
1. Dalda
2. Tyr-arg-phe-lys-nh2
3. Tyrosyl-arginyl-phenylalanyl-lysinamide
1. Dalda
2. 118476-85-0
3. 68425-36-5
4. Tyrosyl-arginyl-phenylalanyl-lysinamide
5. Chembl60444
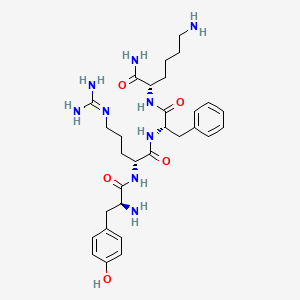
6. (2s)-6-amino-2-[[(2s)-2-[[(2r)-2-[[(2s)-2-amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoyl]amino]-5-(diaminomethylideneamino)pentanoyl]amino]-3-phenylpropanoyl]amino]hexanamide
7. Tyr-arg-phe-lys-nh2
8. Cas_122222
9. Nsc_122222
10. Hydrogenated Peanut Oil
11. (d-arg2,lys4)-dermorphin (1-4) Amide
12. Oils, Peanut, Hydrogenated
13. Unii-fs8087fl3x
14. L-lysinamide, L-tyrosyl-d-arginyl-l-phenylalanyl-
15. Fs8087fl3x
16. Schembl8975803
17. Bdbm85737
18. Dtxsid001045851
19. Einecs 270-350-9
20. Bdbm50016867
21. Mfcd00144042
22. Zinc14951239
23. (d-arg2,lys4) Dermorphin Fragment*1-4 Am Ide
24. (s)-6-amino-2-((s)-2-{(r)-2-[(s)-2-amino-3-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-propionylamino]-5-guanidino-pentanoylamino}-3-phenyl-propionylamino)-hexanoic Acid Amide
25. 6-amino-2-[1-[1-[1-amino-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-(1s)-ethylcarboxamido]-4-amino(imino)methylamino-(1r)-butylcarboxamido]-2-phenyl-(1s)-ethylcarboxamido]-(2s)-hexanamide
| Molecular Weight | 611.7 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C30H45N9O5 |
| XLogP3 | -0.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 19 |
| Exact Mass | 611.35436557 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 611.35436557 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 267 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 44 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 932 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 4 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Analgesics
Compounds capable of relieving pain without the loss of CONSCIOUSNESS. (See all compounds classified as Analgesics.)
Anti-Arrhythmia Agents
Agents used for the treatment or prevention of cardiac arrhythmias. They may affect the polarization-repolarization phase of the action potential, its excitability or refractoriness, or impulse conduction or membrane responsiveness within cardiac fibers. Anti-arrhythmia agents are often classed into four main groups according to their mechanism of action: sodium channel blockade, beta-adrenergic blockade, repolarization prolongation, or calcium channel blockade. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Arrhythmia Agents.)