make up 3-8% of the total dose each. Ciprofloxacin is also converted to the minor metabolites desethylene ciprofloxacin and formylciprofloxacin. These 4 metabolites account for 15% of a total oral dose. There is a lack of available data on the enzymes and types of reactions involved in forming these metabolites.
The drug is partially metabolized in the liver by modification of the piperazinyl group to at least 4 metabolites. These metabolites, which have been identified as desethyleneciprofloxacin (M1), sulfociprofloxacin (M2), oxociprofloxacin (M3), and N-formylciprofloxacin (M4), have microbiologic activity that is less than that of the parent drug but may be similar to or greater than that of some other quinolones (e.g., M3 and M4 are comparable to norfloxacin for certain organisms).
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 380
The average half life following a 250mg oral dose was 4.71 hours and 3.65 hours following a 100mg intravenous dose. Generally the half life is reported as 4 hours.
The serum elimination half-life of ciprofloxacin in adults with normal renal function is 3-7 hours. Following IV administration in healthy adults, the distribution half-life of ciprofloxacin averages 0.18-0.37 hours and the elimination half-life averages 3-4.8 hours. The elimination half-life of the drug is slightly longer in geriatric adults than in younger adults, and ranges from 3.3-6.8 hours in adults 60-91 years of age with renal function normal for their age. Based on population pharmacokinetic analysis of pediatric patients with various infections, the predicted mean half-life of ciprofloxacin in children is approximately 4-5 hours. In patients with impaired renal function, serum concentrations of ciprofloxacin are higher and the half-life prolonged. In adults with creatinine clearances of 30 mL/minute or less, half-life of the drug ranges from 4.4-12.6 hours.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 380
t1/2 for ciprofloxacin- normal: 4 (hr), anephric: 8.5 (hr) /from table/
Young, L.Y., M.A. Koda-Kimble (eds.). Applied Therapeutics. The Clinical Use of Drugs. 6th ed. Vancouver, WA., Applied Therapeutics, Inc. 1995., p. 32-7
Ciprofloxacin acts on bacterial topoisomerase II (DNA gyrase) and topoisomerase IV. Ciprofloxacin's targeting of the alpha subunits of DNA gyrase prevents it from supercoiling the bacterial DNA which prevents DNA replication.
The mechanism by which ciprofloxacin's inhibition of DNA gyrase or topoisomerase IV results in death in susceptible organisms has not been fully determined. Unlike beta-lactam anti-infectives, which are most active against susceptible bacteria when they are in the logarithmic phase of growth, studies using Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa indicate that ciprofloxacin can be bactericidal during both logarithmic and stationary phases of growth; this effect does not appear to occur with gram-positive bacteria (e.g., Staphylococcus aureus). In vitro studies indicate that ciprofloxacin concentrations that approximate the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of the drug induce filamentation in susceptible organisms; high concentrations of the drug result in enlarged or elongated cells that may not be extensively filamented. Although the bactericidal effect of some fluoroquinolones (e.g., norfloxacin) evidently requires competent RNA and protein synthesis in the bacterial cell, and concurrent use of anti-infectives that affect protein synthesis (e.g., chloramphenicol, tetracyclines) or RNA synthesis (e.g., rifampin) inhibit the in vitro bactericidal activity of these drugs, the bactericidal effect of ciprofloxacin is only partially reduced in the presence of these anti-infectives. This suggests that ciprofloxacin has an additional mechanism of action that is independent of RNA and protein synthesis.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 375
Ciprofloxacin usually is bactericidal in action. Like other fluoroquinolone anti-infectives, ciprofloxacin inhibits DNA synthesis in susceptible organisms via inhibition of the enzymatic activities of 2 members of the DNA topoisomerase class of enzymes, DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV. DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV have distinct essential roles in bacterial DNA replication. DNA gyrase, a type II DNA topoisomerase, was the first identified quinolone target; DNA gyrase is a tetramer composed of 2 GyrA and 2 GyrB subunits. DNA gyrase introduces negative superhelical twists in DNA, an activity important for initiation of DNA replication. DNA gyrase also facilitates DNA replication by removing positive super helical twists. Topoisomerase IV, another type II DNA topoisomerase, is composed of 2 ParC and 2 ParE subunits. DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV are structurally related; ParC is homologous to GyrA and ParE is homologous to GyrB. Topoisomerase IV acts at the terminal states of DNA replication by allowing for separation of interlinked daughter chromosomes so that segregation into daughter cells can occur. Fluoroquinolones inhibit these topoisomerase enzymes by stabilizing either the DNA-DNA gyrase complex or the DNA-topoismerase IV complex; these stabilized complexes block movement of the DNA replication fork and thereby inhibit DNA replication resulting in cell death.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 375
... Ciprofloxacin is cytotoxic to a variety of cultured mammalian cell lines at concn that deplete cells of mtDNA. The IC50 values for ciprofloxacin varied from 40-80 ug/ml depending on the cell line tested. Cytotoxicity required continuous exposure of cells to drug for 2-4 days, which corresponded to approx three or four cell doublings. Shorter times of drug exposure did not cause significant cytotoxicity. In addition, cells became drug resistant when they were grown under conditions that bypassed the need for mitochondrial respiration. Resistance was not due to a decr in cellular drug accumulation, ... /indicating/ that ciprofloxacin cytotoxicity is caused by the loss of mtDNA encoded functions. Analysis of mtDNA from ciprofloxacin treated cells revealed the presence of site specific, double stranded DNA breaks. ... Exonuclease protection studies indicated that the 5'-, but not the 3', ends of the drug induced DNA breaks were tightly associated with protein. These results suggest that ciprofloxacin may be causing cytotoxicity by interfering with a mitochondrial topoisomerase II like activity, resulting in a loss of mtDNA.
PMID:8913349 Lawrence JW, et al; Mol Pharmacol 50 (5): 1178-88 (1996)
Fluoroquinolones prolong the QT interval by blocking voltage-gated potassium channels, especially the rapid component of the delayed rectifier potassium current I(Kr), expressed by HERG (the human ether-a-go-go-related gene). According to the available case reports and clinical studies, moxifloxacin carries the greatest risk of QT prolongation from all available quinolones in clinical practice and it should be used with caution in patients with predisposing factors for Torsades de pointes (TdP).
PMID:22156660 Briasoulis A et al; Cardiology 120 (2): 103-10 (2011)