
1. Ara C
2. Ara-c
3. Arabinofuranosylcytosine
4. Arabinoside, Cytosine
5. Arabinosylcytosine
6. Aracytidine
7. Aracytine
8. Beta Ara C
9. Beta-ara C
10. Cytarabine Hydrochloride
11. Cytonal
12. Cytosar
13. Cytosar U
14. Cytosar-u
15. Cytosine Arabinoside
1. 147-94-4
2. Ara-c
3. Cytosine Arabinoside
4. Arabinocytidine
5. Aracytin
6. Depocyt
7. Cytosar-u
8. Aracytine
9. Tarabine
10. Udicil
11. 1-beta-d-arabinofuranosylcytosine
12. Arabinofuranosylcytosine
13. Aracytidine
14. Depocyte
15. Cytarabinoside
16. Cytarabin
17. Cytosar
18. Arabinocytosine
19. Cytarabinum
20. Arabinosylcytosine
21. Cytosine Beta-d-arabinofuranoside
22. Spongocytidine
23. Cytosinearabinoside
24. Citarabina
25. Alexan
26. Beta-d-arabinosylcytosine
27. Cytarabinum [inn-latin]
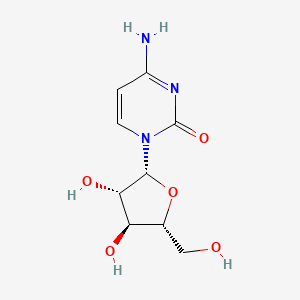
28. 4-amino-1-((2r,3s,4s,5r)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydrofuran-2-yl)pyrimidin-2(1h)-one
29. Citarabina [inn-spanish]
30. Arac
31. Cytosine Beta-d-arabinoside
32. Arabitin
33. Cytarabina
34. Arafcyt
35. Erpalfa
36. Iretin
37. Cytosine-1-beta-d-arabinofuranoside
38. 1beta-d-arabinosylcytosine
39. 4-amino-1-beta-d-arabinofuranosyl-2(1h)-pyrimidinone
40. Cytosine Arabinose
41. 1beta-arabinofuranasylcytosine
42. Cytosine 1-beta-d-arabinofuranoside
43. Cytarabine Liposome
44. 1beta-d-arabinofuranosylcytosine
45. 1-beta-d-arabinofaranosylcytosine
46. U 19920a
47. Cytosine-beta-d-arabinofuranoside
48. Cytosine Arabinofuranoside
49. Depocyt (liposomal)
50. 1-arabinofuranosylcytosine
51. 4-amino-1-beta-d-arabinofuranosylpyrimidin-2(1h)-one
52. U-19,920
53. 1-beta-d-arabinosylcytosine
54. Arabinoside C
55. 1-beta-d-arabinofuranosyl-4-amino-2(1h)pyrimidinone
56. Chembl803
57. U-19920
58. 4-amino-1-arabinofuranosyl-2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyrimidin
59. 4-amino-1-[(2r,3s,4s,5r)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]-1,2-dihydropyrimidin-2-one
60. 2(1h)-pyrimidinone, 4-amino-1-.beta.-d-arabinofuranosyl-
61. Ar3
62. Cytonal
63. Chebi:28680
64. Chx 3311
65. 04079a1rdz
66. 1-beta-d-arabinofuranosyl-cytosine
67. Ccris 913
68. Beta-ara C
69. 4-amino-1-[(2r,3s,4s,5r)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]pyrimidin-2-one
70. Nsc-287459
71. Cytosine, 1-beta-d-arabinosyl-
72. Hsdb 3049
73. (beta-d-arabinofuranosyl)cytosine
74. Ncgc00093356-03
75. 2(1h)-pyrimidinone, 4-amino-1-y-d-arabinofuranosyl- [cas]
76. 4-amino-1-arabinofuranosyl-2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyrimidine
77. Mfcd00066487
78. Dsstox_cid_2877
79. Cytosine, 1-beta-d-arabinofuranosyl-
80. Nsc 287459
81. Ac-1075
82. Dsstox_rid_76771
83. Dsstox_gsid_22877
84. Ai3-52329
85. Cytosine Arabinoside (van)
86. 2(1h)-pyrimidinone, 4-amino-1-beta-d-arabinofuranosyl-
87. Beta-arabinosylcytosine
88. Beta-cytosine Arabinoside
89. Cytosine-beta-arabinoside
90. Ara-cytidine
91. Cytarabine Liposome Injection
92. Arabinosyl Cytosine
93. Cytosine, Beta-d-arabinoside
94. Cas-147-94-4
95. Smr000449317
96. Depocyt (tn)
97. 69-74-9
98. Cytosine B-d-arabinofuranoside
99. Einecs 205-705-9
100. 1-(arabinofuranosyl)cytosine
101. Cytartbine
102. Unii-04079a1rdz
103. 1-beta-arabinofuranosylcytosine
104. 1-.beta.-d-arabinofuranosylcytosine
105. Sr-01000075773
106. Nsc287459
107. 4-amino-1-beta-d-arabinofuranosyl-2(1h)-pyrimidinon [czech]
108. 4-amino-1-arabinofuranosyl-2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyrimidin [czech]
109. 1-.beta.-d-arabinofuranosyl-cytosine
110. 4-amino-1-b-d-arabinofuranosyl-2-(1h)-pyrimidinone
111. 4-amino-1-beta-d-arabinofuranosyl-2(1h)-pyrimidinon
112. 1-beta-d-arabinofuranosylcytosine, Cytosine Arabinoside
113. Cytarabine [usan:usp:inn:ban:jan]
114. Mk 8242
115. Beta -arabinosylcytosine
116. Cytarabine [mi]
117. Cytarabine [inn]
118. Cytarabine [jan]
119. Cytarabine [hsdb]
120. Cytarabine [usan]
121. Beta -cytosine Arabinoside
122. Beta -d-arabinosylcytosine
123. Cytosine-beta -arabinoside
124. Cytarabine [vandf]
125. Cytarabine [mart.]
126. Schembl3140
127. 1beta -d-arabinosylcytosine
128. Cytarabine [usp-rs]
129. Cytarabine [who-dd]
130. Cytarabine [who-ip]
131. Bidd:pxr0139
132. Lopac0_000316
133. Mls000758310
134. Mls001066340
135. Mls001424023
136. 1-beta-d-arabinosyl-cytosine
137. Bidd:gt0371
138. Cytarabine [ema Epar]
139. Cytosine, Beta -d-arabinoside
140. 1beta -arabinofuranasylcytosine
141. Cytarabine (jp17/usp/inn)
142. Gtpl4827
143. 1-ss-d-arabinofuranosylcytosine
144. Cytarabine [orange Book]
145. Dtxsid3022877
146. Schembl22591193
147. Schembl23152019
148. 1beta -d-arabinofuranosylcytosine
149. Cytarabine [ep Monograph]
150. Cytarabine [usp Impurity]
151. Cytosine, 1-beta -d-arabinosyl-
152. Vyxeos Component Cytarabine
153. 1-beta -d-arabinofuranosylcytosine
154. 1-beta-d-arabinofuranosyl Cytosine
155. Cytarabine [usp Monograph]
156. Cytosine-beta -d-arabinofuranoside
157. Hms2051k19
158. Hms2090a18
159. Hms2230m16
160. Hms3713n12
161. 1-beta -d-arabinofaranosylcytosine
162. Cytarabine Liposome [vandf]
163. Cytarabinum [who-ip Latin]
164. Bcp02876
165. Zinc3795098
166. Tox21_111203
167. Tox21_301971
168. Bdbm50087289
169. Ccg-51297
170. S1648
171. (non-labelled)cytarabine-13c-15n2
172. Akos007930145
173. Akos015896896
174. Am84428
175. Cytosine, 1-beta -d-arabinofuranosyl-
176. Db00987
177. Ks-5063
178. Nc00070
179. Sdccgsbi-0050304.p002
180. Ncgc00093356-04
181. Ncgc00093356-05
182. Ncgc00093356-06
183. Ncgc00093356-19
184. Ncgc00142483-02
185. Ncgc00255381-01
186. Ba164339
187. Hy-13605
188. Sri-10828-19
189. Sri-10828-20
190. Sri-10828_24
191. Sl-000002
192. Sw197450-5
193. C02961
194. D00168
195. 1-beta-d-arabinofuranosylcytosine; Ara-c
196. 147c944
197. A808710
198. Q180983
199. Sr-01000721860
200. J-520199
201. J-700005
202. J-700166
203. Sr-01000075773-3
204. Sr-01000075773-5
205. Sr-01000721860-6
206. 1-beta -d-arabinofuranosyl-4-amino-2(1h)pyrimidinone
207. 2(1h)-pyrimidinone, 4-amino-1- -d-arabinofuranosyl
208. Brd-k33106058-001-07-7
209. Brd-k33106058-003-20-6
210. 2(1h)-pyrimidinone, 4-amino-1beta -d-arabinofuranosyl-
211. Z1522566619
212. 2(1h)-pyrimidinone, 4-amino-1-beta -d-arabinofuranosyl-
213. Cytarabine, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
214. Cytarabine, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
215. Cytosine Beta-d-arabinofuranoside, Crystalline, >=90% (hplc)
216. Cytosine Beta-d-arabinofuranoside, Vetec(tm) Reagent Grade, 90%
217. Cytarabine, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
218. 4-amino-1-[(2r,3s,4s,5r)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydrofuran-2-yl]pyrimidin-2-one
| Molecular Weight | 243.22 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C9H13N3O5 |
| XLogP3 | -2.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 243.08552052 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 243.08552052 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 129 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 17 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 383 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 4 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Cytarabine |
| PubMed Health | Cytarabine |
| Drug Classes | Antimetabolite, Antineoplastic Agent |
| Drug Label | Cytarabine Injection, an antineoplastic agent, is a sterile preserved solution for intravenous or subcutaneous administration, and is available in a 500 mg (20 mg/mL) multidose vial. Each mL contains: 20 mg Cytarabine, USP and the following inactive... |
| Active Ingredient | Cytarabine |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 20mg/ml; 500mg/vial; 100mg/vial; 100mg/ml; 2gm/vial; 1gm/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Fresenius Kabi Usa; Hospira; Onco Therapies; Eurohlth Intl |
| 2 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Cytosar-u |
| PubMed Health | Cytarabine, Liposome (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent |
| Drug Label | DepoCyt (cytarabine liposome injection) is a sterile, injectable suspension of the antimetabolite cytarabine, encapsulated into multivesicular lipid-based particles using proprietary DepoFoam formulation technology. Chemically, cytarabine is 4-am... |
| Active Ingredient | Cytarabine |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 500mg/vial; 100mg/vial; 1gm/vial; 2gm/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Teva Pharms Usa |
| 3 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Depocyt |
| Active Ingredient | Cytarabine |
| Dosage Form | Injectable, liposomal |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 10mg/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pacira Pharms |
| 4 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Cytarabine |
| PubMed Health | Cytarabine |
| Drug Classes | Antimetabolite, Antineoplastic Agent |
| Drug Label | Cytarabine Injection, an antineoplastic agent, is a sterile preserved solution for intravenous or subcutaneous administration, and is available in a 500 mg (20 mg/mL) multidose vial. Each mL contains: 20 mg Cytarabine, USP and the following inactive... |
| Active Ingredient | Cytarabine |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 20mg/ml; 500mg/vial; 100mg/vial; 100mg/ml; 2gm/vial; 1gm/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Fresenius Kabi Usa; Hospira; Onco Therapies; Eurohlth Intl |
| 5 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Cytosar-u |
| PubMed Health | Cytarabine, Liposome (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent |
| Drug Label | DepoCyt (cytarabine liposome injection) is a sterile, injectable suspension of the antimetabolite cytarabine, encapsulated into multivesicular lipid-based particles using proprietary DepoFoam formulation technology. Chemically, cytarabine is 4-am... |
| Active Ingredient | Cytarabine |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 500mg/vial; 100mg/vial; 1gm/vial; 2gm/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Teva Pharms Usa |
| 6 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Depocyt |
| Active Ingredient | Cytarabine |
| Dosage Form | Injectable, liposomal |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 10mg/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pacira Pharms |
Antimetabolites, Antineoplastic; Antiviral Agents; Immunosuppressive Agents; Teratogens
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
DepoCyt (cytarabine liposome injection) is indicated for the intrathecal treatment of lymphomatous meningitis. This indication is based on demonstration of increased complete response rate compared to unencapsulated cytarabine. There are no controlled trials that demonstrate a clinical benefit resulting from this treatment, such as improvement in disease-related symptoms, or increased time to disease progression, or increased survival. /Cytarabine liposome injection/
Physicians Desk Reference 61st ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2007., p. 1143
Cytarabine is indicated, in combination with other antineoplastic agents, for treatment of acute nonlymphocytic leukemia in adults and children. /Included US product label/
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2007., p. 933
Cytarabine is indicated for treatment of acute lymphocytic leukemia and chronic myelocytic leukemia (blast phase). /Included in US product label/
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2007., p. 933
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for CYTARABINE (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
The patient's hematologic status must be carefully monitored. Leukocyte and platelet counts should be performed frequently during cytarabine therapy. The manufacturers state that leukocyte and platelet counts should be determined daily during remission induction therapy of acute leukemia. The manufacturers also recommend frequent bone marrow examinations after blast cells have disappeared from the peripheral blood.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2007., p. 992
Patients who receive myelosuppressive drugs experience an increased frequency of infections (e.g., viral, bacterial, fungal) as well as possible hemorrhagic complications. Because these complications are potentially fatal, the patient should be instructed to notify the clinician if fever, sore throat, or unusual bleeding or bruising occurs. ...Treatment with cytarabine should be initiated only with extreme caution in patients with preexisting drug-induced bone marrow suppression.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2007., p. 992
The manufacturers recommend that periodic determinations of renal function be performed in patients receiving cytarabine. Periodic determinations of hepatic function should also be performed in patients receiving cytarabine, and the manufacturers state that the drug should be used with caution and in reduced dosage in patients with poor hepatic function.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2007., p. 992
Cytarabine is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to the drug.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2007., p. 992
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for CYTARABINE (30 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For the treatment of acute non-lymphocytic leukemia, acute lymphocytic leukemia and blast phase of chronic myelocytic leukemia. Cytarabine is indicated in combination with [daunorubicin] for the treatment of newly-diagnosed therapy-related acute myeloid leukemia (t-AML) or AML with myelodysplasia-related changes (AML-MRC) in adults and pediatric patients 1 year and older.
FDA Label
Intrathecal treatment of lymphomatous meningitis. In the majority of patients such treatment will be part of symptomatic palliation of the disease.
Cytarabine is an antineoplastic anti-metabolite used in the treatment of several forms of leukemia including acute myelogenous leukemia and meningeal leukemia. Anti-metabolites masquerade as purine or pyrimidine - which become the building blocks of DNA. They prevent these substances becoming incorporated in to DNA during the "S" phase (of the cell cycle), stopping normal development and division. Cytarabine is metabolized intracellularly into its active triphosphate form (cytosine arabinoside triphosphate). This metabolite then damages DNA by multiple mechanisms, including the inhibition of alpha-DNA polymerase, inhibition of DNA repair through an effect on beta-DNA polymerase, and incorporation into DNA. The latter mechanism is probably the most important. Cytotoxicity is highly specific for the S phase of the cell cycle.
Antiviral Agents
Agents used in the prophylaxis or therapy of VIRUS DISEASES. Some of the ways they may act include preventing viral replication by inhibiting viral DNA polymerase; binding to specific cell-surface receptors and inhibiting viral penetration or uncoating; inhibiting viral protein synthesis; or blocking late stages of virus assembly. (See all compounds classified as Antiviral Agents.)
Antimetabolites, Antineoplastic
Antimetabolites that are useful in cancer chemotherapy. (See all compounds classified as Antimetabolites, Antineoplastic.)
Immunosuppressive Agents
Agents that suppress immune function by one of several mechanisms of action. Classical cytotoxic immunosuppressants act by inhibiting DNA synthesis. Others may act through activation of T-CELLS or by inhibiting the activation of HELPER CELLS. While immunosuppression has been brought about in the past primarily to prevent rejection of transplanted organs, new applications involving mediation of the effects of INTERLEUKINS and other CYTOKINES are emerging. (See all compounds classified as Immunosuppressive Agents.)
L01BC01
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01B - Antimetabolites
L01BC - Pyrimidine analogues
L01BC01 - Cytarabine
Absorption
Less than 20% of the orally administered dose is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract.
Route of Elimination
The primary route of elimination of cytarabine is metabolism to the inactive compound ara-U, followed by urinary excretion of ara-U.
Less than 20% of a dose of conventional cytarabine is absorbed from the GI tract, and the drug is not effective when administered orally. Following subcutaneously or im injection of conventional cytarabine H 3, peak plasma concentrations of radioactivity occur within 20-60 min and are considerably lower than those attained after iv administration. Continuous iv infusions of conventional cytarabine produce relatively constant plasma concn of the drug in 8-24 hr.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2007., p. 993
Cytarabine is rapidly and widely distributed into tissues and fluids, including liver, plasma, and peripheral granulocytes. Following rapid IV injection of cytarabine in one study, approximately 13% of the drug was bound to plasma proteins.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2007., p. 993
Cytarabine crosses the blood-brain barrier to a limited extent. During a continuous IV or subcutaneous infusion, cytarabine concentrations in the CSF are higher than those attained after rapid IV injection and are about 40-60% of plasma concentrations. Most of an intrathecal dose of cytarabine diffuses into the systemic circulation but is rapidly metabolized and usually only low plasma concentrations of unchanged drug occur.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2007., p. 993
The drug apparently crosses the placenta. It is not known if cytarabine or ara-U is distributed into milk.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2007., p. 993
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for CYTARABINE (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Hepatic.
Cytarabine is rapidly and extensively metabolized mainly in the liver but also in kidneys, GI mucosa, granulocytes, and to a lesser extent in other tissues by the enzyme cytidine deaminase, producing the inactive metabolite 1--d-arabinofuranosyluracil (ara-U, uracil arabinoside). After the initial distribution phase, more than 80% of the drug in plasma is present as ara-U. In the CSF, only minimal amounts of cytarabine are converted to ara-U because of low CSF concentrations of cytidine deaminase. Intracellularly, cytarabine is metabolized by deoxycytidine kinase and other nucleotide kinases to cytarabine triphosphate, the active metabolite of the drug. Cytarabine triphosphate is inactivated by a pyrimidine nucleoside deaminase, which produces the uracil derivative.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2007., p. 994
The primary route of elimination of cytarabine is metabolism to the inactive compound ara-U (1-(beta)-D-arabinofuranosyluracil or uracilarabinoside), followed by urinary excretion of ara-U. In contrast to systemically administered cytarabine, which is rapidly metabolized to ara-U, conversion to ara-U in the CSF is negligible after intrathecal administration because of the significantly lower cytidine deaminase activity in the CNS tissues and CSF. The CSF clearance rate of cytarabine is similar to the CSF bulk flow rate of 0.24 mL/min. /Cytarabine liposome injection/
Physicians Desk Reference 61st ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2007., p. 1143
Cytarabine must be converted to the 5'-monophosphate nucleotide by deoxycytidine kinase to be active. Ara-cytidine diphosphate &/or ara-cytidine triphosphate are presumably the form that inhibit DNA polymerase & block ribonucleoside diphosphate reductase.
Booth, N.H., L.E. McDonald (eds.). Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 5th ed. Ames, Iowa: Iowa State University Press, 1982., p. 792
10 minutes
After rapid IV injection of cytarabine, plasma drug concentrations appear to decline in a biphasic manner with a half-life of about 10 minutes in the initial phase and about 1-3 hours in the terminal phase. Cytarabine reportedly undergoes triphasic elimination in some patients. After intrathecal injection, cytarabine concentrations in the CSF reportedly decline with a half-life of about 2 hours.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2007., p. 994
Peak levels were followed by a biphasic elimination profile with a terminal phase half-life of 100 to 263 hours over a dose range of 12.5 mg to 75 mg. In contrast, intrathecal administration of 30 mg of free cytarabine showed a biphasic CSF concentration profile with a terminal phase half-life of 3.4 hours. /Cytarabine liposome injection/
Physicians Desk Reference 61st ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2007., p. 1143
After iv admin, there is a rapid phase of disappearance of AraC (half-life = 10 min), followed by a slower phase of elimination with a half-time of about 2.5 hr ... After intrathecal admin of the drug at a dose of 50 mg/sq m ... peak concn of 1 to 2 mM are achieved, which decline slowly with a terminal half-life of approx 3.4 hr.
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B., A.G. Gilman. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2001., p. 1410
Cytarabine acts through direct DNA damage and incorporation into DNA. Cytarabine is cytotoxic to a wide variety of proliferating mammalian cells in culture. It exhibits cell phase specificity, primarily killing cells undergoing DNA synthesis (S-phase) and under certain conditions blocking the progression of cells from the G1 phase to the S-phase. Although the mechanism of action is not completely understood, it appears that cytarabine acts through the inhibition of DNA polymerase. A limited, but significant, incorporation of cytarabine into both DNA and RNA has also been reported.
Cytarabine is converted intracellularly to the nucleotide, cytarabine triphosphate (ara-CTP, cytosine arabinoside triphosphate). Although the exact mechanism(s) of action of cytarabine has not been fully elucidated, cytarabine triphosphate appears to inhibit DNA polymerase by competing with the physiologic substrate, deoxycytidine triphosphate, resulting in the inhibition of DNA synthesis. Although limited, incorporation of cytarabine triphosphate into DNA and RNA may also contribute to the cytotoxic effects of the drug.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2007., p. 993
Cytarabine is a potent immunosuppressant which can suppress humoral and/or cellular immune responses; however, the drug does not decrease preexisting antibody titers and has no effect on established delayed hypersensitivity reactions.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2007., p. 993
Cytarabine liposome injection is a sustained-release formulation of the active ingredient cytarabine designed for direct administration into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Cytarabine is a cell cycle phase-specific antineoplastic agent, affecting cells only during the S-phase of cell division. Intracellularly, cytarabine is converted into cytarabine-5'-triphosphate (ara-CTP), which is the active metabolite. The mechanism of action is not completely understood, but it appears that ara-CTP acts primarily through inhibition of DNA polymerase. Incorporation into DNA and RNA may also contribute to cytarabine cytotoxicity. Cytarabine is cytotoxic to a wide variety of proliferating mammalian cells in culture. /Cytarabine liposome injection/
Physicians Desk Reference 61st ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2007., p. 1143