
1. B 663
2. B-663
3. B663
4. G 30,320
5. G-30,320
6. G30,320
7. Lamprene
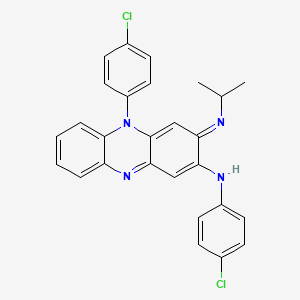
8. N,5-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-3,5-dihydro-3-((1-methylethyl)imino)-2-phenazinamine
1. 2030-63-9
2. Lamprene
3. Chlofazimine
4. Lampren
5. Clofazimina
6. Clofaziminum
7. Nsc-141046
8. B 663 (pharmaceutical)
9. Clofaziminum [inn-latin]
10. Clofazimina [inn-spanish]
11. G 30320
12. N,5-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-3-propan-2-yliminophenazin-2-amine
13. B-663
14. 3-(p-chloranilino)-10-(p-chlorphenyl)-2,10-dihydro-2-(isopropylimino)-phenazin
15. 3-(p-chloroanilino)-10-(p-chlorophenyl)-2,10-dihydro-2-(isopropylimino)phenazine
16. B 663
17. 3-(p-chloranilino)-10-(p-chlorophenyl)-2,10-dihydro-2-(isopropylimino)-phenazine
18. G-30320
19. D959ae5usf
20. 2-phenazinamine, N,5-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-3,5-dihydro-3-((1-methylethyl)imino)-
21. Chembl1083384
22. N,5-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-3,5-dihydro-3-(isopropylimino)phenazin-2-amine
23. 2-phenazinamine, 3,5-dihydro-n,5-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-3-((1-methylethyl)imino)-
24. N,5-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-3,5-dihydro-3-[(1-methylethyl)imino]-2-phenazinamine
25. Mmv687800
26. Nsc141046
27. Phenazine, 2,10-dihydro-3-(p-chloroanilino)-10-(p-chlorophenyl)-2-(isopropylimino)-
28. Phenazine, 3-(p-chloroanilino)-10-(p-chlorophenyl)-2,10-dihydro-2-(isopropylimino)-
29. Ncgc00016600-01
30. Cas-2030-63-9
31. N,5-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-3-(propan-2-ylimino)-3,5-dihydrophenazin-2-amine
32. 2-phenazinamine, N,5-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-3,5-dihydro-3-[(1-methylethyl)imino]-
33. 3-(p-chloranilino)-10-(p-chlorophenyl)-2,10-dihydro-2-(isopropylimino)phenazine
34. Riminophenazine
35. (e)-n,5-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-3-(isopropylimino)-3,5-dihydrophenazin-2-amine
36. N,5-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-3,5-dihydro-3-(isopropyliaino)phenazin-2-amine
37. B 663 (van)
38. (3z)-n,5-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-3-[(1-methylethyl)imino]-3,5-dihydrophenazin-2-amine
39. Lamprene (tn)
40. Smr000058704
41. B 663, Pharmaceutical
42. Sr-05000001807
43. Einecs 217-980-2
44. Unii-d959ae5usf
45. Nsc 141046
46. Brn 0060420
47. Colfazimine
48. Clofazimine (jan/usp/inn)
49. (3e)-n,5-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-3-isopropylimino-phenazin-2-amine
50. Liposome-encapsulated Clofazimine
51. Clofazimine [usan:usp:inn:ban]
52. Prestwick_685
53. Mfcd00056793
54. 3-(p-chloranilino)-10-(p-chlorphenyl)-2,10-dihydro-2-(isopropylimino)-phenazin [german]
55. Smp2_000339
56. (non-d)clofazimine-d7
57. B663
58. Cpd000058704
59. Clofazimine [mi]
60. Prestwick0_000376
61. Prestwick1_000376
62. Prestwick2_000376
63. Prestwick3_000376
64. Clofazimine [inn]
65. Clofazimine [jan]
66. Dsstox_cid_2839
67. Clofazimine [usan]
68. B. 663
69. Clofazimine [vandf]
70. Colfazimine [vandf]
71. Cid_2794
72. Chembl1292
73. Clofazimine [mart.]
74. Dsstox_rid_76752
75. Bidd:pxr0147
76. Dsstox_gsid_22839
77. Schembl26757
78. Schembl26758
79. Bspbio_000531
80. Clofazimine [usp-rs]
81. Clofazimine [who-dd]
82. Clofazimine [who-ip]
83. 4-25-00-03033 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
84. Mls000028617
85. Mls001424318
86. Mls006010789
87. Spbio_002452
88. Bpbio1_000585
89. Chebi:3749
90. Gtpl9184
91. Schembl5663361
92. Dtxsid7022839
93. Clofazimine [orange Book]
94. Clofazimine [ep Monograph]
95. Clofazimine [usp Impurity]
96. Hms1569k13
97. Hms2052b05
98. Hms2093j10
99. Hms2096k13
100. Hms2231b04
101. Hms3370n05
102. Hms3394b05
103. Hms3652a16
104. Hms3713k13
105. Kuc109573n
106. Pharmakon1600-01505974
107. Clofazimine [usp Monograph]
108. Amy22515
109. Bcp07792
110. Clofaziminum [who-ip Latin]
111. Hy-b1046
112. Ksc-27-052a
113. Tox21_110516
114. Bdbm50318909
115. Bdbm50378783
116. Nsc759283
117. S4107
118. Zinc17953024
119. Akos015896438
120. Akos026749881
121. Zinc100037101
122. Zinc253916263
123. Ccg-101159
124. Ccg-269477
125. Cs-4567
126. Db00845
127. Ks-1412
128. Nc00409
129. Nsc-759283
130. Ncgc00016600-02
131. Ncgc00016600-03
132. Ncgc00016600-04
133. Ncgc00016600-05
134. Ncgc00016600-07
135. Ncgc00016600-08
136. Ncgc00016600-09
137. Ncgc00179529-01
138. Smr004701474
139. Clofazimine 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
140. Phenazine,10-dihydro-2-(isopropylimino)-
141. Sbi-0206865.p001
142. Ft-0657414
143. Sw196840-4
144. A16462
145. C06915
146. D00278
147. 030c639
148. A814428
149. Q418611
150. Sr-01000000259
151. J-013203
152. Sr-01000000259-6
153. Sr-05000001807-1
154. Sr-05000001807-2
155. Brd-k56614220-001-10-9
156. Z2037279473
157. Clofazimine, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
158. N,5-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-3-propan-2-ylimino-2-phenazinamine
159. N,5-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-3-propan-2-ylimino-phenazin-2-amine
160. Clofazimine, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
161. 2-p-chloranilino-5-p-chlorphenyl-3,5-dihydro-3-isopropylimino-phenazin
162. N,5-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-3-(isopropylimino)-3,5-dihydrophenazin-2-amine
163. (4-chloro-phenyl)-[5-(4-chloro-phenyl)-3-isopropylimino-3,5-dihydro-phenazin-2-yl]-amine
164. 2-phenazinamine,5-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-3,5-dihydro-3-[(1-methylethyl)imino]-
165. 2-phenazinamine,5-dihydro-n,5-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-3-[(1-methylethyl)imino]-
166. 2-phenazinamine,n,5-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-3,5-dihydro-3-[(1-methylethyl)imino]-
167. Clofazimine For System Suitability, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
168. N,5-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-3-([1-methylethyl]imino)-3,5-dihydro-2-phenazinamine #
169. N,5-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-3-[(propan-2-yl)imino]-3,5-dihydrophenazin-2-amine
170. Phenazine,10-dihydro-3-(p-chloroanilino)-10-(p-chlorophenyl)-2-(isopropylimino)-
| Molecular Weight | 473.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C27H22Cl2N4 |
| XLogP3 | 7.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 472.1221521 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 472.1221521 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 40 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 33 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 829 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Lamprene |
| PubMed Health | Clofazimine (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Leprostatic |
| Active Ingredient | Clofazimine |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 50mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Novartis |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Lamprene |
| PubMed Health | Clofazimine (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Leprostatic |
| Active Ingredient | Clofazimine |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 50mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Novartis |
Clofazimine is indicated for the treatment of lepromatous leprosy, including dapsone-resistant lepromatous leprosy and lepromatous leprosy complicated by erythema nodosum leprosum. To prevent the development of drug resistance, it should be used only in combination with other antimycobacterial leprosy treatments.
Clofazimine exerts a slow bactericidal effect on Mycobacterium leprae (Hansen's bacillus) due primarily to its action on the bacterial outer membrane, though there is some evidence that activity on the bacterial respiratory chain and ion transporters may play a role. It also exerts anti-inflammatory properties due to the suppression of T-lymphocyte activity. Clofazimine has a relatively long duration of action owing to its long residence time in the body, but is still administered daily. Approximately 75-100% of patients receiving clofazimine will experience an orange-pink to brownish-black discoloration of the skin, conjunctivae, and bodily fluids. Skin discoloration may take several months or years to reverse following the cessation of therapy. Clofazimine has also been implicated in abdominal obstruction, in some cases fatal, due to the deposition of drug and formation of crystals in the intestinal mucosa - complaints of abdominal pain and nausea/vomiting should be investigated promptly, and the doses of clofazimine should be lowered or discontinued if it is found to be the culprit. Its use should be avoided in patients with hepatic dysfunction.
Leprostatic Agents
Substances that suppress Mycobacterium leprae, ameliorate the clinical manifestations of leprosy, and/or reduce the incidence and severity of leprous reactions. (See all compounds classified as Leprostatic Agents.)
Anti-Inflammatory Agents
Substances that reduce or suppress INFLAMMATION. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Inflammatory Agents.)
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J04 - Antimycobacterials
J04B - Drugs for treatment of lepra
J04BA - Drugs for treatment of lepra
J04BA01 - Clofazimine
Absorption
Absorption varies from 45 to 62% following oral administration in leprosy patients. Co-administration of a 200mg dose of clofazimine with food resulted in a Cmax of 0.41 mg/L with a Tmax of 8 h; administered in a fasting state, the corresponding Cmax was 30% lower while the time to Cmax was 12 h.
Route of Elimination
Part of an ingested dose of clofazimine is found in the feces, which may represent excretion in the bile, and a small amount is also eliminated in the sputum, sebum, and sweat. Excretion of unchanged drug and metabolites in a 24-hour urine collection was negligible.
Volume of Distribution
Clofazimine is highly lipophilic and therefore deposits primarily in fatty tissues and cells of the reticuloendothelial system, where it is taken up by macrophages and further distributed throughout the body. Crystalized deposits have been found in the mesenteric lymph nodes, adrenals, subcutaneous fat, liver, bile, gall bladder, spleen, small intestine, muscles, bones, and skin.
Three metabolites have been identified in the urine following repeated oral doses of clofazimine. It is unclear whether these metabolites are pharmacologically active. Metabolite I may be the result of the hydrolytic dehalogenation of clofazimine and metabolite II presumably is formed by a hydrolytic deamination reaction followed by glucuronidation.
The mean elimination half-life is approximately 25 days.
Although the precise mechanism(s) of action of clofazimine have not been elucidated, its antimicrobial activity appears to be membrane-directed. It was previously thought that, due to its lipophilicity, clofazimine participated in the generation of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) via redox cycling, specifically H2O2 and superoxide, which then exerted an antimicrobial effect. A more recent and compelling theory involves clofazimine interacting with bacterial membrane phospholipids to generate antimicrobial lysophospholipids - bactericidal efficacy may, then, arise from the combined membrane-destabilizing effects of both clofazimine and lysophospholipids, which interfere with K+ uptake and, ultimately, ATP production. The anti-inflammatory activity of clofazimine is the result of its inhibition of T-lymphocyte activation and proliferation. Several mechanisms have been proposed, including direct antagonism of T-cell Kv 1.3 potassium channels and indirect action by promoting the release of E-series prostaglandins and reactive oxygen species from bystander neutrophils and monocytes.