
1. 4,4' Diaminophenyl Sulfone
2. 4,4'-diaminophenyl Sulfone
3. Avlosulfone
4. Dadps
5. Dapsoderm-x
6. Dapson-fatol
7. Diaminodiphenylsulfone
8. Diaphenylsulfone
9. Disulone
10. Sulfona
11. Sulfone, 4,4'-diaminophenyl
12. Sulfonyldianiline
1. 80-08-0
2. 4,4'-sulfonyldianiline
3. Diaphenylsulfone
4. 4,4'-diaminodiphenyl Sulfone
5. Dapson
6. 4-aminophenyl Sulfone
7. 4,4'-diaminodiphenylsulfone
8. Diaphenylsulfon
9. Novophone
10. Sulfona
11. Dadps
12. Bis(4-aminophenyl) Sulfone
13. Avlosulfone
14. Diphenasone
15. Sulfadione
16. Sulphadione
17. Dapsonum
18. Disulone
19. Aczone
20. Udolac
21. P-aminophenyl Sulfone
22. Avlosulfon
23. Croysulfone
24. Dumitone
25. Diphone
26. Eporal
27. Diaphenylsulphon
28. Diaphenylsulphone
29. Metabolite C
30. Sulfonyldianiline
31. Sumicure S
32. Bis(p-aminophenyl) Sulfone
33. Sulphonyldianiline
34. P,p-sulphonylbisbenzamine
35. Sulfona-mae
36. Avlosulphone
37. Croysulphone
38. Dubronax
39. 4,4'-dapsone
40. Diaminodiphenyl Sulfone
41. Tarimyl
42. P,p-sulphonylbisbenzenamine
43. Sulfone Ucb
44. 4,4'-sulfonylbisaniline
45. P,p'-diaminodiphenyl Sulfone
46. 4-(4-aminophenyl)sulfonylaniline
47. Dapsona
48. Nsc-6091
49. Benzenamine, 4,4'-sulfonylbis-
50. Diaminodiphenylsulfone
51. Bis(4-aminophenyl)sulfone
52. Di(p-aminophenyl) Sulfone
53. P,p-sulphonyldianiline
54. 4,4'-sulfonylbisbenzamine
55. Di(4-aminophenyl) Sulfone
56. P,p'-sulfonyldianiline
57. 4,4'-sulfonylbisbenzenamine
58. P,p-sulfonylbisbenzamine
59. Diaminodifenilsulfona
60. Dds, Pharmaceutical
61. Di(p-aminophenyl)sulphone
62. P,p-sulfonylbisbenzenamine
63. Araldite Ht 976
64. Bis(p-aminophenyl)sulphone
65. Di(4-aminophenyl)sulphone
66. Bis(4-aminophenyl)sulphone
67. P,p-diaminodiphenyl Sulphone
68. N,n'-diphenyl Sulfondiamide
69. 1,1'-sulfonylbis(4-aminobenzene)
70. 4,4'-sulphonyldianiline
71. Dds
72. Servidapson
73. 4,4'-sulphonylbisbenzamine
74. 4,4'-sulphonylbisbenzenamine
75. 4,4'-diaminodiphenyl Sulphone
76. Wr 448
77. 4,4-diaminodifenylsulfon
78. Diamino-4,4'-diphenyl Sulfone
79. Diamino-4,4'-diphenyl Sulphone
80. Nsc 6091d
81. Nci-c01718
82. 1,1'-sulfonylbis[4-aminobenzene]
83. 1,1'-sulphonylbis(4-aminobenzene)
84. Aniline, 4,4'-sulfonyldi-
85. Ht 976
86. 4,4'-diamino Diphenyl Sulphone
87. F 1358
88. 4,4'-sulfonyldianiline (dapsone)
89. 1358f
90. 4-[(4-aminobenzene)sulfonyl]aniline
91. 4,4'-sulfonylbisbenzeneamine
92. 4,4'-sulfonyldianilin
93. Diaphenylsulfone (jan)
94. Chembl1043
95. Mls000069409
96. Chebi:4325
97. Dtxsid4020371
98. Nsc-6091d
99. Sulfanona-mae
100. J04ba02
101. Nsc6091
102. Sulfon-mere
103. 4,4'-dds
104. Di(4-aminophenyl)sulfone
105. 4-(4-amino-benzenesulfonyl)-phenylamine
106. Ncgc00016322-08
107. Smr000059064
108. Hardener Ht 976
109. Dds (pharmaceutical)
110. Sulphon-mere
111. Dsstox_cid_371
112. 8w5c518302
113. Dapsonum [inn-latin]
114. Dapsona [inn-spanish]
115. Dsstox_rid_75547
116. Dsstox_gsid_20371
117. Dss (van)
118. Diaphenylsulfone [jan]
119. 4-aminophenylsulfone
120. 4 4-diamino Diphenyl Sulfone 99.5%min Cas:80-08-8
121. Dds, Diaphenylsulfone
122. 4,4'-diaminodiphenyl Suphone
123. Atrisone
124. Diaminodifenilsulfona [spanish]
125. 4,4-diaminodifenylsulfon [czech]
126. Cas-80-08-0
127. Hy 976
128. Ccris 192
129. Dapsone (usp)
130. Aczone (tn)
131. 1632119-29-9
132. Hsdb 5073
133. Sr-01000002976
134. Nsc 6091
135. 4-[(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl]aniline
136. Sulfone, Diphenyl, 4,4'-diamino-
137. Einecs 201-248-4
138. (4-sulfanilylphenyl)amine
139. Mfcd00007887
140. Azt + Dapsone Cominbation
141. Brn 0788055
142. Ai3-08087
143. Diaphenyl Sulfone
144. Dapsone [usan:usp:inn:ban]
145. Unii-8w5c518302
146. Dapsone,(s)
147. Prestwick_152
148. Albb-005917
149. Dapsone-d8(major)
150. Dapsone-[d4]
151. In-201
152. Dapsone-13c12
153. Bis Sulfone
154. 4,4''-dapsone
155. 4-[(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl]phenylamine
156. Dapsone-[15n2]
157. Spectrum_000888
158. Dapsone [vandf]
159. Aniline,4'-sulfonyldi-
160. Dapsone [hsdb]
161. Dapsone [iarc]
162. Dapsone [usan]
163. Dapsone [inn]
164. Dapsone [mi]
165. Dapsone [mart.]
166. Opera_id_1950
167. Prestwick0_000035
168. Prestwick1_000035
169. Prestwick2_000035
170. Prestwick3_000035
171. Spectrum2_001133
172. Spectrum3_000375
173. Spectrum4_000310
174. Spectrum5_000825
175. Wln: Zr Dswr Dz
176. 4,4''-sulfonyldianiline
177. Dapsone [usp-rs]
178. Dapsone [who-dd]
179. Dapsone [who-ip]
180. 4,4''-sulfonylbisaniline
181. Ec 201-248-4
182. 4,4'-sulfonyldiphenylamine
183. Benzenamine,4'-sulfonylbis-
184. Oprea1_143052
185. Schembl21428
186. Bspbio_000129
187. Bspbio_002129
188. Cbdive_013582
189. Dianiline, 4,4'-sulfonyl-
190. Kbiogr_000900
191. Kbioss_001368
192. Mls001055349
193. Mls001076146
194. 4,4''-sulfonylbisbenzenamine
195. 4,4'-sulfonylbis[benzamine]
196. 4-aminophenyl Sulfone, 97%
197. Bidd:gt0770
198. Dapsone [ep Impurity]
199. Dapsone [orange Book]
200. Divk1c_000573
201. P,p''-diaminodiphenyl Sulfone
202. Spectrum1500222
203. Spbio_001025
204. Spbio_002050
205. Dapsone [ep Monograph]
206. 4,4''-diaminodiphenyl Sulfone
207. 4,4'-diamino Diphenyl Sulfone
208. Bpbio1_000143
209. Zinc6310
210. Dapsone [usp Monograph]
211. Dapsonum [who-ip Latin]
212. Gtpl10934
213. Hms501m15
214. Kbio1_000573
215. Kbio2_001368
216. Kbio2_003936
217. Kbio2_006504
218. Kbio3_001349
219. 4-(4-aminophenylsulfonyl)aniline
220. Ninds_000573
221. Hms1568g11
222. Hms1920c14
223. Hms2091k04
224. Hms2095g11
225. Hms2231g09
226. Hms3259c13
227. Hms3369b11
228. Hms3712g11
229. Pharmakon1600-01500222
230. Dapson 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
231. Act07431
232. Amy40781
233. Hy-b0688
234. 1,1''-sulfonylbis(4-aminobenzene)
235. Tox21_110371
236. Tox21_201347
237. Tox21_300558
238. 4-(4-aminophenylsulfonyl)benzenamine
239. Bbl002412
240. Bdbm50029764
241. Ccg-40260
242. Nsc756716
243. S4612
244. Stk387118
245. Akos000119322
246. Tox21_110371_1
247. Db00250
248. Ht 9664
249. Ks-1450
250. Nc00488
251. Nsc-756716
252. Idi1_000573
253. Ncgc00016322-01
254. Ncgc00016322-02
255. Ncgc00016322-03
256. Ncgc00016322-04
257. Ncgc00016322-05
258. Ncgc00016322-06
259. Ncgc00016322-07
260. Ncgc00016322-09
261. Ncgc00016322-10
262. Ncgc00016322-13
263. Ncgc00023946-03
264. Ncgc00023946-04
265. Ncgc00023946-05
266. Ncgc00023946-06
267. Ncgc00254533-01
268. Ncgc00258899-01
269. Ac-10922
270. 4-[(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl]phenylamine #
271. Sbi-0051331.p003
272. Db-056406
273. Ab00051962
274. D0089
275. Dapsone, Vetranal(tm), Analytical Standard
276. Ft-0624447
277. Ft-0665473
278. 4 Inverted Exclamation Marka-sulfonyldianiline
279. C07666
280. D00592
281. Ab00051962_19
282. A839828
283. Q422226
284. 4 Inverted Exclamation Marka-diaminodiphenyl Sulfone
285. 4,4 Inverted Exclamation Mark(r)-sulfonyldianiline
286. Q-200435
287. Sr-01000002976-2
288. Sr-01000002976-4
289. Brd-k62363391-001-05-8
290. Brd-k62363391-001-15-7
291. Sulfacetamide Sodium Impurity D [ep Impurity]
292. Dapsone, British Pharmacopoeia (bp) Reference Standard
293. Dapsone, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
294. F0266-3067
295. 2-(piperazin-1-yl)-aceticacidn-(2-phenylethyl)-amide
296. 4-(4-aminophenyl)sulfonylaniline;4,4'-diaminodiphenyl Sulfone
297. Dapsone, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
298. Dapsone, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
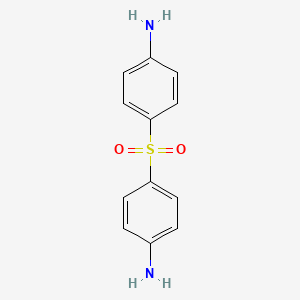
| Molecular Weight | 248.30 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C12H12N2O2S |
| XLogP3 | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 248.06194880 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 248.06194880 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 94.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 17 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 306 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Aczone |
| PubMed Health | Dapsone |
| Drug Classes | Antiacne, Leprostatic |
| Drug Label | ACZONE Gel, 5%, contains dapsone, a sulfone, in an aqueous gel base for topical dermatologic use. ACZONE Gel, 5% is a gritty translucent material with visible drug substance particles. Chemically, dapsone has an empirical formula of C12H12N2O2S.... |
| Active Ingredient | Dapsone |
| Dosage Form | Gel |
| Route | Topical |
| Strength | 5% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Allergan |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Dapsone |
| PubMed Health | Dapsone |
| Drug Classes | Antiacne, Leprostatic |
| Drug Label | Dapsone-USP, 4,4'-diaminodiphenylsulfone (DDS), is a primary treatment for Dermatitis herpetiformis. It is an antibacterial drug for susceptible cases of leprosy. It is a white, odorless crystalline powder, practically in-soluble in water and insolub |
| Active Ingredient | Dapsone |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 100mg; 25mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Jacobus |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Dapsone |
| PubMed Health | Dapsone |
| Drug Classes | Antiacne, Leprostatic |
| Drug Label | Dapsone-USP, 4,4'-diaminodiphenylsulfone (DDS), is a primary treatment for Dermatitis herpetiformis. It is an antibacterial drug for susceptible cases of leprosy. It is a white, odorless crystalline powder, practically in-soluble in water and insolub |
| Active Ingredient | Dapsone |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 100mg; 25mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Jacobus |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Aczone |
| PubMed Health | Dapsone |
| Drug Classes | Antiacne, Leprostatic |
| Drug Label | ACZONE Gel, 5%, contains dapsone, a sulfone, in an aqueous gel base for topical dermatologic use. ACZONE Gel, 5% is a gritty translucent material with visible drug substance particles. Chemically, dapsone has an empirical formula of C12H12N2O2S.... |
| Active Ingredient | Dapsone |
| Dosage Form | Gel |
| Route | Topical |
| Strength | 5% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Allergan |
Anti-Infective Agents; Antimalarials; Folic Acid Antagonists; Leprostatic Agents
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings. Dapsone. Online file (MeSH, 2016). Available from, as of August 12, 2016: https://www.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/2016/mesh_browser/MBrowser.html
/CLINICAL TRIALS/ ClinicalTrials.gov is a registry and results database of publicly and privately supported clinical studies of human participants conducted around the world. The Web site is maintained by the National Library of Medicine (NLM) and the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Each ClinicalTrials.gov record presents summary information about a study protocol and includes the following: Disease or condition; Intervention (for example, the medical product, behavior, or procedure being studied); Title, description, and design of the study; Requirements for participation (eligibility criteria); Locations where the study is being conducted; Contact information for the study locations; and Links to relevant information on other health Web sites, such as NLM's MedlinePlus for patient health information and PubMed for citations and abstracts for scholarly articles in the field of medicine. Dapsone is included in the database.
NIH/NLM; ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available from, as of March 17, 2016: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?term=dapsone&Search=Search
Dapsone is administered as an oral agent. Dapsone is combined with chlorproguanil for the treatment of malaria. Dapsone is also used for P. jiroveci infection and prophylaxis, and for the prophylaxis for T. gondii ... The anti-inflammatory effects are the basis for therapy for pemphigoid, dermatitis herpetiformis, linear IgA bullous disease, relapsing chondritis, and ulcers caused by the brown recluse spider.
Brunton, L. Chabner, B, Knollman, B. Goodman and Gillman's The Pharmaceutical Basis of Therapeutics, Twelth Edition, McGraw Hill Medical, New York, NY. 2011, p. 1574
Dapsone is approved for use in dermatitis herpetiformis and leprosy. It is particularly useful in the treatment of linear immunoglobulin (IgA) dermatosis, bullous systemic lupus erythematosus, erythema elevatum diutinum, and subcorneal pustular dermatosis.
Brunton, L. Chabner, B, Knollman, B. Goodman and Gillman's The Pharmaceutical Basis of Therapeutics, Twelth Edition, McGraw Hill Medical, New York, NY. 2011, p. 1823
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for DAPSONE (14 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Peripheral neuropathy with motor loss has been reported rarely in patients receiving high dosage of dapsone (200-500 mg daily). ... Insomnia, headache, nervousness, vertigo, and psychosis have also been reported with dapsone.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2016; Drug Information 2016. Bethesda, MD. 2016, p. 601
Resistance to dapsone in P. falciparum, P. jiroveci, and M. leprae results primarily from mutations in genes encoding dihydropteroate synthase.
Brunton, L. Chabner, B, Knollman, B. Goodman and Gillman's The Pharmaceutical Basis of Therapeutics, Twelth Edition, McGraw Hill Medical, New York, NY. 2011, p. 1564
Hemolysis develops in almost every individual treated with 200-300 mg of dapsone per day. ... Methemoglobinemia is also common. A genetic deficiency in the NADH-dependent methemoglobin reductase can result in severe methemoglobinemia after administration of dapsone. Isolated instances of headache, nervousness, insomnia, blurred vision, paresthesias, reversible peripheral neuropathy (thought to be sue to axonal degeneration), drug fever, hematuria, pruritus, and a variety of skin rashes have been reported. An infectious mononucleosis-like syndrome, which may be fatal, occurs occasionally.
Brunton, L. Chabner, B, Knollman, B. Goodman and Gillman's The Pharmaceutical Basis of Therapeutics, Twelth Edition, McGraw Hill Medical, New York, NY. 2011, p. 1564
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) protects red cells against oxidative damage. However, G6PD deficiency is encountered in nearly half a billion people worldwide, the most common of 100 variants being G6PD-A-. Dapsone, an oxidant, causes severe hemolysis in patients with G6PD deficiency. Thus, G6PD deficiency testing should be performed prior to use of dapsone wherever possible.
Brunton, L. Chabner, B, Knollman, B. Goodman and Gillman's The Pharmaceutical Basis of Therapeutics, Twelth Edition, McGraw Hill Medical, New York, NY. 2011, p. 1564
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for DAPSONE (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For the treatment and management of leprosy and dermatitis herpetiformis.
FDA Label
Dapsone is a sulfone with anti-inflammatory immunosuppressive properties as well as antibacterial and antibiotic properties. Dapsone is the principal drug in a multidrug regimen recommended by the World Health Organization for the treatment of leprosy. As an anti-infective agent, it is also used for treating malaria and, recently, for Pneumocystic carinii pneumonia in AIDS patients. Dapsone is absorbed rapidly and nearly completely from the gastrointestinal tract. Dapsone is distributed throughout total body water and is present in all tissues. However, it tends to be retained in skin and muscle and especially in the liver and kidney: traces of the drug are present in these organs up to 3 weeks after therapy cessation.
Antimalarials
Agents used in the treatment of malaria. They are usually classified on the basis of their action against plasmodia at different stages in their life cycle in the human. (From AMA, Drug Evaluations Annual, 1992, p1585) (See all compounds classified as Antimalarials.)
Leprostatic Agents
Substances that suppress Mycobacterium leprae, ameliorate the clinical manifestations of leprosy, and/or reduce the incidence and severity of leprous reactions. (See all compounds classified as Leprostatic Agents.)
Anti-Infective Agents
Substances that prevent infectious agents or organisms from spreading or kill infectious agents in order to prevent the spread of infection. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Infective Agents.)
Folic Acid Antagonists
Inhibitors of the enzyme, dihydrofolate reductase (TETRAHYDROFOLATE DEHYDROGENASE), which converts dihydrofolate (FH2) to tetrahydrofolate (FH4). They are frequently used in cancer chemotherapy. (From AMA, Drug Evaluations Annual, 1994, p2033) (See all compounds classified as Folic Acid Antagonists.)
D - Dermatologicals
D10 - Anti-acne preparations
D10A - Anti-acne preparations for topical use
D10AX - Other anti-acne preparations for topical use
D10AX05 - Dapsone
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J04 - Antimycobacterials
J04B - Drugs for treatment of lepra
J04BA - Drugs for treatment of lepra
J04BA02 - Dapsone
Absorption
Bioavailability is 70 to 80% following oral administration.
Route of Elimination
Renal
After oral administration, absorption is almost complete ... . CL increases 0.03 L/hour and Vd 0.7 L increases for each 1-kg increase in body weight above 62.3 kg. Dapsone undergoes N-acetylation by NAT2. N-oxidation to dapsone hydroxylamine is via CYP2E1, and to a lesser extent by CYP2C. Dapsone hydroxylamine enters red blood cells, leading to methemoglobin formation. Sulfones tend to be retained for up to 3 weeks in skin and muscle and especially in liver and kidney. Intestinal reabsorption of sulfones excreted in the bile contributes to long-term retention in the bloodstream; periodic interruption of treatment is advisable for this reason. Epithelial lining fluid to plasma ratio is between 0.76 and 2.91; CSF-to-plasma ration is 0.21-2.01.
Brunton, L. Chabner, B, Knollman, B. Goodman and Gillman's The Pharmaceutical Basis of Therapeutics, Twelth Edition, McGraw Hill Medical, New York, NY. 2011, p. 1564
Approximately 70-80% of a dose of dapsone is excreted in the urine as an acid-labile mono-N-glucuronide and mono-N-sulfamate.
Brunton, L. Chabner, B, Knollman, B. Goodman and Gillman's The Pharmaceutical Basis of Therapeutics, Twelth Edition, McGraw Hill Medical, New York, NY. 2011, p. 1564
Following oral administration, dapsone is rapidly and almost completely absorbed from the GI tract and peak serum concentrations of the drug are attained within 4-8 hours. ... The volume of distribution of dapsone is reportedly 1.5-2.5 L/kg in adults. Dapsone is distributed into most body tissues. Dapsone is reportedly retained in skin, muscle, kidneys, and liver; trace concentrations of the drug may be present in these tissues up to 3 weeks after discontinuance of dapsone therapy. Dapsone is also distributed into sweat, saliva, sputum, and tears, The drug is also distributed into bile. ... Dapsone crosses the placenta. Dapsone is distributed into milk. ... Dapsone is 50-90% bound to plasma proteins. The major metabolite of dapsone, monoacetyldapsone, is almost completely bound to plasms proteins.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2016; Drug Information 2016. Bethesda, MD. 2016, p. 603
Approximately 20% of each dose of dapsone is excreted in urine as unchanged drug, 70-85% is excreted in urine as water-soluble metabolites, and a small amount is excreted in feces. Dapsone is excreted in urine as an acid-labile mono-N-glucuronide and mono-N-sulfamate derivatives in addition to some unidentified metabolites.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2016; Drug Information 2016. Bethesda, MD. 2016, p. 603
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for DAPSONE (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Hepatic, mostly CYP2E1-mediated.
Leukocyte colony forming unit cell proliferation of bone marrow was markedly suppressed by 0.1 mmol & 1.0 mmol 4'-amino-4'-hydroxylaminodiphenyl sulfone (dapsone metab) when cells were cultured for 10-14 days.
Weetman RM et al; Br J Haematol 45 (3): 361 (1980)
Dapsone is acetylated in the liver to monoacetyl and diacetyl derivatives. The major metabolite of dapsone is monoacetyldapsone (MADDS). The rate of acetylation of dapsone is genetically determined and is subject to interindividual variation, although the rate is usually constant for each individual. The drug also is hydroxylated in the liver to hydroxylamine dapsone (NOH-DDS). NOH-DDS appears to be responsible for methemoglobinemia and hemolysis induced by the drug.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2016; Drug Information 2016. Bethesda, MD. 2016, p. 603
Dapsone has known human metabolites that include Monoacetyldapsone and N-Hydroxydapsone.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
28 hours (range 10-50 hours)
The elimination half-life is 20-30 hours.
Brunton, L. Chabner, B, Knollman, B. Goodman and Gillman's The Pharmaceutical Basis of Therapeutics, Twelth Edition, McGraw Hill Medical, New York, NY. 2011, p. 1564
There are large interindividual variations in the plasma half-life of dapsone. The plasma half-life of dapsone may range from 10-83 hours and averages 20-30 hours.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2016; Drug Information 2016. Bethesda, MD. 2016, p. 603
Dapsone acts against bacteria and protozoa in the same way as sulphonamides, that is by inhibiting the synthesis of dihydrofolic acid through competition with para-amino-benzoate for the active site of dihydropteroate synthetase. The anti-inflammatory action of the drug is unrelated to its antibacterial action and is still not fully understood.
Dapsone is a structural analog of para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) and a competitive inhibitor of dihydropteroate synthase (folP1P2) in the folate pathway ... The effect on this evolutionarily conserved pathway also explains why dapsone is a broad-spectrum agent with antibacterial, anti-protozoal, and antifungal effects. The anti-inflammatory effects of dapsone occur via inhibition of tissue damage by neutrophils. First, dapsone inhibits neutrophil myeloperoxidase activity and respiratory burst. Second, it inhibits activity of neutrophil lysosomal enzymes. Third, it may also act as a free radical scavenger, counteracting the effect of free radicals generated by neutrophils. Fourth, dapsone may also inhibit migration of neutrophils to inflammatory lesions.
Brunton, L. Chabner, B, Knollman, B. Goodman and Gillman's The Pharmaceutical Basis of Therapeutics, Twelth Edition, McGraw Hill Medical, New York, NY. 2011, p. 1563
1-30 Ug/mL dapsone interfered with myeloperoxidase-H2O2-halide-mediated cytotoxic system in polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Kinetic studies revealed competitive inhibition of myeloperoxidase. Its action in dermatitis herpetiformis may be explained by effect on this system.
Stendahl O et al; J Clin Invest 62 (1): 214 (1978)