
1. Acid, Docosahexaenoic
2. Acids, Docosahexaenoic
3. Acids, Docosahexenoic
4. Docosahexaenoate
5. Docosahexaenoic Acid (all-z Isomer)
6. Docosahexaenoic Acid Dimer (all-z Isomer)
7. Docosahexaenoic Acid, 3,6,9,12,15,18-isomer
8. Docosahexaenoic Acid, 4,7,10,13,16,19-(all-z-isomer)
9. Docosahexaenoic Acid, 4,7,10,13,16,19-(all-z-isomer), Cerium Salt
10. Docosahexaenoic Acid, 4,7,10,13,16,19-(all-z-isomer), Cesium Salt
11. Docosahexaenoic Acid, 4,7,10,13,16,19-(all-z-isomer), Potassium Salt
12. Docosahexaenoic Acid, 4,7,10,13,16,19-(z,z,z,z,z,e-isomer)
13. Docosahexaenoic Acid, 4,7,10,13,16,19-isomer
14. Docosahexaenoic Acid, 4,7,10,13,16,19-isomer, Sodium Salt
15. Docosahexaenoic Acid, Sodium Salt
16. Docosahexaenoic Acids
17. Docosahexenoic Acids
1. Doconexent
2. Cervonic Acid
3. 6217-54-5
4. Cis-4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexaenoic Acid
5. Docosahexaenoate
6. (4z,7z,10z,13z,16z,19z)-docosa-4,7,10,13,16,19-hexaenoic Acid
7. All-cis-dha
8. Doconexento
9. Doconexentum
10. Doxonexent
11. Aquagrow Advantage
12. All-z-docosahexaenoic Acid
13. Doconexent [inn]
14. Martek Dha Hm
15. Ropufa 60
16. All-cis-4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexaenoic Acid
17. (4z,7z,10z,13z,16z,19z)-docosahexaenoic Acid
18. Docosaheaenoic-acid
19. Docosahexaenoic Acid (all-z)
20. Ccris 7670
21. All-cis-docosa-4,7,10,13,16,19-hexaenoic Acid
22. Zad9okh9jc
23. Docosahexanoic Acid
24. (all-z)-4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexaenoic Acid
25. Docosa-4,7,10,13,16,19-hexaenoic Acid
26. (4z,7z,10z,13z,16z,19z)-4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexaenoic Acid
27. Chembl367149
28. Docosahexaenoic Acid(dha)
29. Chebi:28125
30. Delta4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexaenoic Acid
31. 4-cis,7-cis,10-cis,13-cis,16-cis,19-cis-docosahexaenoic Acid
32. 4z,7z,10z,13z,16z,19z-docosahexaenoic Acid
33. Docosahexaenoic Acid (c22:6 N3)
34. Omega-3 Marine Triglycerides
35. Mfcd00065722
36. 4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexaenoic Acid, (all-z)-
37. Fa 22:6
38. Efalex
39. Ncgc00161345-04
40. C22:6 (n-3)
41. Docosahexaenoic Acid (22:6 N-3)
42. 22:6 N-3
43. 22:6(n-3)
44. Cis-4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexanoic Acid
45. 4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexaenoic Acid
46. C22:6n-3,6,9,12,15,18
47. Monolife 50
48. Marinol D 50tg
49. Sr-05000002130
50. Unii-zad9okh9jc
51. Doconexentum [inn-latin]
52. Doconexento [inn-spanish]
53. Dha-[21,21,22,22,22-d5]
54. Cervonate
55. Dtxsid5040465
56. 1fdq
57. Algal Dha
58. Docohexanenoic Acid
59. Docosahexanenoic Acid
60. Omega 3 Fatty Acid
61. All-z-docosahexaenoate
62. Spectrum5_002062
63. Docosahexaenoic Acid (6ci)
64. Dsstox_cid_20465
65. Dsstox_rid_79498
66. Dsstox_gsid_40465
67. Schembl19577
68. Bspbio_001298
69. Docoshexaenoic Acid (powder)
70. Mls004773950
71. Bml3-b02
72. Gtpl1051
73. Retriacyl (proposed Trade Name)
74. Bcbcmap01_000145
75. Docosahexaenoic Acid [mi]
76. Hms1361a20
77. Hms1791a20
78. Hms1989a20
79. Hms3402a20
80. Hms3649j15
81. Docosahexaenoic Acid [inci]
82. Hy-b2167
83. Zinc4474564
84. Docosahexaenoic Acid [vandf]
85. Tox21_111992
86. Bdbm50210259
87. Docosahexaenoic Acid [mart.]
88. Lmfa01030185
89. Docosahexaenoic Acid [usp-rs]
90. Docosahexaenoic Acid [who-dd]
91. Akos015962159
92. Ac-1010
93. Ccg-207958
94. Ccg-208135
95. Cs-6261
96. Db03756
97. Kl-0761
98. Idi1_033768
99. 4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexaenoate
100. Ncgc00161345-01
101. Ncgc00161345-02
102. Ncgc00161345-03
103. Ncgc00161345-05
104. Ncgc00161345-07
105. All Cis- Docosahexaenoic Acid (cis-dha)
106. Smr001881493
107. Cas-6217-54-5
108. Cis-4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexanoate
109. D2226
110. S6454
111. C06429
112. H10987
113. Ab01563379_01
114. Docosahexaenoic Acid (dha) (c22:6 N3)
115. Docosahexaenoic Acid-rich Single Cell Oil
116. 217d545
117. Q423345
118. Sr-05000002130-1
119. Sr-05000002130-4
120. Brd-k39965020-001-02-6
121. 4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexaenoic Acid, (all Cis)-
122. A320050000
123. Cis-4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexaenoic Acid, >=98%
124. Fa(22:6(4z,7z,10z,13z,16z,19z))
125. Z,z,z,z,z,z-docosa-4,7,10,13,16,19-hexaenoic Acid
126. (all-z)-4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexaenoic Acid, Dha
127. 800e8e72-bbf4-46f7-a60b-b8f2b54669c7
128. C22h32o2 (cis-4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexaenoic Acid)
129. 4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexaenoic Acid, (all-z)- (8ci)
130. Cis-4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexaenoic Acid, Analytical Standard
131. Docosa-4z,7z,10z,13z,16z,19z-hexaenoic Acid (22:6, N-3)
132. (4z,7z,10z,13z,16z, 19z)-docosa-4,7,10,13,16,19-hexaenoic Acid
133. (4z,7z,10z,13z,16z,19z)-docosa-4, 7,10,13,16,19-hexaenoic Acid
134. (4z,7z,10z,13z,16z,19z)-docosa-4,7,10,13,16,19- Hexaenoic Acid
135. Cis-4,7,13,16,19-docosahexaenoic Acid (stabilized With Vitamine E)
136. 4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexaenoic Acid, (4z,7z,10z,13z,16z,19z)- (9ci)
137. Docosahexaenoic Acid (dha) (c22:6) (constituent Of Krill Oil) [dsc]
138. 1024594-51-1
139. Cis-4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexaenoic Acid, 500 Mug/ml In Ethanol, Certified Reference Material
| Molecular Weight | 328.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
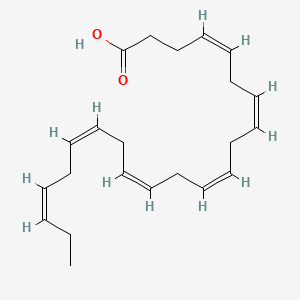
| Molecular Formula | C22H32O2 |
| XLogP3 | 6.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 14 |
| Exact Mass | 328.240230259 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 328.240230259 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 37.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 24 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 462 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 6 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Used as a high-docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) oral supplement.
Treatment of Retinitis Pigmentosa
DHA in the central nervous system is found in the phospholipid bilayers where it modulates the physical environment and increase the free volume within the membrane bilayer. It influences the G-protein coupled receptor activity and affects transmembrane transport and cell interaction with the exterior world. It is also reported to promote apoptosis, neuronal differentiation and ion channel activity. Like other polyunsaturated fatty acids, DHA acts as a ligand at PPARs that plays an anti-inflammatory effect and regulate inflammatory gene expression and NFB activation. DHA also gives rise to resolvins and related compounds (e.g., protectins) through pathways involving cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase enzymes to resolve the inflammatory responses.
Absorption
Like other omega-3 fatty acids, DHA is hydrolyzed from the intestines and delivered through the lymphatic circulation. Plasma DHA concentrations increase in a dose-dependent and saturable manner.
Volume of Distribution
DHA is the most abundant n3 fatty acid in membranes and is present in all organs. It is also the most variable among organs and is particularly abundant in neural tissue, such as brain and retina, where it is several hundred-fold more abundant than EPA.
DHA can be metabolized into DHA-derived specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs), DHA epoxides, electrophilic oxo-derivatives (EFOX) of DHA, neuroprostanes, ethanolamines, acylglycerols, docosahexaenoyl amides of amino acids or neurotransmitters, and branched DHA esters of hydroxy fatty acids, among others. It is converted to 17-hydroperoxy-DHA derivatives via COX-2 and 15-LOX and 5-LOX activity. These derivatives are further converted into D-series resolvins and protectins with potent anti-inflammatory potential and potent neuroprotective effect. DHA may also be metabolized to 19,20-epoxydocosapentaenoic acids (EDPs) and isomers via CYP2C9 activity. Epoxy metabolites are reported to mediate anti-tumor activity by inhibiting angiogenesis, tumor growth, and metastasis.
Approximately 20 hours.
DHA and its conversion to other lipid signalling moleccules compete with the arachidonic acid cascade from endogenous phospholipids and shift the inflammatory state to being more anti-inflammatory. DHA inhibits endotoxin-stimulated production of IL-6 and IL-8 in human endothelial cells. Derivatives of DHA are anti-inflammatory lipid mediators. Lipid mediators resolvin D1 and protectin D1 all inhibit transendothelial migration of neutrophils, so preventing neutrophilic infiltration at sites of inflammation, resolvin D1 inhibits IL-1 production, and protectin D1 inhibits TNF and IL-1 production. Monoxydroxy derivative of DHA converted by LOX inhibit thromboxane-induced platelet aggregation. DHA supplementation has also shown to reduce the levels of serum C-reactive protein (CRP) and other circulating markers of inflammation such as neutrophils in hypertriglyceridemic men. DHA acts as a ligand at peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) gamma and alpha that regulate lipid signalling molecule-mediated transduction pathways and modulate inflammation. As a natural ligand, DHA induces a protective effect in retinal tissues by activating retinoid x receptors and subsequent ERK/MAPK signaling pathway in photoreceptors to promote their survival and differentiation, stimulating the expression of antiapoptotic proteins such as Bcl-2 and preserving mitochondrial membrane potential.