

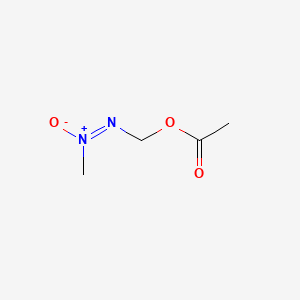

1. (methyl-onn-azoxy)methanol Acetate
2. Acetate, Methylazoxymethanol
3. Methylazoxymethanol Acetate
1. Methylazoxymethanol Acetate
2. 592-62-1
3. Methylazoxy Methanol Acetate
4. Dtxsid1025568
5. Akos006282597
| Molecular Weight | 132.12 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C4H8N2O3 |
| XLogP3 | -0.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 132.05349212 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 132.05349212 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 67.4 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 9 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 132 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Neurotoxins
Toxic substances from microorganisms, plants or animals that interfere with the functions of the nervous system. Most venoms contain neurotoxic substances. Myotoxins are included in this concept. (See all compounds classified as Neurotoxins.)
Nucleic Acid Synthesis Inhibitors
Compounds that inhibit cell production of DNA or RNA. (See all compounds classified as Nucleic Acid Synthesis Inhibitors.)
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors
Compounds which inhibit the synthesis of proteins. They are usually ANTI-BACTERIAL AGENTS or toxins. Mechanism of the action of inhibition includes the interruption of peptide-chain elongation, the blocking the A site of ribosomes, the misreading of the genetic code or the prevention of the attachment of oligosaccharide side chains to glycoproteins. (See all compounds classified as Protein Synthesis Inhibitors.)
IN RATS INJECTED WITH (3)H-METHYLAZOXYMETHANOL ACETATE ON DAY 14 OF PREGNANCY, 4% OF INJECTED RADIOACTIVITY WAS FOUND IN FETUSES; RADIOACTIVITY WAS ALSO FOUND IN LIVER & KIDNEY OF TREATED MOTHERS. DNA & RNA FROM FETAL BRAIN CONTAINED GUANINE METHYLATED IN 7-POSITION.
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V10 133 (1976)