


1. Opc-67683
1. 681492-22-8
2. Opc-67683
3. Delamanid (opc-67683)
4. Opc 67683
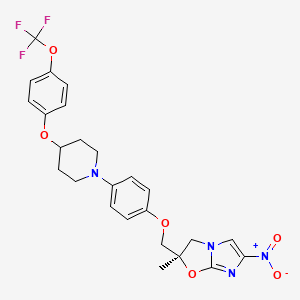
5. (r)-2-methyl-6-nitro-2-((4-(4-(4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenoxy)piperidin-1-yl)phenoxy)methyl)-2,3-dihydroimidazo[2,1-b]oxazole
6. 8oot6m1pc7
7. Mmv688262
8. Deltyba
9. (2r)-2-methyl-6-nitro-2-((4-(4-(4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenoxy)piperidin-1- Yl)phenoxy)methyl)-2,3-dihydroimidazo(2,1-b)oxazole
10. (2r)-2-methyl-6-nitro-2-[[4-[4-[4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenoxy]piperidin-1-yl]phenoxy]methyl]-3h-imidazo[2,1-b][1,3]oxazole
11. Imidazo(2,1-b)oxazole, 2,3-dihydro-2-methyl-6-nitro-2-((4-(4-(4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenoxy)-1-piperidinyl)phenoxy)methyl)-, (2r)-
12. (2r)-2,3-dihydro-2-methyl-6-nitro-2-[[4-[4-[4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenoxy]-1-piperidinyl]phenoxy]methyl]imidazo[2,1-b]oxazole
13. (2r)-2-methyl-6-nitro-2-[(4-{4-[4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenoxy]-1-piperidinyl}phenoxy)methyl]-2,3-dihydroimidazo[2,1-b][1,3]oxazole
14. (r)-2-methyl-6-nitro-2-{4-[4-(4-trifluoromethoxyphenoxy)piperidin-1-yl]phenoxymethyl}-2,3-dihydroimidazo[2,1-b]oxazole
15. Delamanid [usan]
16. Unii-8oot6m1pc7
17. (2r)-2-methyl-6-nitro-2-[[4-[4-[4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenoxy]-1-piperidyl]phenoxy]methyl]-3h-imidazo[2,1-b]oxazole
18. (r)-2-methyl-6-nitro-2-(4-[4-(4-trifluoromethoxyphenoxy)piperidin-1-yl]phenoxymethyl}-2,3-dihydroimidazo[2,1-b]oxazole
19. Deltyba (tn)
20. Delamanid [inn]
21. Delamanid [jan]
22. Delamanid [mi]
23. Delamanid (jan/usan)
24. Delamanid [who-dd]
25. Opc-67683; Delamanid
26. Schembl57791
27. Delamanid [usan:inn:jan]
28. Chembl218650
29. Dtxsid60218326
30. Chebi:134742
31. Bcp07838
32. Ex-a2414
33. Mfcd18251539
34. Nsc794689
35. S5007
36. Zinc43100810
37. Akos025289781
38. Ccg-269934
39. Cs-5866
40. Db11637
41. Nsc-794689
42. Sb14863
43. Ncgc00348214-01
44. Ac-35849
45. As-56105
46. Delamanid; Opc 67683; Opc67683
47. Hy-10846
48. D09785
49. A856044
50. Q15408413
51. (2r)-2-methyl-6-nitro-2-((4-(4-(4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenoxy)piperidin-1-yl)phenoxy)methyl)-2,3-dihydroimidazo(2,1-b)(1,3)oxazole
52. (2r)-2-methyl-6-nitro-2-[4-[4-[4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenoxy]piperidino]phenoxymethyl]-2,3-dihydroimidazo[2,1-b]oxazole
53. [(2r)-2-methyl-2-[[4-[4-[4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenoxy]-1-piperidyl]phenoxy]methyl]-3h-imidazo[2,1-b]oxazol-6-yl]azinic Acid
54. 2-methyl-6-nitro-2-[(4-{4-[4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenoxy]piperidin-1-yl}phenoxy)methyl]-2,3-dihydroimidazo[2,1-b]oxazole, (2r)-
| Molecular Weight | 534.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C25H25F3N4O6 |
| XLogP3 | 5.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 11 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 534.17261902 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 534.17261902 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 104 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 38 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 795 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Indicated for use as part of an appropriate combination regimen for pulmonary multi-drug resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) in adult patients when an effective treatment regimen cannot otherwise be composed for reasons of resistance or tolerability.
Deltyba is indicated for use as part of an appropriate combination regimen for pulmonary multi-drug resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) in adults, adolescents, children and infants with a body weight of at least 10 kg when an effective treatment regimen cannot otherwise be composed for reasons of resistance or tolerability (see sections 4. 2, 4. 4 and 5. 1).
Consideration should be given to official guidance on the appropriate use of antibacterial agents.
The minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) of delamanid against _Mycobacterium tuberculosis_ isolates ranges from 0.006 to 0.024 g/mL. Among non-tuberculosis mycobacteria, delamanid has _in vitro_ activity against _M. kansasii_ and _M. bovis_. Delamanid has no in vitro activity against Gram negative or positive bacterial species and does not display cross-resistance to other anti-tuberculosis drugs. In murine models of chronic tuberculosis, the reduction of _M. tuberculosis_ colony counts by delamanid was demonstrated in a dose-dependent manner. Repeated dosing of delamanid may cause QTc-prolongation via inhibition of cardiac potassium channel (hERG channel), and this effect is mostly contributed by the main metabolite of delamanid, DM-6705. Animal studies indicate that delamanid may attenuate vitamin K-dependent blood clotting, increase prothrombin time (PT), and activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT).
J04AK06
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J04 - Antimycobacterials
J04A - Drugs for treatment of tuberculosis
J04AK - Other drugs for treatment of tuberculosis
J04AK06 - Delamanid
Absorption
Following a single oral dose administration of 100 mg delamanid, the peak plasma concentration was 135 ng/mL. Steady-state concentration is reached after 10-14 days. Delamanid plasma exposure increases less than proportionally with increasing dose. In animal models (dog, rat, mouse), the oral bioavailability of delamanid was reported to be 35%60%. The absolute oral bioavailability in humans is estimated to range from 25 to 47%. Oral bioavailability in humans is enhanced when administered with a standard meal, by about 2.7 fold compared to fasting conditions because delamanid exhibits poor water solubility.
Route of Elimination
Delamanid is excreted primarily in the stool, with less than 5% excretion in the urine.
Volume of Distribution
The apparent volume of distribution (Vz/F) is 2,100 L. Pharmacokinetic data in animals have shown excretion of delamanid and/or its metabolites into breast milk. In lactating rats, the Cmax for delamanid in breast milk was 4-fold higher than that of the blood.
Delamanid predominantly undergoes metabolism by albumin and to a lesser extent, CYP3A4.. The metabolism of delamanid may also be mediated by hepatic CYP1A1, CYP2D6, and CYP2E1 to a lesser extent [31966]. Four major metabolites (M1M4) have been identified in plasma in patients receiving delamanid where M1 and M3 accounts for 13%18% of the total plasma exposure in humans. While they do not retain significant pharmacological activity, they may still contribute to QT prolongation. This is especially true for the main metabolite of delamanid, M1 (DM-6705). Delamanid is predominantly metabolized by serum albumin to form M1 (DM-6705) via hydrolytic cleavage of the 6-nitro-2,3-dihydroimidazo[2,1-b] oxazole moiety. The formation of this major metabolite is suggested to be a crucial starting point in the metabolic pathway of delamanid. M1 (DM-6705) can be further catalyzed by three pathways. In the first metabolic pathway, DM-6705 undergoes hydroxylation of the oxazole moiety to form M2 ((4RS,5S)-DM-6720), followed by CYP3A4-mediated oxidation of hydroxyl group and tautomerization of oxazole to an imino-ketone metabolite, M3 ((S)-DM-6718). The second metabolic pathway involves the hydrolysis and deamination of the oxazole amine to form M4 (DM-6704) followed by hydroxylation to M6 ((4R,5S)-DM-6721) and M7 ((4S,5S)-DM-6722) and oxidation of oxazole to another ketone metabolite, M8 ((S)-DM-6717). The third pathway involves the hydrolytic cleavage of the oxazole ring to form M5 (DM-6706).
The half life ranges from 30 to 38 hours.
Delamanid is a prodrug that requires biotransformation via via the mycobacterial F420 coenzyme system, including the deazaflavin dependent nitroreductase (Rv3547), to mediate its antimycobacterial activity against both growing and nongrowing mycobacteria. Mutations in one of five coenzyme F420 genes, _fgd, Rv3547, fbiA, fbiB, and fbiC_ has been proposed as the mechanism of resistance to delamanid. Upon activation, the radical intermediate formed between delamanid and desnitro-imidazooxazole derivative is thought to mediate antimycobacterial actions via inhibition of methoxy-mycolic and keto-mycolic acid synthesis, leading to depletion of mycobacterial cell wall components and destruction of the mycobacteria. Nitroimidazooxazole derivative is thought to generate reactive nitrogen species, including nitrogen oxide (NO). However unlike isoniazid, delamanid does not alpha-mycolic acid.
