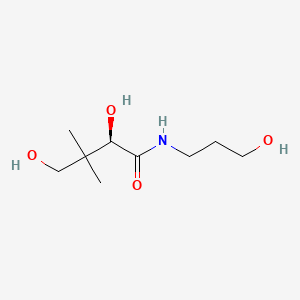

1. (+)-2,4-dihydroxy-n-(3-hydroxypropyl)-3,3-dimethylbutyramide
2. 2,4-dihydroxy-n-(3-hydroxypropyl)-3,3-dimethylbutanamide
3. Bepanthen
4. Butanamide, 2,4-dihydroxy-n-(3-hydroxypropyl)-3,3-dimethyl-, (+--)-
5. Corneregel
6. D-panthenol
7. Dexpanthenol Heumann
8. Dl-panthenol
9. Ilopan
10. Marolderm
11. Nasenspray Ratiopharm Panthenol
12. Nasicur
13. Otriven Dexpanthenol
14. Pan Rhinol
15. Pan-ophtal
16. Panthenol
17. Panthenol Braun
18. Panthenol Jenapharm
19. Panthenol Law
20. Panthenol Lichtenstein
21. Panthenol Von Ct
22. Panthenol-ratiopharm
23. Panthoderm
24. Panthogenat
25. Pantothenol
26. Repa-ophtal
27. Rhinoclir
28. Siozwo Sana
29. Ucee D
30. Urupan
31. Wund- Und Heilsalbe Law
1. D-panthenol
2. 81-13-0
3. Pantothenol
4. Ilopan
5. D-pantothenyl Alcohol
6. Bepanthen
7. Pantol
8. Bepanthene
9. Bepantol
10. (+)-panthenol
11. Provitamin B
12. Motilyn
13. Panadon
14. Panthoderm
15. Thenalton
16. Zentinic
17. D-pantothenol
18. Pantothenyl Alcohol
19. Cozyme
20. D-p-a Injection
21. D(+)-panthenol
22. Pantenyl
23. Synapan
24. Urupan
25. D(+)-pantothenyl Alcohol
26. Intrapan
27. D Panthenol
28. D-panthenol 50
29. Provitamin B5
30. Pantothenylol
31. (2r)-2,4-dihydroxy-n-(3-hydroxypropyl)-3,3-dimethylbutanamide
32. Dexpantenol
33. (r)-2,4-dihydroxy-n-(3-hydroxypropyl)-3,3-dimethylbutanamide
34. Dextro Pantothenyl Alcohol
35. Propanolamine, N-pantoyl-
36. Dexpanthenolum
37. Alcopan-250
38. Penthenol
39. Varitan
40. N-pantoyl-propanolamine
41. Panthenol (d)
42. Butanamide, 2,4-dihydroxy-n-(3-hydroxypropyl)-3,3-dimethyl-, (2r)-
43. Panthenol (jan)
44. Prestwick_529
45. Dexpanthenol (1.20 G/ml)
46. Ilopan (tn)
47. D-(+)-panthenol
48. Panthenol, (+)-
49. D-(+)-2,4-dihydroxy-n-(3-hydroxypropyl)-3,3-dimethylbutyramide
50. N-pantoyl-3-propanolamine
51. Nsc 302962
52. D-(+)-pantothenyl Alcohol
53. 1o6c93ri7z
54. Chebi:27373
55. Butanamide, 2,4-dihydroxy-n-(3-hydroxypropyl)-3,3-dimethyl-, (r)-
56. Pro-itamin B5
57. Butyramide, 2,4-dihydroxy-n-(3-hydroxypropyl)-3,3-dimethyl-, D-(+)-
58. Component Of Pantho-f
59. Ncgc00142622-03
60. Panthenol [jan]
61. 2,4-dihydroxy-n-(3-hydroxypropyl)-3,3-dimethylbutanamide, (r)-
62. 2,4-dihydroxy-n-(3-hydroxypropyl)-3,3-dimethylbutyramide, D-(+)-
63. Dsstox_cid_2906
64. Dsstox_rid_76783
65. Dsstox_gsid_22906
66. Panthenolum
67. Pantenol
68. Pantenolo
69. Sinecort
70. (r)-2,4-dihydroxy-n-(3-hydroxypropyl)-3,3-dimethylbutyramide
71. D(+)-2,4-dihydroxy-n-(3-hydroxypropyl)-3,3-dimethylbutyramide
72. Component Of Zentinic
73. Pantothenol, D-
74. Alcool Dl-pantotenilico
75. (+-)-pantothenyl Alcohol
76. Dexpanthenol [usan]
77. Dexpantenol [inn-spanish]
78. Dexpanthenolum [inn-latin]
79. Unii-1o6c93ri7z
80. (r)-2,4-dihydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutyric 3-hydroxypropylamide
81. Dexpanthenol;
82. Ccris 3947
83. Hsdb 296
84. Nsc302962
85. Fancol Dl
86. Nsc-302962
87. Cas-81-13-0
88. Ncgc00186658-01
89. Dexpanthenol [usan:usp:inn:ban]
90. Einecs 201-327-3
91. Dexpanthenol (usp)
92. Mfcd00065006
93. Cornergel
94. Dolobene
95. Bay 81-2996
96. Brn 1724947
97. Panthenol, (+ )-
98. Panthenol 50w
99. Prestwick0_000022
100. Prestwick1_000022
101. Prestwick2_000022
102. Prestwick3_000022
103. Dexpanthenol (usp/inn)
104. Dexpanthenol [mi]
105. D-panthenol Usp/bp/ip
106. Compnent Of Ilopan-choline
107. Dexpanthenol [fcc]
108. Dexpanthenol [inn]
109. Bmse000445
110. Panthenol, (r)-
111. Dexpanthenol [hsdb]
112. Ec 201-327-3
113. Alcopan 250
114. D-panthenol [vandf]
115. Dexpanthenol [vandf]
116. Schembl15861
117. Bspbio_000083
118. Dexpanthenol [mart.]
119. 4-04-00-01652 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
120. Dexpanthenol [usp-rs]
121. Dexpanthenol [who-dd]
122. Spbio_002004
123. Bpbio1_000093
124. Chembl1200979
125. Dexpanthenol - Usp/fcc Kosher
126. Dtxsid3022906
127. Schembl20553090
128. Dexpanthenol [orange Book]
129. Hms1568e05
130. Hms2094e09
131. Hms2095e05
132. Hms3712e05
133. Dexpanthenol [ep Monograph]
134. (r)-2,4-dihydroxy-n-(3-hydroxy-propyl)-3,3-dimethylbutanamide
135. Hy-b1391
136. Zinc1530303
137. D-panthenol, >=98.0% (nt)
138. Dexpanthenol [usp Monograph]
139. Tox21_111563
140. Lmfa08020198
141. S4695
142. Akos015841507
143. Akos015901947
144. Calcium D-pantothenate Usp/bp/ep/ip
145. D(+)-alpha,gamma-dihydroxy-n-(3-hydroxypropyl)-beta,beta-dimethylbutyramide
146. Tox21_111563_1
147. Ccg-213429
148. Cs-8175
149. Db09357
150. Alpha,gamma-dihydroxy-n-(3-hydroxypropyl)-beta,beta-dimethylbutyramide, D-(+)-
151. Ncgc00142622-01
152. Ncgc00142622-04
153. As-14732
154. D-panthenol 10 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
155. Dexpanthenol, Tested According To Ph.eur.
156. Sbi-0206936.p001
157. D-panthenol, Vetec(tm) Reagent Grade, 98%
158. P0692
159. C05944
160. D00193
161. D70909
162. Q-201048
163. Q47495755
164. A6cf1a81-5b98-4c28-a379-ea28fa9dd210
165. (r)-3-(2,4-dihydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutyramido)-1-propanol
166. Dexpanthenol, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
167. (2r)-2,4-dihydroxy-n-(3-hydroxypropyl)-3,3-dimethyl-butanamide
168. (r)-()-2,4-dihydroxy-n-(3-hydroxypropyl)-3,3-dimethylbutyramide
169. (r)-(+)-2,4-dihydroxy-n-(3-hydroxypropyl)-3,3-dimethylbutanamide
170. (r)-2,4-dihydroxy-3,3-dimethyl-n-(3-hydroxypropyl)-butanamide
171. (r)-2,4-dihydroxy-n-(3-hydroxy-propyl)-3,3-dimethyl-butyramide
172. D-(+)-2,4-dihydroxy-3,3-dimethyl-n-(3-hydroxypropyl)butyramide
173. D-panthenol, >=98% (perchloric Acid Titration), >=98% (tlc)
174. Dexpanthenol, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
175. (d)-(+)-2, 4-dihydroxy-n-(3-hydroxypropyl)-3,3-dimethylbutyramide
176. Butanamide, 2,4-dihydroxy-n-(3-hydroxypropyl)-3,3-dimethyl-, (theta)-
177. D(+)-.alpha.,.gamma.-dihydroxy-n-(3-hydroxypropyl)-.beta.,.beta.-dimethylbutyramide
178. Dexpanthenol, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
179. 1113-70-8
| Molecular Weight | 205.25 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C9H19NO4 |
| XLogP3 | -0.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 205.13140809 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 205.13140809 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 89.8 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 14 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 182 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Dexpanthenol (topical) relieves itching and aids healing of skin in mild eczemas and dermatoses; itching skin, minor wounds, stings, bites, poison ivy, poison oak (dry sage) and minor skin irritations. Also, used in infants and children for diaper rash, chafing and mild skin irritations.
Novak, K.M. (ed.). Drug Facts and Comparisons2008 Edition. Wolters Kluwer Health. St. Louis, Missouri 2008., p. 2636
Prophylactic use immediately after major abdominal surgery to minimize the possibility of paralytic ileus. Intestinal atony causing abdominal distention; postoperative or post partum retention of flatus, or post operative delay in resumption of intestinal motility; paralytic ileus.
Novak, K.M. (ed.). Drug Facts and Comparisons2008 Edition. Wolters Kluwer Health. St. Louis, Missouri 2008., p. 1767
Vet: ... Dexpanthenol ... /is/ often used as source of B5. Only the D-isomers are active biologically, but dl-isomers are often used ... Equivalents: 1 g D-pantothenic acid = 936 mg D-dexpanthenol.
Rossoff, I.S. Handbook of Veterinary Drugs. New York: Springer Publishing Company, 1974., p. 645
/Exptl Use (Vet)/: The effect of B-complex vitamin on experimental liver damage in rats was studied. Ip injection of panthenol inhibited initial deposit of lipids after having removed 2/3 of the regenerating fatty liver in rats.
PMID:4235781 Petzold H, Weigel K; Int Z Vitaminforsch 38 (1): 97 (1968)
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for Dexpanthenol (13 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Administration of dexpanthenol injection directly into the vein is not advised.
Novak, K.M. (ed.). Drug Facts and Comparisons2008 Edition. Wolters Kluwer Health. St. Louis, Missouri 2008., p. 1767
One case of heartburn and a few cases of GI cramps have been reported after dexpanthenol administration. Allergic reactions to dexpanthenol have been reported occasionally; however, these reactions have not been directly attributed to the drug. Although isolated reports of itching, tingling, difficulty in breathing, erythema, generalized dermatitis, urticaria, temporary respiratory difficulty (when dexpanthenol injection was administered 5 minutes after succinylcholine had been discontinued), hypotension, persistent (up to 10 days) diarrhea, and agitation have been associated with use of dexpanthenol injection, a causal relationship to the drug has not been established.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009)
It is not known whether dexpanthenol can cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women. Dexpanthenol injection should be used during pregnancy only when clearly needed.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009)
Dexpanthenol injection should not be used for the management of mechanical obstruction; in these patients, therapy should be directed mainly at correcting the obstruction. The manufacturer of dexpanthenol injection cautions that the management of adynamic ileus includes correction of fluid and electrolyte abnormalities (especially hypokalemia), anemia, and hypoproteinemia; treatment of infection; avoidance of drugs that decrease GI motility; and decompression of the GI tract using nasogastric suction or a long intestinal tube when there is considerable distention.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009)
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Dexpanthenol (9 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Injection: Prophylactic use immediately after major abdominal surgery to minimize the possibility of paralytic ileus. Intestinal atony causing abdominal distention; postoperative or postpartum retention of flatus, or postoperative delay in resumption of intestinal motility; paralytic ileus. Topical: This medication is used as a moisturizer to treat or prevent dry, rough, scaly, itchy skin and minor skin irritations (e.g., diaper rash, skin burns from radiation therapy).
Pantothenic acid is a precursor of coenzyme A, which serves as a cofactor for a variety of enzyme-catalyzed reactions involving transfer of acetyl groups. The final step in the synthesis of acetylcholine consists of the choline acetylase transfer of acetyl group from acetylcoenzyme A to choline. Acetylcholine is the neurohumoral transmitter in the parasympathetic system and as such maintains the normal functions of the intestine. Decrease in acetylcholine content would result in decreased peristalsis and in extreme cases adynamic ileus.
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A11 - Vitamins
A11H - Other plain vitamin preparations
A11HA - Other plain vitamin preparations
A11HA30 - Dexpanthenol
D - Dermatologicals
D03 - Preparations for treatment of wounds and ulcers
D03A - Cicatrizants
D03AX - Other cicatrizants
D03AX03 - Dexpanthenol
S - Sensory organs
S01 - Ophthalmologicals
S01X - Other ophthalmologicals
S01XA - Other ophthalmologicals
S01XA12 - Dexpanthenol
Absorption
Dexpanthenol is soluble in water and alcohol, although insoluble in fats and oil based substances. With the appropriate vehicle, Dexpanthenol is easily penetrated into the skin. Rate of penetration and absorption is reduced when Dexpanthenol is administered as an oil/water formula.
Route of Elimination
Milk of nursing mothers receiving a normal diet contains about 2 ug of pantothenic acid per mL. About 70% of an oral dose of pantothenic acid is excreted unchanged in urine and about 30% in feces.
Volume of Distribution
Dexpanthenol is readily converted to pantothenic acid which is widely distributed into body tissues, mainly as coenzyme A. Highest concentrations are found in the liver, adrenal glands, heart, and kidneys.
Dexpanthenol is readily converted to pantothenic acid which is widely distributed into body tissues, mainly as coenzyme A. Highest concentrations are found in the liver, adrenal glands, heart, and kidneys. Milk of nursing mothers receiving a normal diet contains about 2 ug of pantothenic acid per mL. About 70% of an oral dose of pantothenic acid is excreted unchanged in urine and about 30% in feces.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009)
Dexpanthenol is readily converted to pantothenic acid which is widely distributed into body tissues, mainly as coenzyme A.
Dexpanthenol is readily converted to pantothenic acid which is widely distributed into body tissues, mainly as coenzyme A.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009)
Dexpanthenol is converted to pantothenic acid ... which then produces acetylcholine.
Evaluations of Drug Interactions. 1st ed. and supplements. Washington, DC: American Pharmaceutical Assn., 1973, 1974., p. 396
Half life have not been reported
Dexpanthenol is an alcohol derivative of pantothenic acid, a component of the B complex vitamins and an essential component of a normally functioning epithelium. Dexpanthenol is enzymatically cleaved to form pantothenic acid, which is an essential component of Coenzyme A, which acts as a cofactor in many enzymatic reactions that are important for protein metabolism in the epithelium. Dermatological effects of the topical use of dexpanthenol include increased fibroblast proliferation and accelerated re-epithelialization in wound healing. Furthermore, it acts as a topical protectant, moisturizer, and has demonstrated anti-inflammatory properties.
This alcohol ... is said to increase the amount of coenzyme A available for the synthesis of acetylcholine. Increased formation of acetylcholine is thought to increase peristalsis and intestinal tone.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 752
... To test the functional effect of pantothenate on dermal fibroblasts, cells were cultured and in vitro proliferation tests were performed using a standardized scratch test procedure. For all three donors analyzed, a strong stimulatory effect of pantothenate at a concentration of 20 ug/mL on the proliferation of cultivated dermal fibroblasts was observed. To study the molecular mechanisms resulting in the proliferative effect of pantothenate, gene expression was analyzed in dermal fibroblasts cultivated with 20 ug/mL of pantothenate compared with untreated cells using the GeneChip Human Exon 1.0 ST Array. A number of significantly regulated genes were identified including genes coding for interleukin (IL)-6, IL-8, Id1, HMOX-1, HspB7, CYP1B1 and MARCH-II. Regulation of these genes was subsequently verified by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis. Induction of HMOX-1 expression by pantothenol and pantothenic acid in dermal cells was confirmed on the protein level using immunoblots. Functional studies revealed the enhanced suppression of free radical formation in skin fibroblasts cultured with panthenol. In conclusion, these studies provided new insight in the molecular mechanisms linked to the stimulatory effect of pantothenate and panthenol on the proliferation of dermal fibroblasts. /Calcium pantotenate/
Wiederholt T et al; Exper Dermatol 18 (11): 969-78 (2009). Available from, as of March 16, 2010: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=pubmed&dopt=Abstract&list_uids=19397697
... Pantothenic acid, pantothenol and other derivatives ... are precursors of CoA /that/ protect cells and whole organs against peroxidative damage by increasing the content of cell glutathione...
Slyshenkov V et al; FEBS Lett 569 (1-3): 169-72 (2004). Available from, as of March 16, 2010: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=pubmed&dopt=Abstract&list_uids=15225628