
1. Decaject
2. Decaject L.a.
3. Decaject-l.a.
4. Decameth
5. Decaspray
6. Dexasone
7. Dexpak
8. Hexadecadrol
9. Hexadrol
10. Maxidex
11. Methylfluorprednisolone
12. Millicorten
13. Oradexon
1. 50-02-2
2. Decadron
3. Maxidex
4. Dexamethazone
5. Hexadecadrol
6. Dexasone
7. Hexadrol
8. Decaspray
9. Millicorten
10. Oradexon
11. Prednisolone F
12. Fluormethylprednisolone
13. Aeroseb-dex
14. Cortisumman
15. Desametasone
16. Dexacortal
17. Dexacortin
18. Fortecortin
19. Gammacorten
20. Superprednol
21. Visumetazone
22. Auxiron
23. Calonat
24. Decaderm
25. Dexacort
26. Dexason
27. Azium
28. Dexone
29. Deltafluorene
30. Desamethasone
31. Mediamethasone
32. Aphtasolon
33. Decasone
34. Dectancyl
35. Dekacort
36. Dergramin
37. Desadrene
38. Desameton
39. Dexadeltone
40. Dexalona
41. Dexameth
42. Dexapolcort
43. Dextelan
44. Dinormon
45. Loverine
46. Luxazone
47. Mymethasone
48. Turbinaire
49. Corsone
50. Decalix
51. Mexidex
52. Dexa-cortidelt
53. Dexa-cortisyl
54. Dexa-scheroson
55. Prednisolon F
56. Dexa-sine
57. Isopto-dex
58. Aeroseb-d
59. Sk-dexamethasone
60. Anaflogistico
61. Decacortin
62. Deseronil
63. Dexafarma
64. Dexaprol
65. Dexinolon
66. Dexinoral
67. Policort
68. Spoloven
69. Decagel
70. Deronil
71. Dezone
72. Sunia Sol D
73. Bisu Ds
74. Dexa Mamallet
75. Hexadrol Elixir
76. Lokalison F
77. Ocu-trol
78. Dex-ide
79. Hl-dex
80. Dexamethasonum
81. Dexone 4
82. Fluorocort
83. Decaject
84. Decameth
85. Fluormone
86. Corson
87. Dexpak
88. Pet Derm Iii
89. Dxms
90. Dexamethasone Alcohol
91. Hexadrol Tablets
92. Dexamethasone Intensol
93. Methylfluorprednisolone
94. Desametasone [dcit]
95. Dexone 0.5
96. Dexone 1.5
97. Dexone 0.75
98. Dexametasona
99. Dexacidin
100. Maxitrol
101. Ozurdex
102. Dexametasona [inn-spanish]
103. Dexamethasonum [inn-latin]
104. Dexapos
105. Decadron Tablets, Elixir
106. 9alpha-fluoro-16alpha-methylprednisolone
107. Azium (veterinary)
108. Dexamethansone
109. Dextenza
110. Posurdex
111. Prodex
112. Oto-104
113. Mk 125
114. (3h)-dexamethasone
115. Azimycin (veterinary)
116. Nsc 34521
117. Dexametasone
118. Naquasone (veterinary)
119. Tresaderm (veterinary)
120. Dexycu
121. 16alpha-methyl-9alpha-fluoro-1-dehydrocortisol
122. Dexasite
123. 16alpha-methyl-9alpha-fluoroprednisolone
124. 16-alpha-methyl-9-alpha-fluoroprednisolone
125. 9-alpha-fluoro-16-alpha-methylprednisolone
126. 1-dehydro-16alpha-methyl-9alpha-fluorohydrocortisone
127. Delta1-9alpha-fluoro-16alpha-methylcortisol
128. Decacort
129. (11beta,16alpha)-9-fluoro-11,17,21-trihydroxy-16-methylpregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione
130. 16-alpha-methyl-9-alpha-fluoro-1-dehydrocortisol
131. 16-alpha-methyl-9-alpha-fluoro-delta1-hydrocortisone
132. Delta(sup 1)-9-alpha-fluoro-16-alpha-methylcortisol
133. Isv-305
134. 9a-fluoro-16beta-methylprednisolone
135. 16alpha-methyl-9alpha-fluoro-delta(sup 1)-hydrocortisone
136. 16-alpha-methyl-9-alpha-fluoro-delta(sup 1)-hydrocortisone
137. Nsc-34521
138. Dexamethasone (dhap)
139. 7s5i7g3jql
140. 16.alpha.-methyl-9.alpha.-fluoroprednisolone
141. Chebi:41879
142. [3h]-dexamethasone
143. Decaject-l.a.
144. 23495-06-9
145. Pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione, 9-fluoro-11,17,21-trihydroxy-16-methyl-, Labeled With Tritium, (11beta,16alpha)-
146. Aphthasolone
147. Dexamonozon
148. 9.alpha.-fluoro-16.alpha.-methylprednisolone
149. (1r,2s,10s,11s,13r,14r,15s,17s)-1-fluoro-14,17-dihydroxy-14-(2-hydroxyacetyl)-2,13,15-trimethyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0^{2,7}.0^{11,15}]heptadeca-3,6-dien-5-one
150. (8s,9r,10s,11s,13s,14s,16r,17r)-9-fluoro-11,17-dihydroxy-17-(2-hydroxyacetyl)-10,13,16-trimethyl-6,7,8,11,12,14,15,16-octahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one
151. (8s,9r,10s,11s,13s,14s,16r,17r)-9-fluoro-11,17-dihydroxy-17-(2-hydroxyacetyl)-10,13,16-trimethyl-6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-dodecahydro-3h-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one
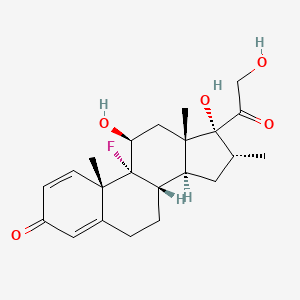
152. C22h29fo5
153. 16.alpha.-methyl-9.alpha.-fluoro-1-dehydrocortisol
154. 1-dehydro-16.alpha.-methyl-9.alpha.-fluorohydrocortisone
155. Osurdex
156. Dexamethasone Base
157. Decadron (tn)
158. (8s,9r,10s,11s,13s,14s,16r,17r)-9-fluoro-11,17-dihydroxy-17-(2-hydroxyacetyl)-10,13,16-trimethyl-6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-dodecahydro-3h-cyclopenta[a]ph
159. Smr000857119
160. Dxm [steroid]
161. Ccris 7067
162. Hsdb 3053
163. Dexamethasone (tetramethyl-rhodamine Conjugated )
164. Prednisolone, 9.alpha.-fluoro-16.alpha.-methyl-
165. Einecs 200-003-9
166. Mfcd00064136
167. Unii-7s5i7g3jql
168. Solurex
169. .delta.(sup 1)-9-.alpha.-fluoro-16-.alpha.-methylcortisol
170. 16.alpha.-methyl-9.alpha.-fluoro-.delta.(sup1)-hydrocortisone
171. Diodex
172. Nsc34521
173. Ai3-50934
174. .gamma.corten
175. 9-fluoro-11,17,21-trihydroxy-16-methylpregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione
176. Apo-dexamethasone
177. Prednisolone, 9alpha-fluoro-16alpha-methyl-
178. Dexasone 4mg
179. Dtxsid3020384
180. Zema-pak
181. Phl-dexamethasone
182. Pms-dexamethasone
183. 9-fluoro-11.beta.,17,21-trihydroxy-16.alpha.-methylpregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione
184. [3h]dexamethasone
185. Dexamethasone-omega
186. Ncgc00091019-08
187. Dexasone 0.5mg
188. Dexamethasone [usp:inn:ban:jan]
189. Dexasone 0.75mg
190. Sandoz Dexamethasone
191. Hemady
192. Pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione, 9-fluoro-11,17,21-trihydroxy-16-methyl-, (11beta,16alpha)-
193. Dexamethasone, Topical
194. Maxidex Ont 0.1%
195. Maxidex Sus 0.1%
196. Dexamethasone-17-acetate
197. Dsstox_cid_384
198. Spectrum5_002019
199. Dexamethasone [mi]
200. Molmap_000018
201. 9-fluoro-11beta,17,21-trihydroxy-16alpha-methylpregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione
202. Dexamethasone [inn]
203. Dexamethasone [jan]
204. Schembl3774
205. 16-alpha-methyl-9-alpha-fluoro-1,4-pregnadiene-11-beta,17-alpha,21-triol-3,20-dione
206. 16-alpha-methyl-9-alpha-fluoro-11-beta,17-alpha,21-trihydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione
207. 4-alpha-fluoro-16-alpha-methyl-11-beta,17,21-trihydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione
208. 9-alpha-fluoro-16-alpha-methyl-1,4-pregnadiene-11-beta,17-alpha,21-triol-3,20-dione
209. Dexamethasone [hsdb]
210. Dsstox_rid_75557
211. Bidd:pxr0060
212. Dsstox_gsid_20384
213. Bspbio_000995
214. Dexamethasone [vandf]
215. Mls001055412
216. Mls001332507
217. Mls001332508
218. Bidd:er0494
219. Dexamethasone [mart.]
220. Sustained-release Dexamethasone
221. Dexamethasone [usp-rs]
222. Dexamethasone [who-dd]
223. Dexamethasone [who-ip]
224. Chembl384467
225. Gtpl2768
226. Gtpl3447
227. Sgcut00126
228. 9-fluoro-16-methylprednisolone
229. Ak Dex Oph Otic Soln 0.1%
230. Dexamethasone [ema Epar]
231. Bdbm18207
232. Dexamethasone (jp17/usp/inn)
233. 1p93
234. Dexamethasone [green Book]
235. Hms1792a17
236. Hms1990a17
237. Hms2089n13
238. Hms2235f08
239. Hms3039l11
240. Hms3259n11
241. Hms3403a17
242. Dexamethasone [orange Book]
243. Amy28815
244. To_000038
245. Zinc3875332
246. Dexamethasone [ep Monograph]
247. Tox21_200122
248. Dexamethasone [usp Monograph]
249. Dexamethasone, >=97.0% (hplc)
250. Ibi-10090
251. Mk-125
252. S1322
253. Dexamethasone 1.0 Mg/ml In Methanol
254. Dexamethasonum [who-ip Latin]
255. Pms Dexamethasone Elixir 0.5mg/5ml
256. Akos005259009
257. Akos015895509
258. Ciprodex Component Dexamethasone
259. Decadron Phosphate, Decdan, Dexacort,
260. Maxitrol Component Dexamethasone
261. Tobradex Component Dexamethasone
262. Ccg-264887
263. Cs-1505
264. Db01234
265. Ks-1451
266. Nc00645
267. Alpha -fluoro-16-alpha -methylcortisol
268. Cas-50-02-2
269. Dexacidin Component Dexamethasone
270. Pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione, 9-fluoro-11beta,17,21-trihydroxy-16alpha-methyl-
271. Smp1_000092
272. Dexamethasone 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
273. Dexamethasone, >=98% (hplc), Powder
274. Dexasporin Component Dexamethasone
275. Ncgc00091019-01
276. Ncgc00091019-02
277. Ncgc00091019-03
278. Ncgc00091019-04
279. Ncgc00091019-05
280. Ncgc00091019-06
281. Ncgc00091019-07
282. Ncgc00091019-23
283. Ncgc00257676-01
284. (11beta,16alpha)-9-fluoro-11,17,21-trihydroxy-16-methylpregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione Labeled With Tritium
285. 9alpha-fluoro-16alpha-methyl-prednisolone
286. Ac-11056
287. Dexamethasone Component Of Ciprodex
288. Dexamethasone Component Of Maxitrol
289. Dexamethasone Component Of Tobradex
290. Hy-14648
291. Nci60_003067
292. Smr001227192
293. Tobradex St Component Dexamethasone
294. Dexamethasone 1000 Microg/ml In Methanol
295. Dexamethasone Component Of Dexacidin
296. 16alpha -methyl-9alpha -fluoroprednisolone
297. 9alpha -fluoro-16alpha -methylprednisolone
298. Dexamethasone Component Of Dexasporin
299. Dexamethasone, Tested According To Ph.eur.
300. Dexamethasone 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
301. Dexamethasone Component Of Tobradex St
302. Betamethasone Impurity A [ep Impurity]
303. En300-52607
304. D00292
305. Dexamethasone, Meets Usp Testing Specifications
306. Prednisolone, 9alpha -fluoro-16alpha -methyl-
307. 9.alpha.-fluoro-16.alpha.-methyl-1,20-dione
308. Ab00918428-05
309. Ab00918428-08
310. Ab00918428-09
311. Ab00918428_10
312. 064d136
313. 16alpha -methyl-9alpha -fluoro-1-dehydrocortisol
314. Dexamethasone, Vetranal(tm), Analytical Standard
315. Q422252
316. Neomycin And Polymyxin B Sulphates And Dexamethasone
317. Q-200939
318. Brd-k38775274-001-02-3
319. Brd-k38775274-001-06-4
320. Dexamethasone Acetate Impurity A [ep Impurity]
321. 1-dehydro-16alpha -methyl-9alpha -fluorohydrocortisone
322. 9-fluoro-11alpha -methylpregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione
323. Dexamethasone, British Pharmacopoeia (bp) Assay Standard
324. Z802671480
325. Pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione, 9-fluoro-11alpha -methyl-
326. Dexamethasone, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
327. Wln: L E5 B666 Ov Ku Mutj A1 Bf Cq E1 Fv1q Fq G1
328. Dexamethasone, Powder, Bioreagent, Suitable For Cell Culture, >=97%
329. Dexamethasone, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
330. 16-.alpha.-methyl-9-.alpha.-fluoro-1,17-.alpha.,21-triol-3,20-dione
331. 4.alpha.-fluoro-16.alpha.-methyl-11.beta.-17,4-diene-3,20-dione
332. Pregna-1,20-dione, 9-fluoro-11.beta.,17,21-trihydroxy-16.alpha.-methyl-
333. 16.alpha.-methyl-9.alpha.-fluoro-11.beta.-17.alpha.-21-trihydroxypregna-1,20-dione
334. 9-fluoro-11.beta.,21-trihydroxy-16.alpha.-methylpregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione
335. 9-fluoro-16alpha-methyl-11beta,17,21-trihydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione
336. 9.alpha.-fluoro-11.beta.-17.alpha.- 21-trihydroxy-16.alpha.-methylpregna-1,20-dione
337. Dexamethasone For Peak Identification, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
338. Dexamethasone For System Suitability, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
339. Dexamethasone Solution, 1.0 Mg/ml In Methanol, Ampule Of 1 Ml, Certified Reference Material
340. Dexamethasone, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
341. Dexamethasone, Powder, Gamma-irradiated, Bioxtra, Suitable For Cell Culture, >=80% (hplc)
342. Pregna-1,20-dione, 9-fluoro-11,17,21-trihydroxy-16-methyl-, (11.beta.,16.alpha.)-
343. (11.beta.,16.alpha.)-9-fluoro-11,17,21-trihydroxy-16-methylpregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione
344. (11alpha,14beta,16alpha,17alpha)-9-fluoro-11,17,21-trihydroxy-16-methylpregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione
345. (1r,2s,10s,11s,13r,14r,15s,17s)-1-fluoro-14,17-dihydroxy-14-(2-hydroxyacetyl)-2,13,15-trimethyltetracyclo-
346. (1r,2s,10s,11s,13r,14r,15s,17s)-1-fluoro-14,17-dihydroxy-14-(2-hydroxyacetyl)-2,13,15-trimethyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0;{2,7}.0;{11,15}]heptadeca-3,6-dien-5-one
347. 1050677-47-8
348. 9.alpha.-fluoro-16.alpha.-methyl-11.beta.,21.beta.-trihydroxy-pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione
349. Pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione, 9-fluoro-11,17,21-trihydroxy-16-methyl-,(11.beta.,16.alpha.)-9-fluoro-11.beta.,17,21-trihydroxy-16.alpha.-methylpregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione
1. Dexamethasone 9,11-epoxide
2. Decadronal
3. Panasone
4. Dexamethasone Acetate
5. 33755-46-3
6. Dexamethasone 17-valerate
7. Dexamethasone Valerate
8. Methaderm
9. 55541-30-5
10. Dexamethasone Dipropionate
| Molecular Weight | 392.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C22H29FO5 |
| XLogP3 | 1.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 392.19990218 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 392.19990218 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 94.8 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 28 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 805 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 8 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 10 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Dexamethasone |
| PubMed Health | Dexamethasone |
| Drug Classes | Antiemetic, Corticosteroid, Weak, Diagnostic Agent, Adrenocortical Function, Endocrine-Metabolic Agent, Immune Suppreant, Ophthalmologic Agent |
| Drug Label | Each 5 mL (teaspoonful) contains:Dexamethasone, USP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.5 mgAlso contains:Benzoic Acid, USP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.1% (as preservative)Alcohol (% v... |
| Active Ingredient | Dexamethasone |
| Dosage Form | Elixir; Tablet; Solution |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 0.5mg/5ml; 4mg; 1.5mg; 0.5mg; 6mg; 2mg; 1mg; 0.75mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Lyne; Vintage Pharms; Ecr; Sti Pharma; Wockhardt Eu Operatn; Par Pharm; Roxane |
| 2 of 10 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Dexamethasone intensol |
| PubMed Health | Dexamethasone |
| Drug Classes | Antiemetic, Corticosteroid, Weak, Diagnostic Agent, Adrenocortical Function, Endocrine-Metabolic Agent, Immune Suppreant, Ophthalmologic Agent |
| Drug Label | Dexamethasone Tablets 0.5, 0.75, 1, 1.5, 2, 4 and 6 mg USP, Dexamethasone Oral Solution, 0.5 mg per 5 mL and Dexamethasone Intensol Oral Solution (Concentrate), 1 mg per mL are for oral administration.Each tablet contains:Dexamethasone 0.5, 0.75,... |
| Active Ingredient | Dexamethasone |
| Dosage Form | Concentrate |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 1mg/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Roxane |
| 3 of 10 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Maxidex |
| PubMed Health | Polymyxin B/Neomycin/Dexamethasone (Into the eye) |
| Drug Classes | Aminoglycoside/Corticosteroid Combination |
| Drug Label | MAXIDEX 0.1% (dexamethasone ophthalmic suspension) is an adrenocortical steroid prepared as a sterile topical ophthalmic suspension. The active ingredient is represented by the chemical structure:Chemical name: Pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione,9-fluoro-... |
| Active Ingredient | Dexamethasone |
| Dosage Form | Suspension/drops |
| Route | Ophthalmic |
| Strength | 0.1% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Alcon |
| 4 of 10 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Maxitrol |
| PubMed Health | Dexamethasone |
| Drug Classes | Antiemetic, Corticosteroid, Weak, Diagnostic Agent, Adrenocortical Function, Endocrine-Metabolic Agent, Immune Suppreant, Ophthalmologic Agent |
| Active Ingredient | Dexamethasone; neomycin sulfate; polymyxin b sulfate |
| Dosage Form | Ointment; Suspension/drops |
| Route | Ophthalmic |
| Strength | 10,000 units/ml; 0.1%; 10,000 units/gm; eq 3.5mg base/ml; eq 3.5mg base/gm |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Alcon; Falcon Pharms |
| 5 of 10 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Ozurdex |
| Drug Label | OZURDEX is an intravitreal implant containing 0.7 mg (700 mcg) dexamethasone in the NOVADUR solid polymer sustained-release drug delivery system. OZURDEX is preloaded into a single-use, DDS applicator to facilitate injection of the rod-shaped... |
| Active Ingredient | Dexamethasone |
| Dosage Form | Implant |
| Route | Intravitreal |
| Strength | 0.7mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Allergan |
| 6 of 10 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Dexamethasone |
| PubMed Health | Dexamethasone |
| Drug Classes | Antiemetic, Corticosteroid, Weak, Diagnostic Agent, Adrenocortical Function, Endocrine-Metabolic Agent, Immune Suppreant, Ophthalmologic Agent |
| Drug Label | Each 5 mL (teaspoonful) contains:Dexamethasone, USP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.5 mgAlso contains:Benzoic Acid, USP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.1% (as preservative)Alcohol (% v... |
| Active Ingredient | Dexamethasone |
| Dosage Form | Elixir; Tablet; Solution |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 0.5mg/5ml; 4mg; 1.5mg; 0.5mg; 6mg; 2mg; 1mg; 0.75mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Lyne; Vintage Pharms; Ecr; Sti Pharma; Wockhardt Eu Operatn; Par Pharm; Roxane |
| 7 of 10 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Dexamethasone intensol |
| PubMed Health | Dexamethasone |
| Drug Classes | Antiemetic, Corticosteroid, Weak, Diagnostic Agent, Adrenocortical Function, Endocrine-Metabolic Agent, Immune Suppreant, Ophthalmologic Agent |
| Drug Label | Dexamethasone Tablets 0.5, 0.75, 1, 1.5, 2, 4 and 6 mg USP, Dexamethasone Oral Solution, 0.5 mg per 5 mL and Dexamethasone Intensol Oral Solution (Concentrate), 1 mg per mL are for oral administration.Each tablet contains:Dexamethasone 0.5, 0.75,... |
| Active Ingredient | Dexamethasone |
| Dosage Form | Concentrate |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 1mg/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Roxane |
| 8 of 10 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Maxidex |
| PubMed Health | Polymyxin B/Neomycin/Dexamethasone (Into the eye) |
| Drug Classes | Aminoglycoside/Corticosteroid Combination |
| Drug Label | MAXIDEX 0.1% (dexamethasone ophthalmic suspension) is an adrenocortical steroid prepared as a sterile topical ophthalmic suspension. The active ingredient is represented by the chemical structure:Chemical name: Pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione,9-fluoro-... |
| Active Ingredient | Dexamethasone |
| Dosage Form | Suspension/drops |
| Route | Ophthalmic |
| Strength | 0.1% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Alcon |
| 9 of 10 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Maxitrol |
| PubMed Health | Dexamethasone |
| Drug Classes | Antiemetic, Corticosteroid, Weak, Diagnostic Agent, Adrenocortical Function, Endocrine-Metabolic Agent, Immune Suppreant, Ophthalmologic Agent |
| Active Ingredient | Dexamethasone; neomycin sulfate; polymyxin b sulfate |
| Dosage Form | Ointment; Suspension/drops |
| Route | Ophthalmic |
| Strength | 10,000 units/ml; 0.1%; 10,000 units/gm; eq 3.5mg base/ml; eq 3.5mg base/gm |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Alcon; Falcon Pharms |
| 10 of 10 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Ozurdex |
| Drug Label | OZURDEX is an intravitreal implant containing 0.7 mg (700 mcg) dexamethasone in the NOVADUR solid polymer sustained-release drug delivery system. OZURDEX is preloaded into a single-use, DDS applicator to facilitate injection of the rod-shaped... |
| Active Ingredient | Dexamethasone |
| Dosage Form | Implant |
| Route | Intravitreal |
| Strength | 0.7mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Allergan |
Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Steroidal; Antiemetics; Antineoplastic Agents, Hormonal; Glucocorticoids, Synthetic; Glucocorticoids, Topical
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
Nasal corticosteroids are used in some patients for prophylaxis of seasonal rhinitis. This form of therapy is generally reserved for patients who have consistently demonstrated a need for nasal corticosteroids to control seasonal rhinitis syndromes. Antihistamines and decongestants are considered primary therapies for this disorder. Dexamethasone nasal aerosol is less frequently used because its use results in a significantly higher incidence of systemic adverse effects with no additional benefit over other nasal corticosteroids. /NOT included in US product labeling/
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2007., p. 897
Ophthalmic corticosteroids are indicated in the treatment of corticosteroid-responsive allergic and inflammatory conditions of the palpebral and bulbar conjunctiva, cornea, and anterior segment of the globe. /Corticosteroids (Ophthalmic); Included in US product labeling/
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2007., p. 906
Otic corticosteroids are indicated in the treatment of corticosteroid-responsive inflammatory disorders of the external auditory meatus such as: allergic otitis externa; infective otitis (treatment adjunct); (chronic eczematoid otitis externa or seborrheic otitis externa /NOT included in US product labeling/). Dexamethasone /is/ used in the treatment of these and other corticosteroid-responsive disorders of the external auditory meatus. /Included in US product labeling/
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2007., p. 911
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for DEXAMETHASONE (42 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Dexamethasone improves the cure rate of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) but causes physical and behavioral adverse events. The objective of the current study was to determine the effect of dexamethasone exposure on sleep and fatigue in pediatric patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. One hundred pediatric patients with low-risk or standard-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia were enrolled on 1 of 3 protocols (St. Jude Total XV, Children's Oncology Group [COG] 9904, or COG 9905) at 3 institutions. The mean age of the cohort was 9.24 +/- 3.23 years (range, 5.03-18.14 years). The majority of patients were white (79%) males (62%) with standard-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia (63%). The cohort was divided into 4 subgroups: St. Jude low-risk, St. Jude standard-risk, COG low-risk, and COG standard-risk. Patients wore a wrist actigraph to monitor sleep activity during 2 consecutive 5-day periods: During the first period, they did not receive dexamethasone; and, during the second period, they did. Patients and their parents completed fatigue instruments on Days 2 and 5 of each period, and parents completed sleep diaries. Actual sleep minutes, sleep duration, total daily nap minutes, and fatigue increased significantly during the dexamethasone treatment for 3 to 4 of the subgroups. Total daily nap minutes increased significantly for both standard-risk groups during the dexamethasone treatment. Parents reported significant increases in their child's nighttime awakenings, restless sleep, and nap time during dexamethasone treatment.Dexamethasone treatment during continuation therapy for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia significantly and adversely altered sleep and fatigue, confirming that sleep and fatigue are behavioral responses to dexamethasone.
PMID:17926333 Hinds PS et al; Cancer 110 (10): 2321-30 (2007)
Excreted in breast milk; nursing by mothers receiving pharmacologic doses not recommended.
US Pharmacopeial Convention; US Pharmacopeia Dispensing Information (USP DI); Drug Information for the Health Care Professional 12th ed, V.I p.59 (1992)
/Dexamethasone/ is distributed into breast milk. Nursing while receiving pharmacologic doses of dexamethasone is not recommended.
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2007., p. 899
Dexamethasone inhalation is not recommended for use in asthma because it has demonstrated a significantly higher incidence of systemic effects with no additional benefit over other inhaled corticosteroids. The high ratio of systemic glucocorticoid activity to local anti-inflammatory activity of inhaled dexamethasone may be due to its greater water solubility and longer metabolic hal life after absorption relative to the other inhaled corticosteroids.
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2007., p. 890
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for DEXAMETHASONE (42 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Dexamethasone and [ciprofloxacin] otic suspension is indicated for bacterial infections with inflammation in acute otitis media and acute otitis externa. Intramuscular and intravenous injections are indicated for a number of endocrine, rheumatic, collagen, dermatologic, allergic, ophthalmic, gastrointestinal, respiratory, hematologic, neoplastic, edematous, and other conditions. Oral tablets are indicated for the treatment of multiple myeloma. An intravitreal implant is indicated for some forms of macular edema and non-infectious posterior uveitis affecting the posterior of the eye. Various ophthalmic formulations are indicated for inflammatory conditions of the eye.
FDA Label
Treatment of multiple myeloma.
Ozurdex is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with macular oedema following either branch retinal-vein occlusion (BRVO) or central retinal-vein occlusion (CRVO).
Ozurdex is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with inflammation of the posterior segment of the eye presenting as noninfectious uveitis.
Ozurdex is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with visual impairment due to diabetic macular oedema (DME) who are pseudophakic or who are considered insufficiently responsive to, or unsuitable for non-corticosteroid therapy.
Treatment of postoperative pain and inflammation associated with ophthalmic surgery
Treatment of diabetic macular oedema
Chronic non-infectious intermediate or posterior uveitis
Other retinal vascular occlusion
Corticosteroids bind to the glucocorticoid receptor, inhibiting pro-inflammatory signals, and promoting anti-inflammatory signals. Dexamethasone's duration of action varies depending on the route. Corticosteroids have a wide therapeutic window as patients may require doses that are multiples of what the body naturally produces. Patients taking corticosteroids should be counselled regarding the risk of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis suppression and increased susceptibility to infections.
Anti-Inflammatory Agents
Substances that reduce or suppress INFLAMMATION. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Inflammatory Agents.)
Glucocorticoids
A group of CORTICOSTEROIDS that affect carbohydrate metabolism (GLUCONEOGENESIS, liver glycogen deposition, elevation of BLOOD SUGAR), inhibit ADRENOCORTICOTROPIC HORMONE secretion, and possess pronounced anti-inflammatory activity. They also play a role in fat and protein metabolism, maintenance of arterial blood pressure, alteration of the connective tissue response to injury, reduction in the number of circulating lymphocytes, and functioning of the central nervous system. (See all compounds classified as Glucocorticoids.)
Antineoplastic Agents, Hormonal
Antineoplastic agents that are used to treat hormone-sensitive tumors. Hormone-sensitive tumors may be hormone-dependent, hormone-responsive, or both. A hormone-dependent tumor regresses on removal of the hormonal stimulus, by surgery or pharmacological block. Hormone-responsive tumors may regress when pharmacologic amounts of hormones are administered regardless of whether previous signs of hormone sensitivity were observed. The major hormone-responsive cancers include carcinomas of the breast, prostate, and endometrium; lymphomas; and certain leukemias. (From AMA Drug Evaluations Annual 1994, p2079) (See all compounds classified as Antineoplastic Agents, Hormonal.)
Antiemetics
Drugs used to prevent NAUSEA or VOMITING. (See all compounds classified as Antiemetics.)
H02AB02
S01BA01
H02AB02
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
H02AB02
S66 | EAWAGTPS | Parent-Transformation Product Pairs from Eawag | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.3754448
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A01 - Stomatological preparations
A01A - Stomatological preparations
A01AC - Corticosteroids for local oral treatment
A01AC02 - Dexamethasone
C - Cardiovascular system
C05 - Vasoprotectives
C05A - Agents for treatment of hemorrhoids and anal fissures for topical use
C05AA - Corticosteroids
C05AA09 - Dexamethasone
D - Dermatologicals
D07 - Corticosteroids, dermatological preparations
D07A - Corticosteroids, plain
D07AB - Corticosteroids, moderately potent (group ii)
D07AB19 - Dexamethasone
D - Dermatologicals
D07 - Corticosteroids, dermatological preparations
D07X - Corticosteroids, other combinations
D07XB - Corticosteroids, moderately potent, other combinations
D07XB05 - Dexamethasone
D - Dermatologicals
D10 - Anti-acne preparations
D10A - Anti-acne preparations for topical use
D10AA - Corticosteroids, combinations for treatment of acne
D10AA03 - Dexamethasone
H - Systemic hormonal preparations, excl. sex hormones and insulins
H02 - Corticosteroids for systemic use
H02A - Corticosteroids for systemic use, plain
H02AB - Glucocorticoids
H02AB02 - Dexamethasone
R - Respiratory system
R01 - Nasal preparations
R01A - Decongestants and other nasal preparations for topical use
R01AD - Corticosteroids
R01AD03 - Dexamethasone
S - Sensory organs
S01 - Ophthalmologicals
S01B - Antiinflammatory agents
S01BA - Corticosteroids, plain
S01BA01 - Dexamethasone
S - Sensory organs
S01 - Ophthalmologicals
S01C - Antiinflammatory agents and antiinfectives in combination
S01CB - Corticosteroids/antiinfectives/mydriatics in combination
S01CB01 - Dexamethasone
S - Sensory organs
S02 - Otologicals
S02B - Corticosteroids
S02BA - Corticosteroids
S02BA06 - Dexamethasone
S - Sensory organs
S03 - Ophthalmological and otological preparations
S03B - Corticosteroids
S03BA - Corticosteroids
S03BA01 - Dexamethasone
Absorption
Absorption via the intramuscular route is slower than via the intravenous route. A 3mg intramuscular dose reaches a Cmax of 34.66.0ng/mL with a Tmax of 2.01.2h and an AUC of 11338ng\*h/mL. A 1.5mg oral dose reaches a Cmax of 13.96.8ng/mL with a Tmax of 2.00.5h and an AUC of 33150ng\*h/mL. Oral dexamethasone is approximately 70-78% bioavailable in healthy subjects.
Route of Elimination
Corticosteroids are generally eliminated predominantly in the urine. However, dexamethasone is <10% elminated in urine.
Volume of Distribution
A 1.5mg oral dose of dexamethasone has a volume of distribution of 51.0L, while a 3mg intramuscular dose has a volume of distribution of 96.0L.
Clearance
A 20mg oral tablet has a clearance of 15.7L/h. A 1.5mg oral dose of dexamethasone has a clearance of 15.64.9L/h while a 3.0mg intramuscular dose has a clearance of 9.91.4L/h.
Absorbed into aqueous humor, cornea, iris, choroid ciliary body, and retina. Systemic absorption occurs, but may be significant only at higher dosages or in extended pediatric therapy. /Corticosteroids (Ophthalmic)/
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2007., p. 906
Dogs (mixed-breed) were administered dexamethasone alcohol or dexamethasone 21-isonicotinate as a solution iv or im (1 mg/kg bw), or dexamethasone 21-isonicotinate as a suspension im (0.1 or 1 mg/kg bw). Plasma concentrations were determined with HPLC up to 120 hours after treatment. The elimination half-life after iv administration was 120-140 minutes for both formulations. Following im administration, absorption was rapid with peak plasma concentrations at 30-40 minutes for both solutions. Bioavailability after im administration was 100% for dexamethasone alcohol but 40% for dexamethasone 21-isonicotinate. After im administration of dexamethasone 21-isonicotinate as a suspension, dexamethasone was not detected in plasma, suggesting a long absorption phase
Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives; WHO Food Additive Series 33: Toxicological Evaluation of Ceratain Veterinary Drug Residues in Food: Dexamethasone (1994). Available from, as of November 6, 2007: https://www.inchem.org/documents/jecfa/jecmono/v33je09.htm
Crl:SD(CD)BR rats were administered a single im dose of 9 ug, (1,2,4-3H)-dexamethasone/kg bw. Radioactivity was measured up to 96 hours after administration in plasma (pre- and post-freeze dried), urine, feces and expired air. Tritium exchange was measured in stored urine. Highest plasma levels were observed 6 hours after dosing (3.7 ug equivalents/g), declining rapidly thereafter to 0.15 ug equivalents/g. Within 24 hours 41% of the radioactivity was excreted in the urine. After 96 hours a mean of 44% of the radio-activity was excreted. Tritium exchange was observed both in plasma and urine. Following freeze-drying, the mean loss of radioactivity 96 hours after dosing was 87% and 37% in plasma and urine, respectively
Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives; WHO Food Additive Series 33: Toxicological Evaluation of Ceratain Veterinary Drug Residues in Food: Dexamethasone (1994). Available from, as of November 6, 2007: https://www.inchem.org/documents/jecfa/jecmono/v33je09.htm
Male Wistar albino rats were administered 0.23 umol (1,2-3H) dexamethasone/kg bw, ip. Urine and feces were collected up to 4 days after treatment. Within 96 hours 74% of the dose was excreted, 30% in the urine and 44% in the feces
Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives; WHO Food Additive Series 33: Toxicological Evaluation of Ceratain Veterinary Drug Residues in Food: Dexamethasone (1994). Available from, as of November 6, 2007: https://www.inchem.org/documents/jecfa/jecmono/v33je09.htm
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for DEXAMETHASONE (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Dexamethasone is 6-hydroxylated by CYP3A4 to 6- and 6-hydroxydexamethasone. Dexamethasone is reversibly metabolized to 11-dehydrodexamethasone by corticosteroid 11-beta-dehydrogenase isozyme 2 and can also be converted back to dexamethasone by Corticosteroid 11-beta-dehydrogenase isozyme 1.
Male Wistar albino rats were administered (3)H-dexamethasone orally at a dose of 1.14 nmol/kg bw. Thirty-one percent of the administered radioactivity was excreted in the urine within 4 days (most of it within the first 24 hours) as unconjugated metabolites. Unchanged dexamethasone accounted for 14%, 6-hydroxydexamethasone for 7.4%, and 20-dihydrodexamethasone for 1.1% of the urine radioactivity.
Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives; WHO Food Additive Series 33: Toxicological Evaluation of Ceratain Veterinary Drug Residues in Food: Dexamethasone (1994). Available from, as of November 6, 2007: https://www.inchem.org/documents/jecfa/jecmono/v33je09.htm
In the urine of rats administered 0.23 umol/kg bw (1,2-3H)- dexamethasone ip, 10% of the administered radioactivity was associated with one polar metabolite of dexamethasone, likely to be 6-hydroxy-dexamethasone
Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives; WHO Food Additive Series 33: Toxicological Evaluation of Ceratain Veterinary Drug Residues in Food: Dexamethasone (1994). Available from, as of November 6, 2007: https://www.inchem.org/documents/jecfa/jecmono/v33je09.htm
No parent compound could be detected in urine of patients after oral administration of a small dose of dexamethasone (<4 mg/day) for a few weeks. However, 60% was recovered as 6-beta-hydroxy-dexamethasone and 5-10% as 6-beta-hydroxy-20-dihydrodexamethasone. After the administration of about 15 mg dexamethasone/day metabolism occurred by an additional route involving epoxidation and subsequent hydrolysis, resulting in glycol formation in ring A
Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives; WHO Food Additive Series 33: Toxicological Evaluation of Ceratain Veterinary Drug Residues in Food: Dexamethasone (1994). Available from, as of November 6, 2007: https://www.inchem.org/documents/jecfa/jecmono/v33je09.htm
Dexamethasone has known human metabolites that include 6-alpha-OH DEXAMETHASONE and 6-beta-OH DEXAMETHASONE.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
The mean terminal half life of a 20mg oral tablet is 4 hours. A 1.5mg oral dose of dexamethasone has a half life of 6.64.3h, while a 3mg intramuscular dose has a half life of 4.21.2h.
190 minutes (plasma) /Dexamethasone sodium phosphate/
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2007., p. 898
Dogs (mixed-breed) were administered dexamethasone alcohol or dexamethasone 21-isonicotinate as a solution iv or im (1 mg/kg bw), or dexamethasone 21-isonicotinate as a suspension im (0.1 or 1 mg/kg bw). Plasma concentrations were determined with HPLC up to 120 hours after treatment. The elimination half-life after iv administration was 120-140 minutes for both formulations.
Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives; WHO Food Additive Series 33: Toxicological Evaluation of Ceratain Veterinary Drug Residues in Food: Dexamethasone (1994). Available from, as of November 6, 2007: https://www.inchem.org/documents/jecfa/jecmono/v33je09.htm
The short term effects of corticosteroids are decreased vasodilation and permeability of capillaries, as well as decreased leukocyte migration to sites of inflammation. Corticosteroids binding to the glucocorticoid receptor mediates changes in gene expression that lead to multiple downstream effects over hours to days. Glucocorticoids inhibit neutrophil apoptosis and demargination; they inhibit phospholipase A2, which decreases the formation of arachidonic acid derivatives; they inhibit NF-Kappa B and other inflammatory transcription factors; they promote anti-inflammatory genes like interleukin-10. Lower doses of corticosteroids provide an anti-inflammatory effect, while higher doses are immunosuppressive. High doses of glucocorticoids for an extended period bind to the mineralocorticoid receptor, raising sodium levels and decreasing potassium levels.
Corticosteroids diffuse across cell membranes and complex with specific cytoplasmic receptors. These complexes then enter the cell nucleus, bind to DNA, and stimulate transcription of mRNA and subsequent protein synthesis of enzymes ultimately responsible for anti-inflammatory effects of topical application of corticosteroids to the eye. In high concentrations which may be achieved after topical application, corticosteroids may exert direct membrane effects. Corticosteroids decrease cellular and fibrinous exudation and tissue infiltration, inhibit fibroblastic and collagen-forming activity, retard epithelial regeneration, diminish postinflammatory neovascularization and reduce toward normal levels the excessive permeability of inflamed capillaries. /Corticosteroids (Otic)/
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2007., p. 911
Glucocorticoids are capable of suppressing the inflammatory process through numerous pathways. They interact with specific intracellular receptor proteins in target tissues to alter the expression of corticosteroid-responsive genes. Glucocorticoid-specific receptors in the cell cytoplasm bind with steroid ligands to form hormone-receptor complexes that eventually translocate to the cell nucleus. There these complexes bind to specific DNA sequences and alter their expression. The complexes may induce the transcription of mRNA leading to synthesis of new proteins. Such proteins include lipocortin, a protein known to inhibit PLA2a and thereby block the synthesis of prostaglandins, leukotrienes, and PAF. Glucocorticoids also inhibit the production of other mediators including AA metabolites such as COX, cytokines, the interleukins, adhesion molecules, and enzymes such as collagenase. /Glucocorticoids/
Kahn, C.M. (Ed.); The Merck Veterinary Manual 9th ed. Merck & Co. Whitehouse Station, NJ. 2005, p. 2128
Corticosteroids diffuse across cell membranes and complex with specific cytoplasmic receptors. These complexes then enter the cell nucleus, bind to DNA (chromatin), and stimulate transcription of messenger RNA (mRNA) and subsequent protein synthesis of various inhibitory enzymes responsible for the anti-inflammatory effects of topical corticosteroids. These anti-inflammatory effects include inhibition of early processes such as edema, fibrin deposition, capillary dilatation, movement of phagocttes into the area, and phagocytic activities. Later processes, such as capillary production, collagen deposition, and keloid formation also are inhibited by corticosteroids. The overall actions of topical corticosteroids are catabolic. /Corticosteroids (topical)/
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2007., p. 919