

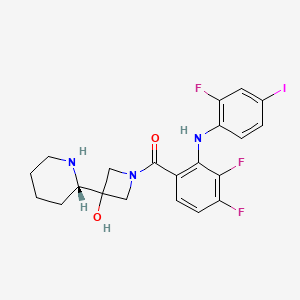

1. (3,4-difluoro-2-(2-fluoro-4-iodophenylamino)phenyl)(3-hydroxy-3-(piperidin-2-yl)azetidin-1-yl)methanone
2. Cotellic
3. Gdc-0973
4. Xl518
1. 934660-93-2
2. Gdc-0973
3. Xl518
4. Xl-518
5. Gdc 0973
6. Rg7420
7. Xl 518
8. Rg 7420
9. Er29l26n1x
10. Chembl2146883
11. [3,4-difluoro-2-(2-fluoro-4-iodoanilino)phenyl]-[3-hydroxy-3-[(2s)-piperidin-2-yl]azetidin-1-yl]methanone
12. Cobimetinib (gdc-0973, Rg7420)
13. (s)-(3,4-difluoro-2-(2-fluoro-4-iodophenylamino)phenyl)(3-hydroxy-3-(piperidin-2-yl)azetidin-1-yl)methanone
14. [3,4-bis(fluoranyl)-2-[(2-fluoranyl-4-iodanyl-phenyl)amino]phenyl]-[3-oxidanyl-3-[(2s)-piperidin-2-yl]azetidin-1-yl]methanone
15. Methanone, (3,4-difluoro-2-((2-fluoro-4-iodophenyl)amino)phenyl)(3-hydroxy-3-((2s)-2-piperidinyl)-1-azetidinyl)-
16. [3,4-difluoro-2-(2-fluoro-4-iodo-phenylamino)-phenyl]-((s)-3-hydroxy-3-piperidin-2-yl-azetidin-1-yl)-methanone
17. Eui
18. Cobimetinib Butyrate
19. Cobimetinib [usan]
20. 934660-94-3
21. Cobimetinib [usan:inn]
22. Cometinib
23. Unii-er29l26n1x
24. C21h21f3in3o2
25. Cobimetinib [mi]
26. Cobimetinib [inn]
27. Cobimetinib (usan/inn)
28. Cobimetinib [who-dd]
29. Schembl189565
30. Gtpl7626
31. Xl518;rg7420;cobimetinib
32. Chebi:90851
33. Dtxsid60239435
34. Ex-a673
35. Gdc0973
36. Gdc0973; Xl518; Cobimetinib
37. Bdbm50391802
38. Mfcd22124461
39. Nsc768068
40. Nsc781257
41. Nsc800075
42. S8041
43. Zinc60325170
44. Bcp9000716
45. Ccg-264727
46. Cs-0521
47. Db05239
48. Nsc-768068
49. Nsc-781257
50. Nsc-800075
51. Vs-0129
52. Xl518 (gdc-0973)
53. Ncgc00346455-03
54. Ncgc00346455-05
55. (3,4-difluoro-2-(2-fluoro-4-iodophenylamino)phenyl)(3-hydroxy-3-(piperidin-2-yl)azetidin-1-yl)methanone
56. (s)-(3,4-difluoro-2-((2-fluoro-4-iodophenyl)amino)phenyl)(3-hydroxy-3-(piperidin-2-yl)azetidin-1-yl)methanone
57. Hy-13064
58. Ro-5514041
59. D10405
60. J-525162
61. Q15708292
62. ((3,4-difluoro-2-(2-fluoro-4-iodoanilino)phenyl)(3-hydroxy-3-((2s)-piperidin-2-yl)azetidin-1-yl)methanone
63. (3,4-difluoro-2-(2-fluoro-4-iodophenylamino)phenyl)(3-hydroxy-3-((s)-piperidin-2-yl)cyclobutyl)methanone
64. [3,4-difluoro-2-(2-fluoro-4-iodoanilino)phenyl]-[3-hydroxy-3-[(2s)-piperidin-2-yl]azetidin
65. [3,4-difluoro-2-(2-fluoro-4-iodoanilino)phenyl]{3-hydroxy-3-[(2s)-piperidin-2-yl]azetidin-1-yl}methanone
66. [3,4-difluoro-2-[(2-fluoro-4-iodophenyl)amino]phenyl]-[3-hydroxy-3-[(2s)-piperidin-2-yl]azetidin-1-yl]methanone
67. {3,4-difluoro-2-[(2-fluoro-4-iodophenyl)amino]phenyl}{3-hydroxy-3-[(2s)-piperidin-2-yl]azetidin-1-yl}methanone
| Molecular Weight | 531.3 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C21H21F3IN3O2 |
| XLogP3 | 3.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 531.06306 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 531.06306 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 64.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 30 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 624 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
For the treatment of patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma with a BRAF V600E or V600K mutation. Cobimetinib is used in combination with vemurafenib, a BRAF inhibitor.
FDA Label
Cotellic is indicated for use in combination with vemurafenib for the treatment of adult patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma with a BRAF V600 mutation.
Treatment of all conditions included in the category of malignant neoplasms (except haematopoietic and lymphoid tissue) with Ras, Raf or MEK pathway activation
Cobimetinib is a reversible inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 (MAPK)/extracellular signal regulated kinase 1 (MEK1) and MEK2. Preclinical studies have demonstrated that this agent is effective in inhibiting the growth of tumor cells bearing a BRAF mutation, which has been found to be associated with many tumor types. A threonine-tyrosine kinase and a key component of the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK signalling pathway that is frequently activated in human tumors, MEK1 is required for the transmission of growth-promoting signals from numerous receptor tyrosine kinases. Cobimetinib is used in combination with vemurafenib because the clinical benefit of a BRAF inhibitor is limited by intrinsic and acquired resistance. Reactivation of the MAPK pathway is a major contributor to treatment failure in BRAF-mutant melanomas, approximately ~80% of melanoma tumors becomes BRAF-inhibitor resistant due to reactivation of MAPK signalling. BRAF-inhibitor resistant tumor cells are sensitive to MEK inhibition, therefore cobimetinib and vemurafenib will result in dual inhibition of BRAF and its downstream target, MEK.
L01XE38
L01XE38
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01E - Protein kinase inhibitors
L01EE - Mitogen-activated protein kinase (mek) inhibitors
L01EE02 - Cobimetinib
Absorption
The bioavailability of cobimetinib is 46%, the AUC and Cmax is unaffected by food.
Route of Elimination
76% of the dose was recovered in feces with 6.6% as unchanged drug. 17.8% of the dose was recovered in urine with 1.6% as unchanged drug.
Volume of Distribution
806L in cancer patients based on a population PK analysis.
Clearance
13.9L/h
Cobimetinib is mainly metabolized via CYP3A oxidation and UGT2B7 glucuronidation with no major metabolites formed.
Average half life was 44 hours.
MEK inhibitor Cobimetinib specifically binds to and inhibits the catalytic activity of MEK1, resulting in inhibition of extracellular signal-related kinase 2 (ERK2) phosphorylation and activation and decreased tumor cell proliferation. Cobimetinib and vemurafenib target two different kinases in the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK pathway.
