

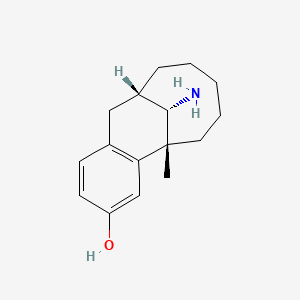

1. (-5alpha, 11alpha,13s)-13-amino-5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12-octahydro-5-methyl-5,11-methanobenzocyclodecen-3-ol
2. 13-amino-5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12-octahydro-5-methyl-5,11-methanobenzocyclodecenol
3. 5,11-methanobenzocyclodecen-3-ol, 13-amino-5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12-octahydro-5-methyl-, (5alpha,11alpha,13s*)
4. Dezocine Hydrobromide, (5alpha,11alpha,13*)-isomer
5. Dezocine Hydrobromide, (5alpha,11alpha,13s*)-isomer
6. Dezocine Hydrobromide, (5r-(5alpha,11alpha,13s*))-isomer
7. Dezocine Hydrobromide, (5s-(5alpha,11alpha,13*))-isomer
8. Dezocine, (5alpha,11alpha,13s*)-isomer
9. Wy-16,225
1. Dalgan
2. 53648-55-8
3. Dezocina
4. Dezocinum
5. Docozine
6. Dozocine
7. Dezocinum [inn-latin]
8. Dezocina [inn-spanish]
9. Wy-16225
10. Vhx8k5sv4x
11. Wy-16,225
12. Chembl1685
13. Chebi:4474
14. Dezocine (usan)
15. (-)-13beta-amino-5,6,7,8,9,10,11alpha,12-octahydro-5alpha-methyl-5,11-methanobenzocyclodecen-3-ol
16. Dezocine [usan]
17. (1r,9s,15s)-15-amino-1-methyltricyclo[7.5.1.02,7]pentadeca-2(7),3,5-trien-4-ol
18. Dezocine [usan:inn]
19. Unii-vhx8k5sv4x
20. Dalgan (tn)
21. Wy 16225
22. Dezocine [inn]
23. Dezocine [mi]
24. Wy 16,225
25. Dezocine [vandf]
26. Dezocine [mart.]
27. Dezocine [who-dd]
28. Schembl3072
29. Dezocine [orange Book]
30. Dtxsid2022911
31. (5r,11s,13s)-13-amino-5-methyl-5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12-octahydro-5,11-methanobenzo[10]annulen-3-ol
32. Bdbm50276568
33. Akos016014025
34. Db01209
35. C08010
36. D00838
37. Q1109018
38. (1r,9s,15s)-15-amino-1-methyltricyclo[7.5.1.0^{2,7}]pentadeca-2,4,6-trien-4-ol
39. 13-amino-5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12-octahydro-5-methyl-5,11-methanobenzocyclodecenol
40. (-)-13.beta.-amino-5,6,7,8,9,10,11.alpha.,12-octahydro-5.alpha.-methyl-5,11-methanobenzocyclodecen-3-ol
41. (5r,11s,13s)-13-amino-5-methyl-5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12-octahydro-5,11-methanobenzocyclodecen-3-ol
42. 5,11-methanobenzocyclodecen-3-ol, 13-amino-5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12-octahydro-5-methyl-, (5.alpha.,11.alpha.,13s*)
43. 5,11-methanobenzocyclodecen-3-ol, 13-amino-5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12-octahydro-5-methyl-, (5alpha,11alpha,13s*)-, (-)-
| Molecular Weight | 245.36 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C16H23NO |
| XLogP3 | 3.7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 245.177964357 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 245.177964357 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 46.2 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 18 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 306 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 3 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Indicated in the treatment of moderate to severe pain.
Dezocine is a parenteral narcotic analgesic possessing both agonist and antagonist activity. It is similar to morphine with respect to analgesic potency and onset and duration of action. The narcotic antagonist activity is greater than that of pentazocine.
Analgesics, Opioid
Compounds with activity like OPIATE ALKALOIDS, acting at OPIOID RECEPTORS. Properties include induction of ANALGESIA or NARCOSIS. (See all compounds classified as Analgesics, Opioid.)
N - Nervous system
N02 - Analgesics
N02A - Opioids
N02AX - Other opioids
N02AX03 - Dezocine
Absorption
Rapid and complete following intramuscular administration.
Hepatic, via conjugation (glucuronidation).
Dezocine has known human metabolites that include Dezocine glucuronide.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
Elimination half-life following intramuscular administration averages 2.2 hours. Elimination half-life following a 5mg intravenous dose averages 1.7 to 2.6 hours (range 0.6 to 4.4 hours) while a 10mg dose averages 2.4 to 2.6 hours (range 1.2 to 7.4 hours). In patients with hepatic cirrhosis, the half-life is increased by 30 to 50%.
Dezocine is a opioid analgesic drug of mixed agonist-antagonist type. It binds with stereospecific receptors at many sites within the central nervous system (CNS) to alter processes affecting both the perception of pain and the emotional response to pain. At least 2 of these types of receptors (mu and kappa) mediate analgesia. Mu receptors are widely distributed throughout the CNS, especially in the limbic system (frontal cortex, temporal cortex, amygdala, and hippocampus), thalamus, striatum, hypothalamus, and midbrain as well as laminae I, II, IV, and V of the dorsal horn in the spinal cord. Kappa receptors are localized primarily in the spinal cord and in the cerebral cortex.