


1. Deoxycortone Pivalate
2. Desoxycoticosterone Trimethylacetate
3. Percoten Pivalate
1. 808-48-0
2. Deoxycortone Pivalate
3. Docp
4. Desoxycortone Pivalate
5. Dtma
6. Deoxycorticosterone Pivalate
7. 11-deoxycorticosterone Pivalate
8. Deoxycortone Trimethylacetate
9. Desoxycorticosterone Trimethylacetate
10. Deoxycorticosterone Trimethylacetate
11. 11-deoxycorticosterone, Pivalate
12. Neodin-depositum
13. Cortexone M
14. Percorten M
15. 11-deoxy Corticosterone Pivalate
16. Percorten Pivalate
17. Desoxycorticosteronepivalate
18. Chebi:50782
19. Desoxycorticosterone Pivalate (usp)
20. Desoxycorticosterone Pivalate [usp]
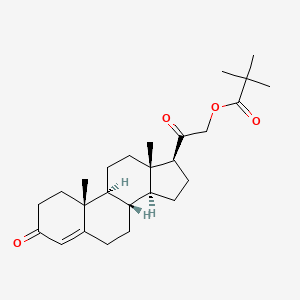
21. 3,20-dioxopregn-4-en-21-yl 2,2-dimethylpropanoate
22. 16665t4a2x
23. Pregn-4-ene-3,20-dione, 21-(2,2-dimethyl-1-oxopropoxy)-
24. [2-[(8s,9s,10r,13s,14s,17s)-10,13-dimethyl-3-oxo-1,2,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-dodecahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]-2-oxoethyl] 2,2-dimethylpropanoate
25. Percorten V
26. Percorten (tn)
27. Nsc 95278
28. 21-(2,2-dimethyl-1-oxopropoxy)pregn-4-ene-3,20-dione
29. Nsc-95278
30. Unii-16665t4a2x
31. 3,20-dioxopregn-4-en-21-yl Pivalate
32. Ncgc00159355-02
33. Einecs 212-366-0
34. Zycortal
35. Brn 3174879
36. Desoxycorticosterone-pivalate
37. Dsstox_cid_26036
38. Dsstox_rid_81301
39. Dsstox_gsid_46036
40. 4-08-00-02196 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
41. Schembl120007
42. Chembl1200592
43. Dtxsid8046036
44. Corticosterone, Deoxy-, Pivalate
45. Zinc4082455
46. Tox21_111599
47. Akos032428733
48. Desoxycortone Pivalate [mart.]
49. Db01134
50. Desoxycortone Pivalate [who-dd]
51. Ncgc00160511-01
52. Cas-808-48-0
53. Desoxycorticosterone Pivalate [mi]
54. Hy-107917
55. Cs-0030864
56. Desoxycorticosterone Pivalate [vandf]
57. Desoxycorticosterone Trimethyl Acetate
58. Desoxycorticosterone Pivalate [usp-rs]
59. D03699
60. 808d480
61. A839987
62. Desoxycorticosterone Pivalate [green Book]
63. Desoxycorticosterone Pivalate [orange Book]
64. Desoxycorticosterone Pivalate [usp Monograph]
65. Desoxycortone Pivalate [ema Epar Veterinary]
66. W-104224
67. Q27092729
68. [2-[(8s,9s,10r,13s,14s,17s)-10,13-dimethyl-3-oxo-1,2,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-dodecahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]-2-oxo-ethyl] 2,2-dimethylpropanoate
| Molecular Weight | 414.6 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C26H38O4 |
| XLogP3 | 4.5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 414.27700969 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 414.27700969 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 60.4 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 30 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 787 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 6 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Examined for treatment of adrenocortical insufficiency especially in multiple sclerosis, congenital cerebral palsy, polyarteritis nodosa, and rheumatoid arthritis. Currently only approved in treating cats and dogs for the treatment of Addison's disease.
For use as replacement therapy for mineralocorticoid deficiency in dogs with primary hypoadrenocorticism (Addison's disease).
Used to treat adrenocortical insufficiency, desoxycorticosterone pivalate is a mineralocorticoid hormone and an analogue of desoxycorticosterone. It primarily acts on the metabolism of sodium, potassium and water. When the drug is given, there is decreased excretion of sodium accompanied by increased excretion of potassium; the concentration of sodium in the blood is thereby increased whereas that of potassium is decreased. There is a concomitant increase in the volume of blood and extracellular fluids, with a fall in hematocrit. It increases the rate of renal tubular absorption of sodium.
QH02AA03
Desoxycorticosterone Pivalate binds to the mineralocorticoid receptor. Mineralocorticoids are a family of steroids, secreted by the adrenal cortex, necessary for the regulation of a number of metabolic processes including electrolyte regulation. Desoxycorticosterone pivalate exerts its effect through its interaction with the mineralocorticoid receptor (MR), whereby it reacts with the receptor proteins to form a steroid-receptor complex. This complex moves into the nucleus, where it binds to chromatin which results in genetic transcription of cellular DNA to messenger RNA. The steroid hormones appear to induce transcription and synthesis of specific proteins, which produce the physiological effects seen after administration.
