
1. Bay B 5097
2. Canesten
3. Fb B 5097
4. Kanesten
5. Klotrimazole
6. Lotrimin
7. Mycelex
1. 23593-75-1
2. Lotrimin
3. Canesten
4. Mycelex
5. Clotrimazol
6. Mycosporin
7. Empecid
8. Mykosporin
9. Gyne Lotrimin
10. Chlotrimazole
11. Trimysten
12. Gyne-lotrimin
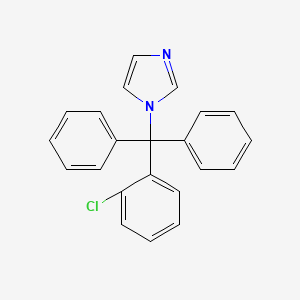
13. 1-(o-chlorotrityl)imidazole
14. Mycelex G
15. Rimazole
16. Mycelex 7
17. Tibatin
18. Gynix
19. Mono-baycuten
20. Lotrimin Af Cream
21. Mycelex Troches
22. Lotrimin Af Solution
23. Mycelex Otc
24. Canestine
25. Pedisafe
26. Veltrim
27. Lotrimin Af
28. Trivagizole 3
29. Desamix F
30. Mycelex-g
31. Bay B 5097
32. Fem Care
33. Gyne-lotrimin 3
34. Mycelex-7
35. Clotrimazolum
36. Monobaycuten
37. (chlorotrityl)imidazole
38. 1-((2-chlorophenyl)diphenylmethyl)-1h-imidazole
39. Canifug
40. Bay 5097
41. Lotrimax
42. Lotrimin Af Jock-itch Cream
43. Mycelax
44. Mycofug
45. Mycelex-7 Combination Pack
46. Gyne-lotrimin Combination Pack
47. 1-(o-chloro-alpha,alpha-diphenylbenzyl)imidazole
48. Gyne-lotrimin 3 Combination Pack
49. Bay-b 5097
50. 1-[(2-chlorophenyl)-diphenylmethyl]imidazole
51. 1h-imidazole, 1-[(2-chlorophenyl)diphenylmethyl]-
52. Fb 5097
53. Lotrimin (tn)
54. Mycelex (tn)
55. 1-(o-chlorophenyldiphenylmethyl)imidazole
56. (2-chlorophenyl)diphenyl-1-imidazolylmethane
57. Trivagizole
58. Diphenyl(2-chlorophenyl)(1-imidazolyl)methane
59. Diphenyl-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-imidazolylmethane
60. 1-(alpha-(2-chlorophenyl)benzhydryl)imidazole
61. Nsc 257473
62. 1-[(2-chlorophenyl)diphenylmethyl]-1h-imidazole
63. 1-[(2-chlorophenyl)(diphenyl)methyl]-1h-imidazole
64. Mycelex: Mycosporinrimazole
65. Bay B 9057
66. Prestwick_120
67. Bis-phenyl-(2-chlorophenyl)(1-imidazoyl)methane
68. Gnf-pf-3499
69. 1h-imidazole, 1-((2-chlorophenyl)diphenylmethyl)-
70. Methane, Bis-phenyl-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-imidazolyl-
71. Bisphenyl-(2-chlorphenyl)-1-imidazolyl-methan
72. Lopac-c-6019
73. Nsc257473
74. Chembl104
75. Nsc-257473
76. 1-(2-chlorotrityl)imidazole
77. Mls000028502
78. Chebi:3764
79. 1-[(2-chlorophenyl)-diphenyl-methyl]imidazole
80. G07gz97h65
81. Bay-5097
82. Svt-15652
83. 1-(o-chloro-.alpha.,.alpha.-diphenylbenzyl)imidazole
84. Ncgc00015251-02
85. Clotrimaderm
86. Canestene
87. Clomatin
88. Cutistad
89. Esparol
90. Smr000058306
91. Stiemazol
92. Nalbix
93. Femcare
94. Lotrimin Lotion
95. Canesten Cream
96. Cas-23593-75-1
97. Clotrimazole 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
98. Gino-lotremine
99. Lotrimin Cream
100. Mycelex Cream
101. Myclo Solution
102. Mycelex Solution
103. Myclo Cream
104. Dsstox_cid_9871
105. Myclo-gyne
106. Pan-fungex
107. Canesten Solution
108. Lotrimin Solution
109. Neo-zol Cream
110. Bis-phenyl-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-imidazoyl)methane
111. Dsstox_rid_78827
112. Mycelex Twin Pack
113. Dsstox_gsid_29871
114. Lotrimin Af Lotion
115. Clotrimazol [inn-spanish]
116. Clotrimazolum [inn-latin]
117. Myclo Spray Solution
118. Clotrimeizol
119. Jidesheng
120. Canesten 1-day Therapy
121. Canesten 3-day Therapy
122. Canesten 6-day Therapy
123. Drg-0072
124. B 5097
125. Ccris 6245
126. Canesten 1-day Cream Combi-pak
127. Hsdb 3266
128. Canesten Combi-pak 1-day Therapy
129. Canesten Combi-pak 3-day Therapy
130. Sr-01000075771
131. Einecs 245-764-8
132. Brn 0622318
133. Chlortrimazole
134. Clortrimazole
135. Otomax
136. Unii-g07gz97h65
137. 1-((o-chloro-phenyl)diphenylmethyl)imidazole
138. Gyne-lotrimin3
139. Bis-fenil-(2-clorofenil)-1-imidazolil-metano
140. Clotrimaderm Cream
141. Clotrimazole,(s)
142. Mfcd00057220
143. Bis-fenil-(2-clorofenil)-1-imidazolil-metano [italian]
144. Bisphenyl-(2-chlorphenyl)-1-imidazolyl-methan [german]
145. Clotrimazole Crystalline
146. Clotrimazole [usan:usp:inn:ban:jan]
147. Spectrum_001343
148. Cpd000058306
149. Clotrimazole (canesten)
150. Prestwick0_000267
151. Prestwick1_000267
152. Prestwick2_000267
153. Prestwick3_000267
154. Spectrum2_000128
155. Spectrum3_000359
156. Spectrum4_000295
157. Spectrum5_000781
158. Clotrimazole [mi]
159. Clotrimazole [inn]
160. Clotrimazole [jan]
161. C 6019
162. Clotrimazole [usan]
163. Ncimech_000609
164. Cid_2812
165. Schembl3850
166. Clotrimazole [vandf]
167. Bidd:pxr0036
168. Lopac0_000315
169. Bspbio_000114
170. Bspbio_002057
171. Clotrimazole [mart.]
172. Kbiogr_000850
173. Kbioss_001823
174. 5-23-04-00291 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
175. Mls000758243
176. Mls001423972
177. Bidd:gt0450
178. Clotrimazole [usp-rs]
179. Clotrimazole [who-dd]
180. Divk1c_000665
181. Spectrum1500200
182. Bay B5097
183. Bayb 5097
184. Imidazole, 1-(o-chloro-alpha,alpha-diphenylbenzyl)-
185. Spbio_000176
186. Spbio_002333
187. Bpbio1_000126
188. Gtpl2330
189. Component Of Otomax (salt/mix)
190. Dtxsid7029871
191. Gyne-lotrimin3 Combination Pack
192. Bdbm31774
193. Clotrimazole (jp17/usp/inn)
194. Hms502b07
195. Kbio1_000665
196. Kbio2_001823
197. Kbio2_004391
198. Kbio2_006959
199. Kbio3_001277
200. Clotrimazole [green Book]
201. Imidazole, 1-(o-chloro-.alpha.,.alpha.-diphenylbenzyl)-
202. Component Of Lotrimax (salt/mix)
203. Ninds_000665
204. Clotrimazole [ep Impurity]
205. Clotrimazole [orange Book]
206. Hms1568f16
207. Hms1920o21
208. Hms2051e11
209. Hms2091g10
210. Hms2095f16
211. Hms2235e20
212. Hms3260p12
213. Hms3369i03
214. Hms3393e11
215. Hms3655i09
216. Hms3712f16
217. Pharmakon1600-01500200
218. Clotrimazole [ep Monograph]
219. Clotrimazole [usp Impurity]
220. Imidazole,.alpha.-diphenylbenzyl)-
221. Bcp02150
222. Clotrimazole For Peak Identification
223. Zinc3807804
224. Clotrimazole [usp Monograph]
225. Tox21_110111
226. Tox21_300415
227. Tox21_500315
228. Ccg-35563
229. Nsc756700
230. S1606
231. Stk700023
232. Akos005607024
233. Lotrisone Component Clotrimazole
234. Tox21_110111_1
235. Cs-1926
236. Db00257
237. Lp00315
238. Nc00035
239. Nsc-756700
240. Sb17418
241. Sdccgsbi-0050303.p005
242. Clotrimazole 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
243. Idi1_000665
244. Mrf-0000070
245. Qtl1_000024
246. Ncgc00015251-01
247. Ncgc00015251-03
248. Ncgc00015251-04
249. Ncgc00015251-05
250. Ncgc00015251-06
251. Ncgc00015251-07
252. Ncgc00015251-08
253. Ncgc00015251-09
254. Ncgc00015251-10
255. Ncgc00015251-11
256. Ncgc00015251-12
257. Ncgc00015251-13
258. Ncgc00015251-14
259. Ncgc00015251-27
260. Ncgc00093761-01
261. Ncgc00093761-02
262. Ncgc00093761-03
263. Ncgc00093761-04
264. Ncgc00093761-05
265. Ncgc00093761-06
266. Ncgc00254538-01
267. Ncgc00261000-01
268. 1-(o-chloro-a,a-diphenylbenzyl)imidazole
269. As-13816
270. Clotrimazole Component Of Lotrisone
271. Hy-10882
272. 1-(2-chloro-?,?-diphenylbenzyl)imidazole
273. Sbi-0050303.p004
274. Db-046195
275. 1-[(2-chlorophenyl)diphenylmethyl]imidazole
276. Ab00051951
277. Eu-0100315
278. Ft-0603193
279. Sw196431-5
280. C06922
281. D00282
282. 1-(.alpha.-(2-chlorophenyl)benzhydryl)imidazole
283. 1-[(2-chlorophenyl)-di(phenyl)methyl]imidazole
284. Ab00051951-14
285. Ab00051951_15
286. Ab00051951_16
287. Clotrimazole, Vetranal(tm), Analytical Standard
288. 593c751
289. A816789
290. Q413546
291. 1h-imidazole, 1-[(2-chlorophenyl)-diphenylmethyl]
292. Sr-01000075771-1
293. Sr-01000075771-6
294. Sr-01000075771-8
295. W-107394
296. 1-[(2-chloro-phenyl)-diphenyl-methyl]-1h-imidazole
297. Brd-k15916496-001-14-7
298. Sr-01000075771-10
299. 3acdfdf8-38e3-4368-85d0-bdf8ae1e6591
300. Clotrimazole, British Pharmacopoeia (bp) Reference Standard
301. Clotrimazole, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
302. Clotrimazole, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
303. 1-(o-chlorotrityl)imidazole;1-(o-chloro-alpha,alpha-diphenylbenzyl)imidazole
304. Clotrimazole For Peak Identification, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
305. Clotrimazole, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
306. 117829-71-7
| Molecular Weight | 344.8 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C22H17ClN2 |
| XLogP3 | 5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 1 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 344.1080262 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 344.1080262 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 17.8 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 25 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 396 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 20 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Clotrimazole |
| PubMed Health | Clotrimazole |
| Drug Classes | Antifungal, Imidazole |
| Drug Label | Each Clotrimazole Troche (clotrimazole lozenges) USP contains 10 mg clotrimazole [1-(o-chloro-,-diphenylbenzyl) imidazole], a synthetic antifungal agent, for topical use in the mouth.Structural Formula:The troche dosage form is a large, slowly di... |
| Active Ingredient | Clotrimazole |
| Dosage Form | Cream; Solution; Troche/lozenge |
| Route | Topical; Vaginal; Oral |
| Strength | 1%; 10mg |
| Market Status | Over the Counter; Prescription |
| Company | Fougera Pharms; Glenmark Pharms; Paddock; Actavis Mid Atlantic; Teva; Taro; Roxane |
| 2 of 20 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Gyne-lotrimin |
| PubMed Health | Clotrimazole |
| Drug Classes | Antifungal, Imidazole |
| Active Ingredient | Clotrimazole |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Cream |
| Route | Vaginal |
| Strength | 1%; 100mg |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Schering Plough |
| 3 of 20 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Gyne-lotrimin 3 |
| PubMed Health | Clotrimazole (Topical route) |
| Drug Classes | Antifungal, Imidazole |
| Active Ingredient | Clotrimazole |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Cream |
| Route | Vaginal |
| Strength | 200mg; 2% |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Schering Plough |
| 4 of 20 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Gyne-lotrimin 3 combination pack |
| PubMed Health | Clotrimazole |
| Drug Classes | Antifungal, Imidazole |
| Active Ingredient | Clotrimazole |
| Dosage Form | Cream, tablet |
| Route | Topical, vaginal |
| Strength | 1%,200mg |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Schering Plough |
| 5 of 20 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Gyne-lotrimin combination pack |
| PubMed Health | Clotrimazole (Vaginal) |
| Drug Classes | Antifungal |
| Active Ingredient | Clotrimazole |
| Dosage Form | Cream, tablet |
| Route | Topical, vaginal |
| Strength | 1%,100mg |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Schering Plough |
| 6 of 20 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Lotrimin af |
| Active Ingredient | Clotrimazole |
| Dosage Form | Cream; Lotion; Solution |
| Route | topical |
| Strength | 1% |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Schering Plough |
| 7 of 20 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Mycelex |
| Active Ingredient | Clotrimazole |
| Dosage Form | Solution |
| Route | topical |
| Strength | 1% |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Bayer Hlthcare |
| 8 of 20 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Mycelex-7 |
| Active Ingredient | Clotrimazole |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Cream |
| Route | Vaginal |
| Strength | 1%; 100mg |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Bayer |
| 9 of 20 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Mycelex-7 combination pack |
| Active Ingredient | Clotrimazole |
| Dosage Form | Cream, tablet |
| Route | Topical, vaginal |
| Strength | 1%,100mg |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Bayer |
| 10 of 20 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Trivagizole 3 |
| Active Ingredient | Clotrimazole |
| Dosage Form | Cream |
| Route | Vaginal |
| Strength | 2% |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Taro |
| 11 of 20 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Clotrimazole |
| PubMed Health | Clotrimazole |
| Drug Classes | Antifungal, Imidazole |
| Drug Label | Each Clotrimazole Troche (clotrimazole lozenges) USP contains 10 mg clotrimazole [1-(o-chloro-,-diphenylbenzyl) imidazole], a synthetic antifungal agent, for topical use in the mouth.Structural Formula:The troche dosage form is a large, slowly di... |
| Active Ingredient | Clotrimazole |
| Dosage Form | Cream; Solution; Troche/lozenge |
| Route | Topical; Vaginal; Oral |
| Strength | 1%; 10mg |
| Market Status | Over the Counter; Prescription |
| Company | Fougera Pharms; Glenmark Pharms; Paddock; Actavis Mid Atlantic; Teva; Taro; Roxane |
| 12 of 20 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Gyne-lotrimin |
| PubMed Health | Clotrimazole |
| Drug Classes | Antifungal, Imidazole |
| Active Ingredient | Clotrimazole |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Cream |
| Route | Vaginal |
| Strength | 1%; 100mg |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Schering Plough |
| 13 of 20 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Gyne-lotrimin 3 |
| PubMed Health | Clotrimazole (Topical route) |
| Drug Classes | Antifungal, Imidazole |
| Active Ingredient | Clotrimazole |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Cream |
| Route | Vaginal |
| Strength | 200mg; 2% |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Schering Plough |
| 14 of 20 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Gyne-lotrimin 3 combination pack |
| PubMed Health | Clotrimazole |
| Drug Classes | Antifungal, Imidazole |
| Active Ingredient | Clotrimazole |
| Dosage Form | Cream, tablet |
| Route | Topical, vaginal |
| Strength | 1%,200mg |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Schering Plough |
| 15 of 20 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Gyne-lotrimin combination pack |
| PubMed Health | Clotrimazole (Vaginal) |
| Drug Classes | Antifungal |
| Active Ingredient | Clotrimazole |
| Dosage Form | Cream, tablet |
| Route | Topical, vaginal |
| Strength | 1%,100mg |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Schering Plough |
| 16 of 20 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Lotrimin af |
| Active Ingredient | Clotrimazole |
| Dosage Form | Cream; Lotion; Solution |
| Route | topical |
| Strength | 1% |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Schering Plough |
| 17 of 20 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Mycelex |
| Active Ingredient | Clotrimazole |
| Dosage Form | Solution |
| Route | topical |
| Strength | 1% |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Bayer Hlthcare |
| 18 of 20 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Mycelex-7 |
| Active Ingredient | Clotrimazole |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Cream |
| Route | Vaginal |
| Strength | 1%; 100mg |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Bayer |
| 19 of 20 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Mycelex-7 combination pack |
| Active Ingredient | Clotrimazole |
| Dosage Form | Cream, tablet |
| Route | Topical, vaginal |
| Strength | 1%,100mg |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Bayer |
| 20 of 20 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Trivagizole 3 |
| Active Ingredient | Clotrimazole |
| Dosage Form | Cream |
| Route | Vaginal |
| Strength | 2% |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Taro |
Anti-Infective Agents, Local; Antifungal Agents; Growth Inhibitors
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
CLOTRIMAZOLE IS A CHLORINATED IMIDAZOLE DERIVATIVE THAT IS USED TO TREAT TOPICAL FUNGAL, DERMATOPHYTE, & YEAST INFECTIONS. WHILE CLOTRIMAZOLE HAS MARKED IN VITRO ACTIVITY AGAINST MANY FUNGI, IT IS OF LITTLE VALUE IN TREATMENT OF SYSTEMIC MYCOSES.
Miller, R. R., and D. J. Greenblatt. Handbook of Drug Therapy. New York: Elsevier North Holland, 1979., p. 166
VAGINAL: 1 TABLET (100 MG) IS INSERTED DAILY FOR 1 WK FOR CANDIDAL VAGINITIS. TOPICAL: SUFFICIENT CREAM OR SOLN IS APPLIED TWICE DAILY TO SKIN INFECTED WITH CANDIDA ALBICANS, TRICOPHYTON, OR MICROSPORUM SPECIES. 2 WK OF THERAPY IS USUALLY SUFFICIENT.
Miller, R. R., and D. J. Greenblatt. Handbook of Drug Therapy. New York: Elsevier North Holland, 1979., p. 167
CLOTRIMAZOLE HAS BEEN USED INVESTIGATIONALLY FOR ORAL TREATMENT OF MUCOCUTANEOUS CANDIDIASIS.
Miller, R. R., and D. J. Greenblatt. Handbook of Drug Therapy. New York: Elsevier North Holland, 1979., p. 167
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for CLOTRIMAZOLE (12 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
PREPN OF CLOTRIMAZOLE ARE NOT INTENDED FOR OPHTHALMIC USE & SHOULD BE USED WITH CAUTION AROUND EYES.
American Medical Association. AMA Drug Evaluations Annual 1991. Chicago, IL: American Medical Association, 1991., p. 1424
Clotrimazole lozenges should not be used for the treatment of systemic myotic infections.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 92. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1992 (Plus Supplements 1992)., p. 2102
Clotrimazole Vaginal tablets ... single-dose therapy is not recommended for the treatment of severe vulvovaginal candidiasis.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 92. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1992 (Plus Supplements 1992)., p. 2102
To achieve maximum theraputic effect of clotrimazole when the drug is administered orally as a lozenge, the lozenge must be dissolved slowly in the mouth. Therefore, patients receiving clotrimazole lozenges must be of such age and physical and/or mental condition that they can comprehend and follow administration instruction. Liver function tests should be conducted periodically during oral therapy with clotrimazole lozenges, especially in patients with preexisting hepatic impairment.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 92. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1992 (Plus Supplements 1992)., p. 2102
Clotrimazole topical cream, lotion, and solution should be used during the first trimester of pregnancy only when the drug is considered essential to the welfare of the patient. Since it is not known whether clotrimazole is distributed into milk, the drug should be used with caution in nursing women.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 92. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1992 (Plus Supplements 1992)., p. 2103
**Topical preparations** Clotrimazole topical cream is indicated for the topical treatment of the following dermal infections,: Tinea pedis, tinea cruris, and tinea corporis due to _Trichophyton rubrum_, _Trichophyton mentagrophytes_, _Epidermophyton floccosum_ Candidiasis due to _Candida albicans_ Tinea versicolor due to _Malassezia furfur_ Diaper rash infected by _Candida albicans_ In some preparations, clotrimazole may be combined with betamethasone dipropionate, a corticosteroid. **Oral preparations** The oral troche preparation is indicated for the local treatment of oropharyngeal candidiasis. It is also indicated as a prophylactic drug to reduce the incidence of oropharyngeal candidiasis in patients immunocompromised by conditions such as chemotherapy, radiotherapy, or steroid therapy utilized in the treatment of leukemia, solid tumors, or renal transplantation. Troche preparations are not indicated for the treatment of any systemic mycoses.
FDA Label
Clotrimazole is a broad-spectrum antifungal agent that inhibits the growth of pathogenic yeasts by changing the permeability of cell membranes. The action of clotrimazole is fungistatic at concentrations of drug up to 20 mcg/mL and may be fungicidal _in vitro_ against Candida albicans and other species of the genus Candida at higher concentrations. Unfortunately, resistance to clotrimazole, which was rare in the past, is now common in various patient populations. Clotrimazole is generally considered to be a fungistatic, and not a fungicidal drug, although this contrast is not absolute, as clotrimazole shows fungicidal properties at higher concentrations.
14-alpha Demethylase Inhibitors
Compounds that specifically inhibit STEROL 14-DEMETHYLASE. A variety of azole-derived ANTIFUNGAL AGENTS act through this mechanism. (See all compounds classified as 14-alpha Demethylase Inhibitors.)
Anti-Infective Agents, Local
Substances used on humans and other animals that destroy harmful microorganisms or inhibit their activity. They are distinguished from DISINFECTANTS, which are used on inanimate objects. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Infective Agents, Local.)
Antifungal Agents
Substances that destroy fungi by suppressing their ability to grow or reproduce. They differ from FUNGICIDES, INDUSTRIAL because they defend against fungi present in human or animal tissues. (See all compounds classified as Antifungal Agents.)
G01AF02
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A01 - Stomatological preparations
A01A - Stomatological preparations
A01AB - Antiinfectives and antiseptics for local oral treatment
A01AB18 - Clotrimazole
D - Dermatologicals
D01 - Antifungals for dermatological use
D01A - Antifungals for topical use
D01AC - Imidazole and triazole derivatives
D01AC01 - Clotrimazole
G - Genito urinary system and sex hormones
G01 - Gynecological antiinfectives and antiseptics
G01A - Antiinfectives and antiseptics, excl. combinations with corticosteroids
G01AF - Imidazole derivatives
G01AF02 - Clotrimazole
Absorption
Because clotrimazole is generally not significantly absorbed, drug interactions are not a major issue with its use.
Route of Elimination
Mainly hepatic.
Volume of Distribution
The topical form is minimally absorbed in the serum and tissues. Clotrimazole is a lipophilic drug, and has been shown to be secreted in breastmilk in animal studies. There are limited data available regarding the volume of distribution following oral troche administration.
GIVEN ORALLY OR IV WAS ABSORBED, DISTRIBUTED, ELIMINATED READILY. EXCRETED AS INACTIVE METABOLITE IN BILE, LITTLE IN URINE.
DUHM B ET AL; POSTGRAD MED J (SUPPL) 500 (1): 13-16 (1974)
Absorption of clotrimazol is less than 0.5% after application to the intact skin: from the vagina, it is 3 to 10%. Fungicidal concentrations remain in the vagina for as long as 3 days after application of the drug. The small amount absorbed is metabolized in the liver and excreted in bile. In adults, an oral dose of 200 mg per day will give rise to plasma concentrations of 0.2 to 0.35 ug/ml.
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 1176
Only very small amounts of clotrimazole appear to be absorbed systemically following topical application to the skin. Following application to the skin, highest concentrations of clotrimazole are present in the stratum corneum; lower drug concentrations occur in the stratum spinosum and the papillary and reticular dermis. Small amounts of clotrimazole are absorbed systemically when the drug is administered intravaginally. Following intravaginal administration of radiolabeled clotrimazole in patients with normal or inflamed vaginal mucosa, peak serum concentrations of clotrimazole 24 hours after insertion of a single 100 mg tablet of the drug are 0.03 ug/ml and peak serum concentrations 24 hours after administration of a cream containing 50 mg of the drug are 0.01 ug/ml. About 3-10% of an intravaginal dose of the drug reaches systemic circulation, principally as metabolites.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 92. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1992 (Plus Supplements 1992)., p. 2101
Clotrimazole is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract ... and excreted in the feces and urine. When applied topically clotrimazole penetrates the epidermis but there is little if any systemic absorption. Slight absorption has been reported following the administration of vaginal tablets.
Reynolds, J.E.F., Prasad, A.B. (eds.) Martindale-The Extra Pharmacopoeia. 28th ed. London: The Pharmaceutical Press, 1982., p. 721
Hepatic (metabolized to inactive metabolites).
Clotrimazole ... is metabolized in the liver to inactive compounds ... .
Reynolds, J.E.F., Prasad, A.B. (eds.) Martindale-The Extra Pharmacopoeia. 28th ed. London: The Pharmaceutical Press, 1982., p. 721
The effect of the antifungal imidazole compound, clotrimazole, on the metabolism of benzo[a]pyrene was studied in cultured keratinocytes prepared from BALB/c mouse epidermis. Varying concentrations of clotrimazole added to the cultured keratinocytes resulted in a dose dependent inhibition of the activities of the microsomal cytochrome p450 dependent monooxygenases aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase and 7-ethoxycoumarin O-deethylase. The major organic solvent soluble metabolites of benzo(a)pyrene identified in the cultured cells were trans-7,8-dihydro-7,8-dihydroxybenzo(a)pyrene, 9-hydroxybenzo(a)pyrene, and 3-hydroxybenzo(a)pyrene, although small amounts of trans-4,5-dihydro-4,5-dihydroxybenzo(a)pyrene, benzo(a)pyrene-quinones, and trans-9,10-dihydroxybenzo(a)pyrene were also present. The major organic solvent extractable metabolites of benzo(a)pyrene found in the extracellular culture medium were primarily the diols with smaller quantities of phenols and quinones. The major water soluble metabolites of benzo(a)pyrene present both intracellularly and extracellularly were glucuronide conjugates of 3-hydroxybenzo(a)pyrene, 9-hydroxybenzo(a)pyrene, and benzo(a)pyrene-3,6-dione and to a lesser extent sulfate conjugates (primarily of the trans-7,8-dihydro-7,8- dihydroxybenzo(a)pyrene). Clotrimazole inhibited the generation of organic solvent soluble and water soluble conjugates in a dose dependent manner. The in vitro metabolism of benzo(a)pyrene by microsomes prepared from control and benz(a)anthracene induced cultured keratinocytes was also inhibited by clotrimazole with greater inhibitory effect on benz(a)anthracene induced keratinocytes especially with respect to the formation of diols and quinones. The enzyme mediated covalent binding of benzo(a)pyrene to mouse keratinocyte DNA and protein was also substantially diminished by clotrimazole in a dose dependent fashion. These results indicate that clotrimazole, a widely used drug for the management of a variety of superficial dermatophyte infections of the skin, is a potent inhibitor of cytochrome p450 dependent transformation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in cultured murine keratinocytes. This system offers a convenient approach for studies as inhibitors of carcinogen metabolism in the epidermis.
PMID:3755152 Das M et al; J Invest Dermatol 87 (1): 4-10 (1986)
Clotrimazole was given by mouth in a dose of 1.5 g to 7 healthy subjects and 47 patients and peak blood concentrations of up to 1 ug/ml were detected microbiologically at 2 or 4 hours. The half-life was between 3.5 and 5.5 hours.
Reynolds, J.E.F., Prasad, A.B. (eds.) Martindale-The Extra Pharmacopoeia. 28th ed. London: The Pharmaceutical Press, 1982., p. 721
Clotrimazole was absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and had a biological half-life of about 4 hours. Liver and kidney dysfunction had little influence on serum concentrations or half-life.
Reynolds, J.E.F., Prasad, A.B. (eds.) Martindale-The Extra Pharmacopoeia. 28th ed. London: The Pharmaceutical Press, 1982., p. 721
Clotrimazole acts primarily by damaging the permeability barrier in the cell membrane of fungi. Clotrimazole causes inhibition of ergosterol biosynthesis, an essential constituent of fungal cell membranes. If ergosterol synthesis is either completely or partially inhibited, the cell is no longer able to construct an intact and functional cell membrane,. Because ergosterol directly promotes the growth of fungal cells in a hormonelike fashion, rapid onset of the above events leads to dose-dependent inhibition of fungal growth. Though decreased ergosterol, due to the inhibition of lanosterol 14-demethylase (also known as _CYP51_) is accepted to be primarily responsible for the antimycotic properties of clotrimazole, this drug also shows other pharmacological effects. These include the inhibition of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ATPase, depletion of intracellular calcium, and blocking of calciumdependent potassium channels and voltagedependent calcium channels. The action of clotrimazole on these targets accounts for other effects of this drug that are separate from its antimycotic activities.
Clotrimazole exerts its antifungal activity by altering cell membrane permeability, apparently by binding with phospholipids in the fungal cell membrane. In contrast to polyene antibiotics (eg, amphotericin B), the action of clotrimazole is less dependent on the sterol content of the cell membrane. As a result of alteration of permeability, the cell membrane is unable to function as a selective barrier, and potassium and other cellular constituents are lost.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 92. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1992 (Plus Supplements 1992)., p. 2101